Blockbridge EPS¶
Introduction¶
Blockbridge is software that transforms commodity infrastructure into secure multi-tenant storage that operates as a programmable service. It provides automatic encryption, secure deletion, quality of service (QoS), replication, and programmable security capabilities on your choice of hardware. Blockbridge uses micro-segmentation to provide isolation that allows you to concurrently operate OpenStack, Docker, and bare-metal workflows on shared resources. When used with OpenStack, isolated management domains are dynamically created on a per-project basis. All volumes and clones, within and between projects, are automatically cryptographically isolated and implement secure deletion.
Architecture reference¶
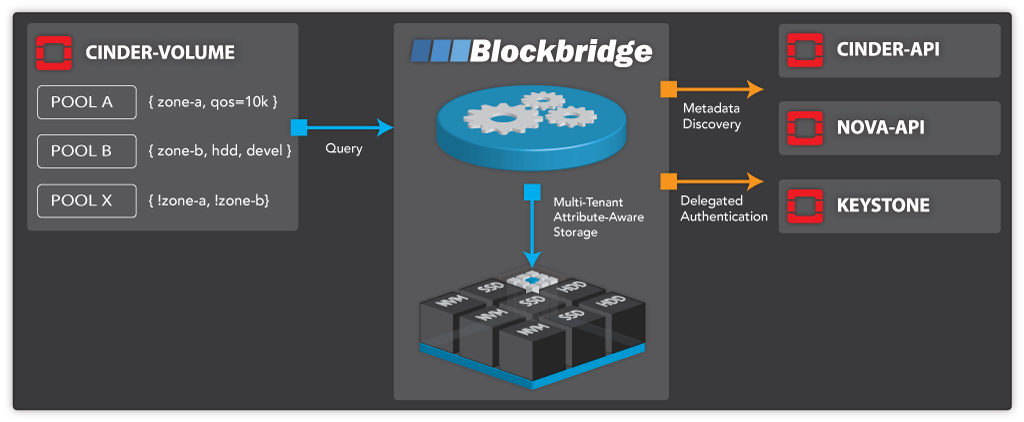
Blockbridge architecture
Control paths¶
The Blockbridge driver is packaged with the core distribution of OpenStack. Operationally, it executes in the context of the Block Storage service. The driver communicates with an OpenStack-specific API provided by the Blockbridge EPS platform. Blockbridge optionally communicates with Identity, Compute, and Block Storage services.
Block storage API¶
Blockbridge is API driven software-defined storage. The system implements a native HTTP API that is tailored to the specific needs of OpenStack. Each Block Storage service operation maps to a single back-end API request that provides ACID semantics. The API is specifically designed to reduce, if not eliminate, the possibility of inconsistencies between the Block Storage service and external storage infrastructure in the event of hardware, software or data center failure.
Extended management¶
OpenStack users may utilize Blockbridge interfaces to manage replication, auditing, statistics, and performance information on a per-project and per-volume basis. In addition, they can manage low-level data security functions including verification of data authenticity and encryption key delegation. Native integration with the Identity Service allows tenants to use a single set of credentials. Integration with Block storage and Compute services provides dynamic metadata mapping when using Blockbridge management APIs and tools.
Attribute-based provisioning¶
Blockbridge organizes resources using descriptive identifiers called attributes. Attributes are assigned by administrators of the infrastructure. They are used to describe the characteristics of storage in an application-friendly way. Applications construct queries that describe storage provisioning constraints and the Blockbridge storage stack assembles the resources as described.
Any given instance of a Blockbridge volume driver specifies a query
for resources. For example, a query could specify
'+ssd +10.0.0.0 +6nines -production iops.reserve=1000
capacity.reserve=30%'. This query is satisfied by selecting SSD
resources, accessible on the 10.0.0.0 network, with high resiliency, for
non-production workloads, with guaranteed IOPS of 1000 and a storage
reservation for 30% of the volume capacity specified at create time.
Queries and parameters are completely administrator defined: they
reflect the layout, resource, and organizational goals of a specific
deployment.
Supported operations¶
- Create, delete, clone, attach, and detach volumes
- Create and delete volume snapshots
- Create a volume from a snapshot
- Copy an image to a volume
- Copy a volume to an image
- Extend a volume
- Get volume statistics
Supported protocols¶
Blockbridge provides iSCSI access to storage. A unique iSCSI data fabric is programmatically assembled when a volume is attached to an instance. A fabric is disassembled when a volume is detached from an instance. Each volume is an isolated SCSI device that supports persistent reservations.
Configuration steps¶
Create an authentication token¶
Whenever possible, avoid using password-based authentication. Even if you have created a role-restricted administrative user via Blockbridge, token-based authentication is preferred. You can generate persistent authentication tokens using the Blockbridge command-line tool as follows:
$ bb -H bb-mn authorization create --notes "OpenStack" --restrict none
Authenticating to https://bb-mn/api
Enter user or access token: system
Password for system:
Authenticated; token expires in 3599 seconds.
== Authorization: ATH4762894C40626410
notes OpenStack
serial ATH4762894C40626410
account system (ACT0762594C40626440)
user system (USR1B62094C40626440)
enabled yes
created at 2015-10-24 22:08:48 +0000
access type online
token suffix xaKUy3gw
restrict none
== Access Token
access token 1/elvMWilMvcLAajl...3ms3U1u2KzfaMw6W8xaKUy3gw
*** Remember to record your access token!
Create volume type¶
Before configuring and enabling the Blockbridge volume driver, register
an OpenStack volume type and associate it with a
volume_backend_name. In this example, a volume type, ‘Production’,
is associated with the volume_backend_name ‘blockbridge_prod’:
$ openstack volume type create Production
$ openstack volume type set --property volume_backend_name=blockbridge_prod Production
Specify volume driver¶
Configure the Blockbridge volume driver in /etc/cinder/cinder.conf.
Your volume_backend_name must match the value specified in the
openstack volume type set command in the previous step.
volume_driver = cinder.volume.drivers.blockbridge.BlockbridgeISCSIDriver
volume_backend_name = blockbridge_prod
Specify API endpoint and authentication¶
Configure the API endpoint and authentication. The following example uses an authentication token. You must create your own as described in Create an authentication token.
blockbridge_api_host = [ip or dns of management cluster]
blockbridge_auth_token = 1/elvMWilMvcLAajl...3ms3U1u2KzfaMw6W8xaKUy3gw
Specify resource query¶
By default, a single pool is configured (implied) with a default
resource query of '+openstack'. Within Blockbridge, datastore
resources that advertise the ‘openstack’ attribute will be selected to
fulfill OpenStack provisioning requests. If you prefer a more specific
query, define a custom pool configuration.
blockbridge_pools = Production: +production +qos iops.reserve=5000
Pools support storage systems that offer multiple classes of service. You may wish to configure multiple pools to implement more sophisticated scheduling capabilities.
Configuration options¶
| Configuration option = Default value | Description |
|---|---|
| [DEFAULT] | |
blockbridge_api_host = None |
(String) IP address/hostname of Blockbridge API. |
blockbridge_api_port = None |
(Integer) Override HTTPS port to connect to Blockbridge API server. |
blockbridge_auth_password = None |
(String) Blockbridge API password (for auth scheme ‘password’) |
blockbridge_auth_scheme = token |
(String) Blockbridge API authentication scheme (token or password) |
blockbridge_auth_token = None |
(String) Blockbridge API token (for auth scheme ‘token’) |
blockbridge_auth_user = None |
(String) Blockbridge API user (for auth scheme ‘password’) |
blockbridge_default_pool = None |
(String) Default pool name if unspecified. |
blockbridge_pools = {'OpenStack': '+openstack'} |
(Dict) Defines the set of exposed pools and their associated backend query strings |
Configuration example¶
cinder.conf example file
[Default]
enabled_backends = bb_devel bb_prod
[bb_prod]
volume_driver = cinder.volume.drivers.blockbridge.BlockbridgeISCSIDriver
volume_backend_name = blockbridge_prod
blockbridge_api_host = [ip or dns of management cluster]
blockbridge_auth_token = 1/elvMWilMvcLAajl...3ms3U1u2KzfaMw6W8xaKUy3gw
blockbridge_pools = Production: +production +qos iops.reserve=5000
[bb_devel]
volume_driver = cinder.volume.drivers.blockbridge.BlockbridgeISCSIDriver
volume_backend_name = blockbridge_devel
blockbridge_api_host = [ip or dns of management cluster]
blockbridge_auth_token = 1/elvMWilMvcLAajl...3ms3U1u2KzfaMw6W8xaKUy3gw
blockbridge_pools = Development: +development
Multiple volume types¶
Volume types are exposed to tenants, pools are not. To offer
multiple classes of storage to OpenStack tenants, you should define
multiple volume types. Simply repeat the process above for each desired
type. Be sure to specify a unique volume_backend_name and pool
configuration for each type. The
cinder.conf example included with
this documentation illustrates configuration of multiple types.
Testing resources¶
Blockbridge is freely available for testing purposes and deploys in seconds as a Docker container. This is the same container used to run continuous integration for OpenStack. For more information visit www.blockbridge.io.

Except where otherwise noted, this document is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. See all OpenStack Legal Documents.