IBM Storage Driver for OpenStack¶
Introduction¶
The IBM Storage Driver for OpenStack is a software component of the OpenStack cloud environment that enables utilization of storage resources provided by supported IBM storage systems.
The driver was validated on the following storage systems:
- IBM DS8000 Family
- IBM FlashSystem A9000
- IBM FlashSystem A9000R
- IBM Spectrum Accelerate
- IBM XIV Storage System
After the driver is configured on the OpenStack Cinder nodes, storage volumes can be allocated by the Cinder nodes to the Nova nodes. Virtual machines on the Nova nodes can then utilize these storage resources.
Note
Unless stated otherwise, all references to XIV storage system in this guide relate all members of the Spectrum Accelerate Family (XIV, Spectrum Accelerate and FlashSystem A9000/A9000R).
Concept diagram¶
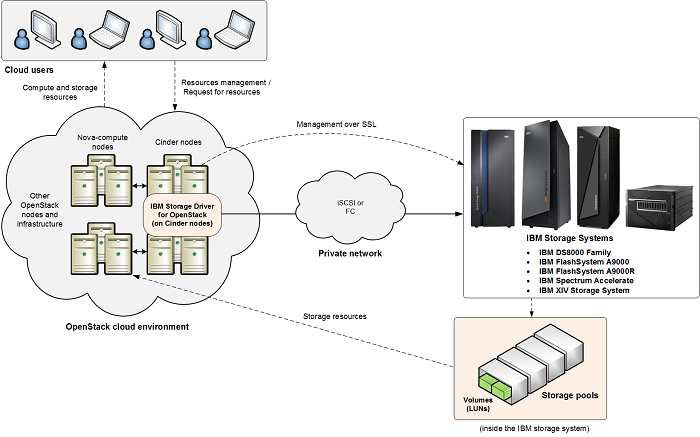
This figure illustrates how an IBM storage system is connected to the OpenStack cloud environment and provides storage resources when the IBM Storage Driver for OpenStack is configured on the OpenStack Cinder nodes. The OpenStack cloud is connected to the IBM storage system over Fibre Channel or iSCSI (DS8000 systems support only Fibre Channel connections). Remote cloud users can issue requests for storage resources from the OpenStack cloud. These requests are transparently handled by the IBM Storage Driver, which communicates with the IBM storage system and controls the storage volumes on it. The IBM storage resources are then provided to the Nova nodes in the OpenStack cloud.
Configuration¶
Configure the driver manually by changing the cinder.conf file as
follows:
volume_driver = cinder.volume.drivers.ibm.ibm_storage.IBMStorageDriver
| Configuration option = Default value | Description |
|---|---|
| [DEFAULT] | |
ds8k_devadd_unitadd_mapping = |
(String) Mapping between IODevice address and unit address. |
ds8k_host_type = auto |
(String) Set to zLinux if your OpenStack version is prior to Liberty and you’re connecting to zLinux systems. Otherwise set to auto. Valid values for this parameter are: ‘auto’, ‘AMDLinuxRHEL’, ‘AMDLinuxSuse’, ‘AppleOSX’, ‘Fujitsu’, ‘Hp’, ‘HpTru64’, ‘HpVms’, ‘LinuxDT’, ‘LinuxRF’, ‘LinuxRHEL’, ‘LinuxSuse’, ‘Novell’, ‘SGI’, ‘SVC’, ‘SanFsAIX’, ‘SanFsLinux’, ‘Sun’, ‘VMWare’, ‘Win2000’, ‘Win2003’, ‘Win2008’, ‘Win2012’, ‘iLinux’, ‘nSeries’, ‘pLinux’, ‘pSeries’, ‘pSeriesPowerswap’, ‘zLinux’, ‘iSeries’. |
ds8k_ssid_prefix = FF |
(String) Set the first two digits of SSID |
proxy = cinder.volume.drivers.ibm.ibm_storage.proxy.IBMStorageProxy |
(String) Proxy driver that connects to the IBM Storage Array |
san_clustername = |
(String) Cluster name to use for creating volumes |
san_ip = |
(String) IP address of SAN controller |
san_login = admin |
(String) Username for SAN controller |
san_password = |
(String) Password for SAN controller |
Security¶
The following information provides an overview of security for the IBM Storage Driver for OpenStack.
Avoiding man-in-the-middle attacks¶
When using a Spectrum Accelerate Family product, you can prevent man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks by following these rules:
Upgrade to IBM XIV storage system version 11.3 or later.
If working in a secure mode, do not work insecurely against another storage system in the same environment.
Validate the storage certificate. If you are using an XIV-provided certificate, use the CA file that was provided with your storage system (
XIV-CA.pem). The certificate files should be copied to one of the following directories:/etc/ssl/certs/etc/ssl/certs/xiv/etc/pki/etc/pki/xiv
If you are using your own certificates, copy them to the same directories
with the prefix “XIV” and in the .pem format. For example: XIV-my_cert.pem.
- In order to prevent the CVE-2014-3566 MITM attack, follow the OpenStack community directions: (http://osdir.com/ml/openstack-dev/2014-10/msg01349.html).
Troubleshooting¶
Refer to this information to troubleshoot technical problems that you might encounter when using the IBM Storage Driver for OpenStack.
Checking the Cinder node log files¶
The Cinder log files record operation information that might be useful for troubleshooting.
To achieve optimal and clear logging of events, activate the verbose
logging level in the cinder.conf file, located in the /etc/cinder
folder. Add the following line in the file, save the file, and then
restart the cinder-volume service:
verbose = True
debug = True
To turn off the verbose logging level, change True to False,
save the file, and then restart the cinder-volume service.
Check the log files on a periodic basis to ensure that the IBM Storage Driver is functioning properly.
To check the log file on a Cinder node: Go to the /var/log/cinder folder and open the activity log file named cinder-volume.log or volume.log. The IBM Storage Driver writes to this log file using the [IBM DS8K STORAGE] or [IBM XIV STORAGE] prefix (depending on the relevant storage system) for each event that it records in the file.
Best practices¶
This section contains the general guidance and best practices.
Working with multi-tenancy¶
The XIV storage systems, running microcode version 11.5 or later, Spectrum Accelerate and FlashSystem A9000/A9000R can employ multi-tenancy.
In order to use multi-tenancy with the IBM Storage Driver for OpenStack:
- For each storage system, verify that all predefined storage pools are in the same domain or, that all are not in a domain.
- Use either storage administrator or domain administrator user’s credentials, as long as the credentials grant a full access to the relevant pool.
- If the user is a domain administrator, the storage system domain
access policy can be CLOSED (
domain_policy: access=CLOSED). Otherwise, verify that the storage system domain access policy is OPEN (domain_policy: access=OPEN). - If the user is not a domain administrator, the host management policy
of the storage system domain can be BASIC (
domain_policy: host_management=BASIC). Otherwise, verify that the storage system domain host management policy is EXTENDED (domain_policy: host_management=EXTENDED).
Working with IBM Real-time Compression™¶
XIV storage systems running microcode version 11.6 or later, Spectrum Accelerate and FlashSystem A9000/A9000R can employ IBM Real-time Compression™.
Follow these guidelines when working with compressed storage resources using the IBM Storage Driver for OpenStack:
- Compression mode cannot be changed for storage volumes, using the IBM Storage Driver for OpenStack. The volumes are created according to the default compression mode of the pool. For example, any volume created in a compressed pool will be compressed as well.
- The minimum size for a compressed storage volume is 87 GB.
Working with QoS¶
The IBM Storage Driver for OpenStack provides QoS per volume for IBM FlashSystem A9000/A9000R storage systems, running microcode version of 12.0 or later. With QoS classes, the user can control the maximum bandwidth and I/O operations for each volume.
See IBM Spectrum Accelerate Family Storage Configuration and Usage for IBM FlashSystem A9000, IBM FlashSystem A9000R and IBM XIV Gen3, SG24-8376 for information about how to set QoS by defining performance classes in terms of IOPS and bandwidth limitation
QoS class types:
- Shared (default). Limits the combined rates of all of the volumes in the same QoS class. The maximum rate is the sum of the combined rate for each volume. For example, two volumes under a QoS class of maximum 100 Gbps are allocated a combined maximum bandwidth rate of 100 Gbps.
- Independent. Sets the maximum rate separately for each volume in the QoS class. For example, for two volumes under a QoS class of maximum 100 Gbps, each volume is limited to a rate of 100 Gbps. Thus, the combined maximum bandwidth rate is up to 200 Gbps.
To define a QoS class:
Create the QoS class:
cinder qos-create <class_name> <class_specs: bw=#, iops=#>Create a type:
cinder type-create type_<qos_class_name>Associate the QoS class with the type:
cinder qos-associate <qos uuid> <type uuid>Announce that the type is supporting QoS:
cinder type-key <type_name or UUID> set QoS_support=TrueCreate a volume:
cinder create 1 --volume-type <type_name>

Except where otherwise noted, this document is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. See all OpenStack Legal Documents.