2.1. Results of measuring of API performance of Kubernetes¶
| Abstract: | This document includes performance test results of Kubernetes API. All tests have been performed regarding Measuring of API performance of container cluster systems |
|---|
2.1.1. Environment description¶
2.1.1.1. Hardware configuration of each server¶
| server | name | node-{1..500}, kuber* | node-{1..355} |
| role | kubernetes cluster | kubernetes cluster | |
| vendor,model | Dell, R630 | Lenovo, RD550-1U | |
| operating_system | 4.4.0-36-generic
Ubuntu-xenial
x86_64
|
4.4.0-36-generic
Ubuntu-xenial
x86_64
|
|
| CPU | vendor,model | Intel, E5-2680v3 | Intel, E5-2680 v3 |
| processor_count | 2 | 2 | |
| core_count | 12 | 12 | |
| frequency_MHz | 2500 | 2500 | |
| RAM | vendor,model | Hynix, HMA42GR7MFR4N-TF | IBM,??? |
| amount_MB | 262144 | 262144 | |
| NETWORK | interface_name | bond0 | bond0 |
| vendor,model | Intel, X710 Dual Port | Intel, X710 Dual Port | |
| interfaces_count | 2 | 2 | |
| bandwidth | 10G | 10G | |
| STORAGE | dev_name | /dev/sda | /dev/sda |
| vendor,model | raid1 PERC H730P Mini
2 disks Intel S3610
|
raid1 - LSI ????
2 disks Intel S3610
|
|
| SSD/HDD | SSD | SSD | |
| size | 800GB | 800GB |
- kuber is a one-node Kubernetes cluster used to run container with test tool
2.1.1.2. Network scheme and part of configuration of hardware network switches¶
Network scheme of the environment:
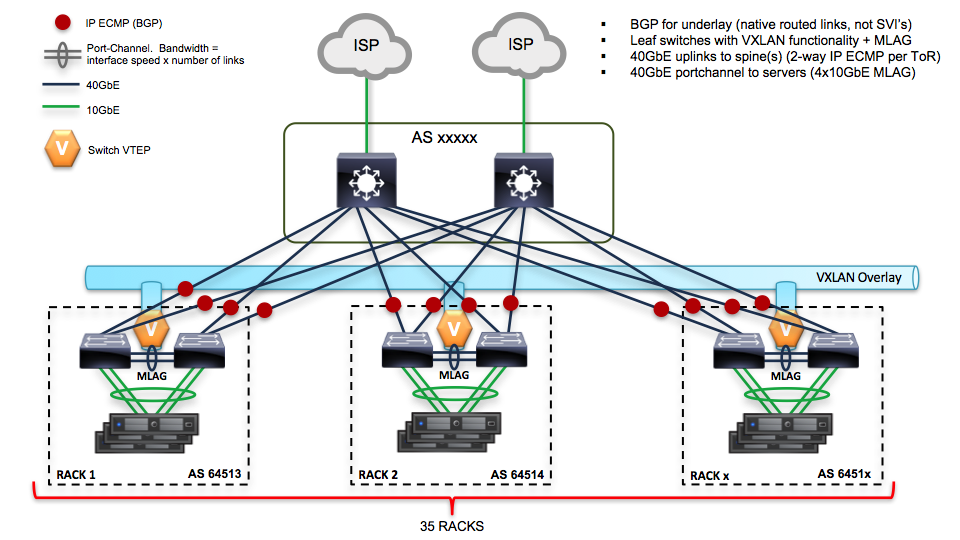
Here is the piece of switch configuration for each switch port which is a part of bond0 interface of a server:
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 600
switchport trunk allowed vlan 600-602,630-649
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
spanning-tree bpduguard enable
no snmp trap link-status
2.1.1.3. Software configuration of Kubernetes service¶
2.1.1.3.1. Setting up Kubernetes¶
Kubernetes was installed using Kargo deplyment tool. Kargo operates the following roles:
- master: Calico, Kubernetes API services
- minion: Calico, kubernetetes minion services
- etcd: etcd service
Kargo deploys Kubernetes cluster with the following matching hostnames and roles:
- node1: minion+master+etcd
- node2: minion+master+etcd
- node3: minion+etcd
- all other nodes: minion
We installed Kargo on top of dedicated node and start deployment (change ADMIN_IP and SLAVE_IPS variables to addresses of your nodes and SLAVES_COUNT to nodes count):
git clone https://review.openstack.org/openstack/fuel-ccp-installer
cd fuel-ccp-installer
cat >> create_env_kargo.sh << EOF
set -ex
export ENV_NAME="kargo-test"
export DEPLOY_METHOD="kargo"
export WORKSPACE="/root/workspace"
export ADMIN_USER="vagrant"
export ADMIN_PASSWORD="kargo"
# for 10 nodes
export SLAVES_COUNT=10
export ADMIN_IP="10.3.58.122"
export SLAVE_IPS="10.3.58.122 10.3.58.138 10.3.58.145 10.3.58.140 10.3.58.124 10.3.58.126 10.3.58.158 10.3.58.173 10.3.58.151 10.3.58.161"
export CUSTOM_YAML='docker_version: 1.12
hyperkube_image_repo: "quay.io/coreos/hyperkube"
hyperkube_image_tag: "v1.3.5_coreos.0"
etcd_image_repo: "quay.io/coreos/etcd"
etcd_image_tag: "v3.0.1"
calicoctl_image_repo: "calico/ctl"
#calico_node_image_repo: "calico/node"
calico_node_image_repo: "l23network/node"
calico_node_image_tag: "v0.20.0"
calicoctl_image_tag: "v0.20.0"
kube_apiserver_insecure_bind_address: "0.0.0.0"
mkdir -p $WORKSPACE
echo "Running on $NODE_NAME: $ENV_NAME"
cd /root/fuel-ccp-installer
bash "./utils/jenkins/run_k8s_deploy_test.sh"
EOF
./create_env_kargo.sh
| Software | Version |
| Ubuntu | Ubuntu 16.04.1 LTS |
| Kargo | 54d64106c74c72433c7c492a8a9a5075e17de35b |
2.1.1.3.2. Operating system configuration¶
You can find outputs of some commands and /etc folder in the following archive:
2.1.1.4. Software configuration of Test tool:¶
2.1.1.4.1. Test tool preparation¶
Kubernetes e2e-tests has been used to collect API latencies during the tests. We’ve run the test having Docker container with the tool. To build the container create e2e-tests directory and copy files from Files and scripts to build Docker container with e2e-test tool section to the directory. Then build the image:
root@kuber:~# cd e2e-tests
root@kuber:~/e2e-tests# docker build -t k8s_e2e ./
2.1.1.4.2. Test tool description¶
- The test creates 30 pods per Kubernetes minion.
- 300 on 10-nodes cluster
- 1500 on 50-nodes cluster
- 10650 on 355-nodes cluster
- The test actually spawns replication controllers, not pods directly
- The test spawns three types of replication controllers:
- small which includes 5 pods
- medium which includes 30 pods
- big which includes 250 pods
- After all containers are spawned the test resizes them
- The test performs 10 actions/sec
You can see more from the load.py code.
| Software | Version |
| Ubuntu | Ubuntu 14.04 LTS |
| e2e-test (Kubernetes repo) | v1.3.5 |
| Docker | 1.11.2, build b9f10c9 |
2.1.1.4.3. Operating system configuration:¶
You can find outputs of some commands and /etc folder in the following archive:
server_description_of_e2e-test_node
2.1.2. Testing process¶
2.1.2.1. Preparation¶
- Kubernetes was set up on top of 10 nodes as described in Setting up Kubernetes section.
- e2e-test container was running on top of infrastructure one-node Kubernetes cluster called “kuber”. You can find k8s_e2e.yaml in Files and scripts to run Docker container with e2e-test tool. You need to change “${API_SERVER}” to URI of Kubernetes API (for example http://10.3.58.66:8080). Also you need to specify filder where results will be stored. For 10-nodes cluster we created “/var/lib/volumes/e2e-test/10_nodes” filder. This folder will be mounted to the container as a volume.
root@kuber:~/e2e-tests# mkdir -p /var/lib/volumes/e2e-test/10_nodes
# set API URI and volume folder:
root@kuber:~/e2e-tests# vim k8s_e2e.yaml
root@kuber:~/e2e-tests# kubectl create -f k8s_e2e.yaml
# To store log to a file:
root@kuber:~/e2e-tests# kubectl attach k8s-e2e 2>&1 | tee -a /var/lib/volumes/e2e-test/10_nodes/k8s-e2e.log
- After that we have a log file which includes JSON with Kubernetes API latency. We can use simple Python script from Script to convert JSON from log file to RST table to create rst tables from the log file.
root@kuber:~/e2e-tests# python create_rst_table_from_k8s_e2e_log.py /var/lib/volumes/e2e-test/10_nodes/k8s-e2e.log
Now we have /var/lib/volumes/e2e-test/10_nodes/k8s-e2e.rst file with rst tables.
We performed the steps from 1 to 3 for Kubernetes cluster on top of 10, 50 and 355 nodes.
2.1.3. Results¶
2.1.3.1. 10-nodes cluster (all values are presented in milliseconds)¶
2.1.3.1.1. resourcequotas¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIST | 1.323 | 1.323 | 1.323 |
2.1.3.1.2. secrets¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | 2.121 | 1.734 | 1.505 |
2.1.3.1.3. replicationcontrollers¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUT | 6.425 | 5.793 | 4.77 |
| POST | 6.849 | 4.074 | 3.433 |
| GET | 1.872 | 1.6 | 1.393 |
| LIST | 7.31 | 6.674 | 3.989 |
| DELETE | 5.573 | 5.468 | 5.122 |
2.1.3.1.4. namespaces¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| POST | 2.514 | 2.514 | 2.514 |
2.1.3.1.5. nodes¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUT | 14.585 | 9.123 | 8.21 |
| GET | 2.342 | 2.255 | 1.971 |
2.1.3.1.6. endpoints¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | 1.786 | 1.575 | 1.327 |
2.1.3.1.7. pods¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUT | 9.142 | 6.858 | 5.742 |
| GET | 2.369 | 1.775 | 1.514 |
| LIST | 4.951 | 1.936 | 1.328 |
| DELETE | 15.229 | 12.946 | 11.485 |
2.1.3.2. 50-nodes cluster (all values are presented in milliseconds)¶
2.1.3.2.1. resourcequotas¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIST | 1.289 | 1.289 | 1.161 |
2.1.3.2.2. jobs¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIST | 1.564 | 1.564 | 1.564 |
2.1.3.2.3. secrets¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | 8.046 | 1.709 | 1.488 |
2.1.3.2.4. replicasets¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIST | 1.801 | 1.801 | 1.801 |
2.1.3.2.5. replicationcontrollers¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUT | 28.672 | 5.783 | 5.244 |
| POST | 11.475 | 4.107 | 3.295 |
| GET | 3.42 | 1.563 | 1.376 |
| LIST | 25.058 | 20.305 | 11.274 |
| DELETE | 7.505 | 5.625 | 4.957 |
2.1.3.2.6. daemonsets¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIST | 1.782 | 1.782 | 1.782 |
2.1.3.2.7. deployments¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIST | 1.988 | 1.988 | 1.988 |
2.1.3.2.8. petsets¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIST | 5.269 | 5.269 | 5.269 |
2.1.3.2.9. namespaces¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| POST | 3.032 | 3.032 | 3.032 |
2.1.3.2.10. services¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIST | 2.084 | 2.084 | 2.084 |
2.1.3.2.11. bindings¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| POST | 17.604 | 5.612 | 4.728 |
2.1.3.2.12. endpoints¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUT | 5.118 | 4.572 | 4.109 |
| GET | 4.355 | 1.417 | 1.238 |
2.1.3.2.13. pods¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUT | 15.325 | 6.657 | 5.43 |
| GET | 5.453 | 1.745 | 1.498 |
| LIST | 14.656 | 4.422 | 2.943 |
| DELETE | 17.64 | 12.753 | 11.651 |
2.1.3.2.14. nodes¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUT | 16.434 | 7.589 | 6.505 |
| GET | 3.959 | 1.836 | 1.558 |
2.1.3.3. 355-nodes cluster (all values are presented in milliseconds)¶
2.1.3.3.1. resourcequotas¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIST | 17.992 | 1.157 | 0.876 |
2.1.3.3.2. jobs¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIST | 16.852 | 16.852 | 0.807 |
2.1.3.3.3. secrets¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | 23.669 | 1.605 | 1.211 |
2.1.3.3.4. replicasets¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIST | 52.656 | 52.656 | 1.282 |
2.1.3.3.5. replicationcontrollers¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUT | 18.369 | 5.031 | 4.116 |
| POST | 28.599 | 7.342 | 2.929 |
| DELETE | 9.61 | 4.845 | 4.137 |
| LIST | 85.6 | 53.296 | 28.359 |
| GET | 16.689 | 1.397 | 1.167 |
2.1.3.3.6. daemonsets¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIST | 53.41 | 53.41 | 17.984 |
2.1.3.3.7. deployments¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIST | 19.634 | 19.634 | 9.899 |
2.1.3.3.8. petsets¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIST | 9.086 | 9.086 | 0.987 |
2.1.3.3.9. namespaces¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| POST | 2.513 | 2.513 | 2.513 |
2.1.3.3.10. services¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIST | 1.542 | 1.542 | 1.258 |
2.1.3.3.11. nodes¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUT | 35.889 | 7.488 | 5.77 |
| GET | 23.749 | 1.832 | 1.407 |
2.1.3.3.12. endpoints¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | 16.444 | 1.359 | 1.095 |
2.1.3.3.13. pods¶
| Method | Perc99 | Perc90 | Perc50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUT | 26.753 | 5.988 | 4.446 |
| GET | 18.755 | 1.579 | 1.258 |
| LIST | 44.249 | 24.433 | 13.045 |
| DELETE | 23.212 | 11.478 | 9.783 |
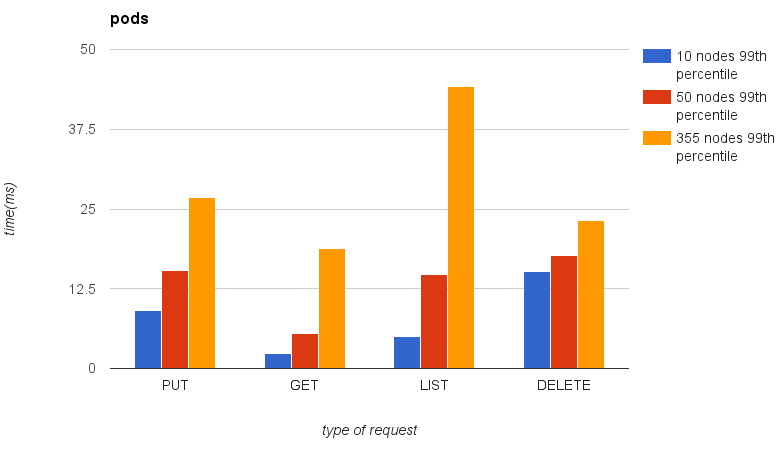
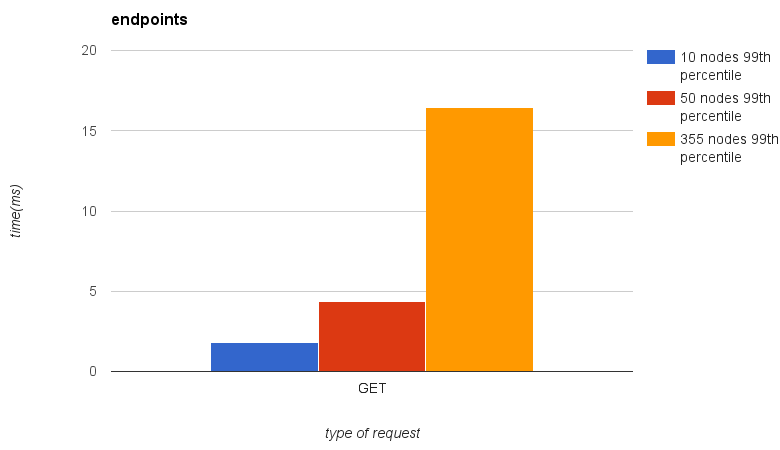
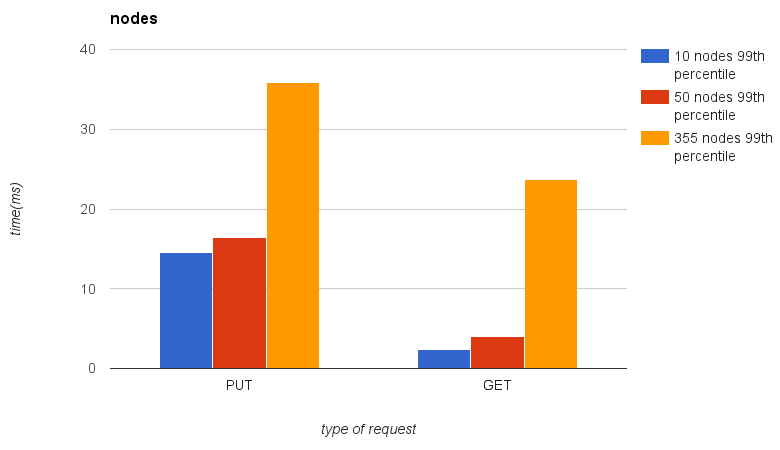
2.1.3.4. Comparation¶
Here is you can see results comparation from 10, 50 and 355 nodes clusters. Please note, that numbers of pods and other items depend on numbers of nodes.
- 300 pods will be spawned on 10-nodes cluster
- 1500 pods will be spawned on 50-nodes cluster
- 10650 pods will be spawned on 355-nodes cluster

|
|
|
|
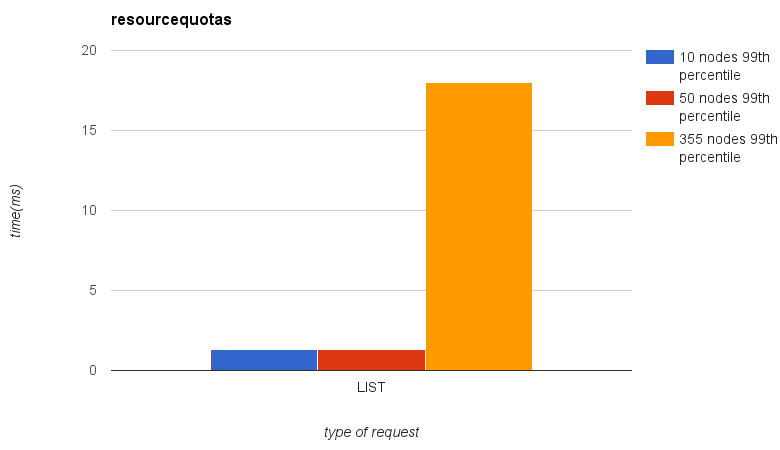
|

|
2.1.3.5. Kubernetes pod startup latency measurement¶
For this testing purposes MMM(MySQL/Master/Minions) testing suite was used (more information in Pod startup time measurement toolkit section).
This toolkit was run against 150 nodes Kubernetes environment installed via Kargo deployment tool (these nodes were taken from the same nodes pool all previous Kubernetes API performance tests were run against). The most basic configuration (1 replication controller, N pods, each pod containing 1 container) was run against the environment. Additional configurations will be tested and results published in terms of further researches.
The first run includes information about 500 pods being run on fresh Kubernetes environment (no tests have been run on it before, warm-up run with about 3 pods per node density):
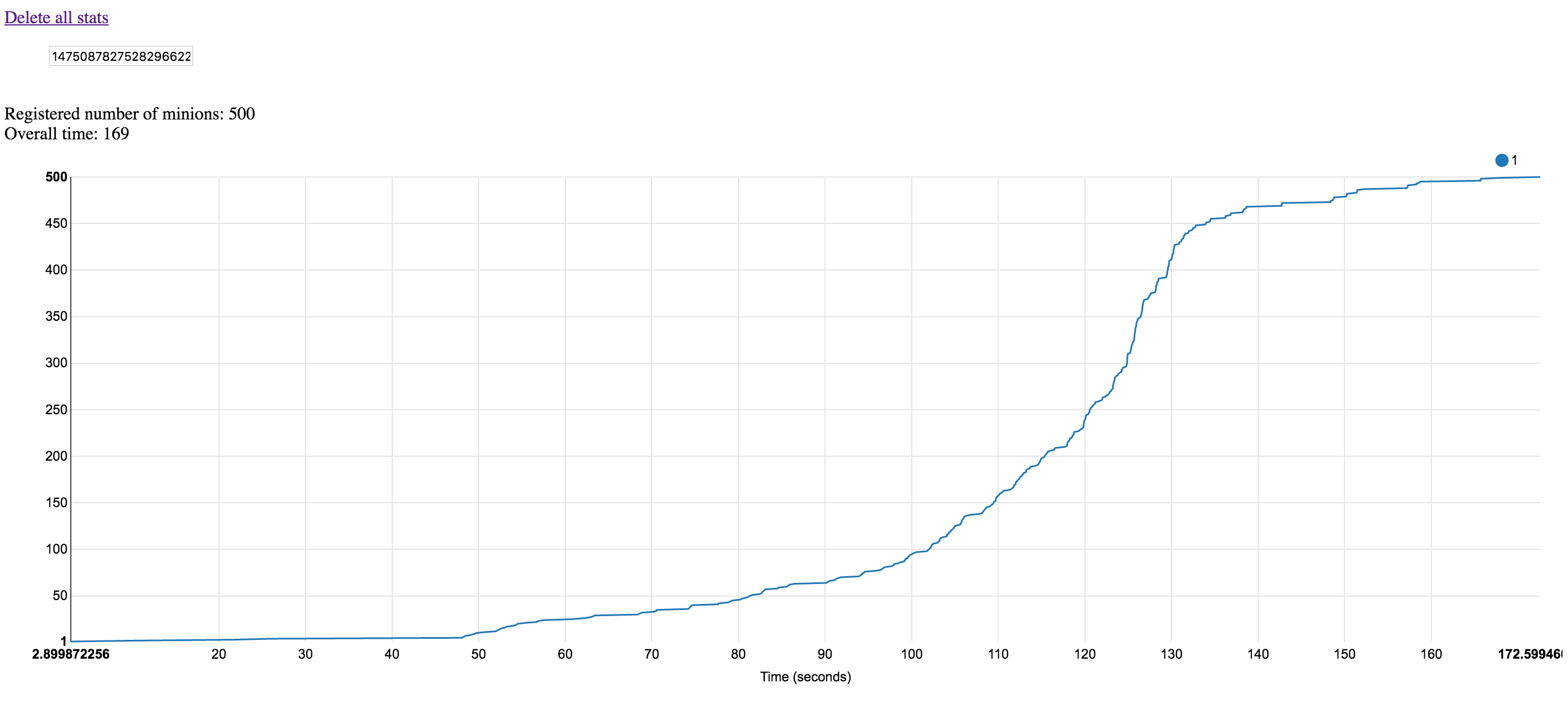
This weird timings pattern is related to the fact that first 500 containers pack was run against not warmed up environment (minions images were not pre-loaded on Kubernetes worker nodes, that means that during first run Docker registry/repo/etc was really stressed).
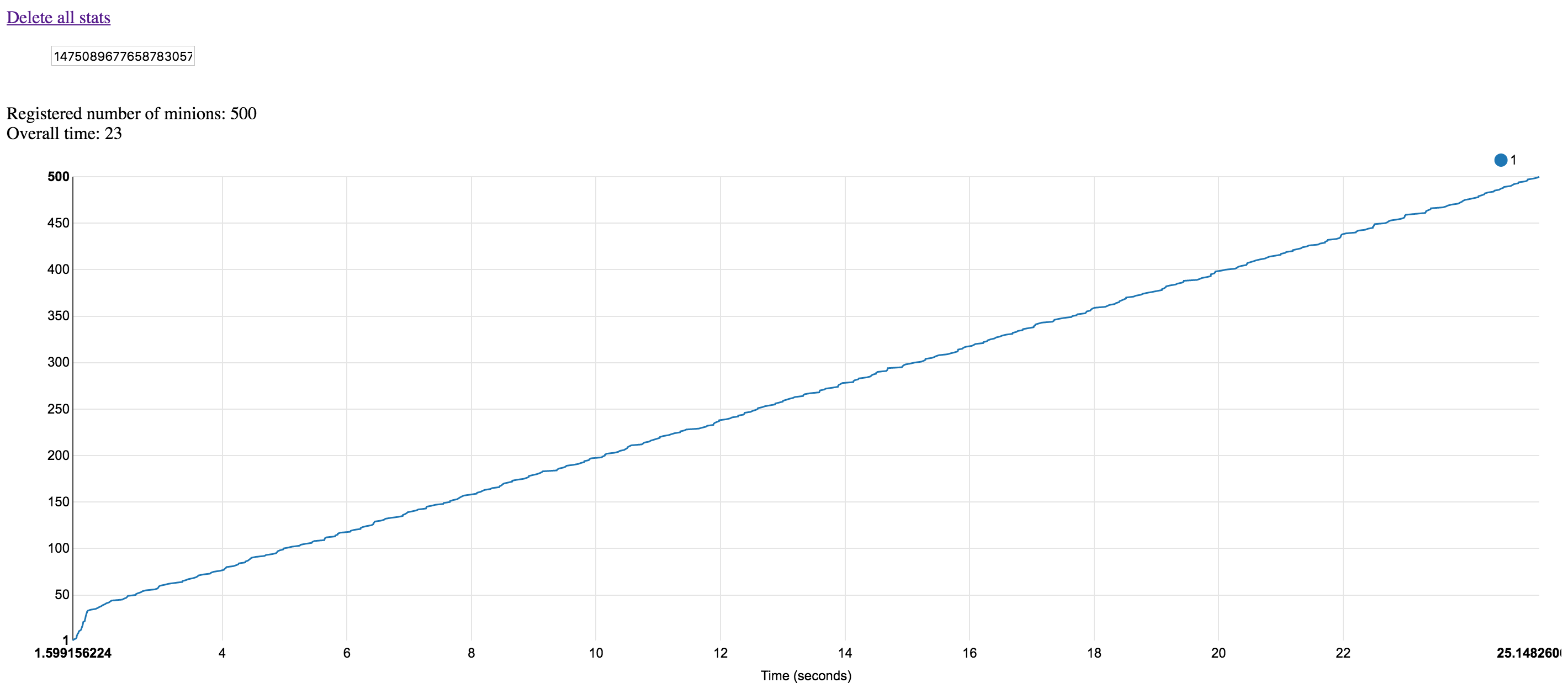
The same scenario run against the warmed-up environment will have linear pattern (with ~50 milliseconds per container startup, about 3 pods per cluster node density):
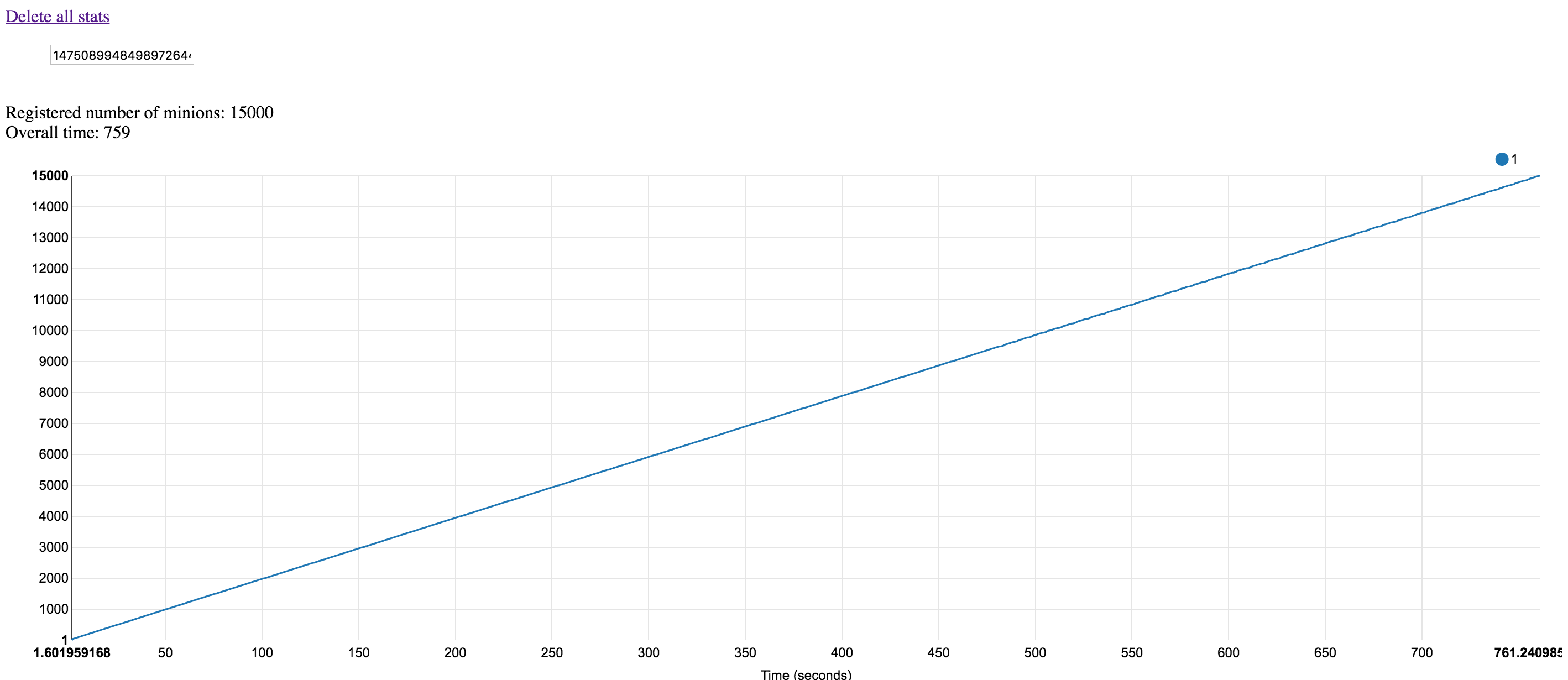
This pattern will remain the same with bigger number of containers (15000 containers, the same ~50 milliseconds per container startup, 100 pods per cluster node density):
2.1.4. Applications¶
2.1.4.1. Files and scripts to build Docker container with e2e-test tool¶
e2e-tests/Dockerfile:
FROM golang:1.6.3
RUN mkdir /reports && \
apt-get update && \
apt-get install -y rsync && \
mkdir -p /go/src/k8s.io && \
go get -u github.com/jteeuwen/go-bindata/go-bindata && \
git clone -b v1.3.5 https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes.git /go/src/k8s.io/kubernetes
WORKDIR /go/src/k8s.io/kubernetes
RUN make all WHAT=cmd/kubectl && \
make all WHAT=vendor/github.com/onsi/ginkgo/ginkgo && \
make all WHAT=test/e2e/e2e.test
COPY entrypoint.sh /
RUN chmod +x /entrypoint.sh
CMD /entrypoint.sh
e2e-tests/entrypoint.sh:
#!/bin/bash
set -u -e
function escape_test_name() {
sed 's/[]\$*.^|()[]/\\&/g; s/\s\+/\\s+/g' <<< "$1" | tr -d '\n'
}
TESTS_TO_SKIP=(
'[k8s.io] Port forwarding [k8s.io] With a server that expects no client request should support a client that connects, sends no data, and disconnects [Conformance]'
'[k8s.io] Port forwarding [k8s.io] With a server that expects a client request should support a client that connects, sends no data, and disconnects [Conformance]'
'[k8s.io] Port forwarding [k8s.io] With a server that expects a client request should support a client that connects, sends data, and disconnects [Conformance]'
'[k8s.io] Downward API volume should update annotations on modification [Conformance]'
'[k8s.io] DNS should provide DNS for services [Conformance]'
'[k8s.io] Load capacity [Feature:ManualPerformance] should be able to handle 3 pods per node'
)
function skipped_test_names () {
local first=y
for name in "${TESTS_TO_SKIP[@]}"; do
if [ -z "${first}" ]; then
echo -n "|"
else
first=
fi
echo -n "$(escape_test_name "${name}")\$"
done
}
if [ -z "${API_SERVER}" ]; then
echo "Must provide API_SERVER env var" 1>&2
exit 1
fi
export KUBERNETES_PROVIDER=skeleton
export KUBERNETES_CONFORMANCE_TEST=y
# Configure kube config
cluster/kubectl.sh config set-cluster local --server="${API_SERVER}" --insecure-skip-tls-verify=true
cluster/kubectl.sh config set-context local --cluster=local --user=local
cluster/kubectl.sh config use-context local
if [ -z "${FOCUS}" ]; then
# non-serial tests can be run in parallel mode
GINKGO_PARALLEL=y go run hack/e2e.go --v --test -check_version_skew=false \
--test_args="--ginkgo.focus=\[Conformance\] --ginkgo.skip=\[Serial\]|\[Flaky\]|\[Feature:.+\]|$(skipped_test_names)"
# serial tests must be run without GINKGO_PARALLEL
go run hack/e2e.go --v --test -check_version_skew=false --test_args="--ginkgo.focus=\[Serial\].*\[Conformance\] --ginkgo.skip=$(skipped_test_names)"
else
go run hack/e2e.go --v --test -check_version_skew=false --test_args="--ginkgo.focus=$(escape_test_name "${FOCUS}") --ginkgo.skip=$(skipped_test_names)"
fi
2.1.4.2. Files and scripts to run Docker container with e2e-test tool¶
e2e-tests/k8s-e2e.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: k8s-e2e
spec:
containers:
- image: k8s-e2e
name: k8s-e2e
env:
- name: E2E_REPORT_DIR
value: /reports
- name: API_SERVER
value: ${API_SERVER}
- name: FOCUS
value: "Load capacity"
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /reports
name: job-params
restartPolicy: Never
volumes:
- hostPath:
path: /var/lib/volumes/e2e-test/10_nodes
name: job-params
2.1.4.3. Script to convert JSON from log file to RST table¶
e2e-tests/create_rst_table_from_k8s_e2e_log.py:
#!/usr/bin/python
import json
import logging
import sys
from tabulate import tabulate
def cut_json_data(file_with_results):
json_data = "{"
start = False
end = False
with open(file_with_results) as f:
for line in f:
end = end or "Finish:Performance" in line
if end:
break
if start:
json_data += line
start = start or "Result:Performance" in line
data = json.loads(json_data)
return data
def get_resources_and_request_types(data):
resources = {}
for data_item in data["dataItems"]:
resource = data_item["labels"]["Resource"]
if resource not in resources:
resources[resource] = {}
type_of_request = data_item["labels"]["Verb"]
resources[resource][type_of_request] = data_item["data"]
return resources
def create_rst_tables(resource):
headers = ["Method"]
data = []
for method, perc in resource.iteritems():
headers += perc.keys()
data.append([method] + perc.values())
tables = tabulate(data, headers=headers, tablefmt="grid")
return tables
def put_tables_to_file(file_with_results):
rst_file = file_with_results.split(".")[0] + ".rst"
data = cut_json_data(file_with_results)
with open(rst_file, 'w') as f:
for resource, data in \
get_resources_and_request_types(data).iteritems():
table_head = "\n" + resource + "\n"
table_head_underline = ""
for character in resource:
table_head_underline += "^"
table_head += table_head_underline + "\n"
f.write(table_head + create_rst_tables(data))
def main(file_with_results):
put_tables_to_file(file_with_results)
if __name__ == '__main__':
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG)
main(sys.argv[1])
2.1.4.4. Pod startup time measurement toolkit¶
for Kubernetes pod startup latency measurement test case MMM(MySQL/Master/Minions) testing suite was used.
This is a client/server set for testing speed of k8s/docker/networking scheduling capabilities speed.
Architecture is simple and consist of the following:
- MariaDB/MySQL service (replication controller with only one replica)
- Master service, a simple Python application based on Flask framework with multiple threads and producer/consumer queue for SQL inserts
- Minion replication controller - a simple bash script which registers minions on master service.
This approach guarantees that container will report about its status itself, so any issues (e.g. too slow startup or unsuccessful at all attempt to create a container will be observed in the testing results).
For more details please proceed to the MMM(MySQL/Master/Minions) testing suite documentation.