Hitachi Hyper Scale-Out Platform File Services Driver for OpenStack¶
The Hitachi Hyper Scale-Out Platform File Services Driver for OpenStack provides the management of file shares, supporting NFS shares with IP based rules to control access. It has a layer that handles the complexity of the protocol used to communicate to Hitachi Hyper Scale-Out Platform via a RESTful API, formatting and sending requests to the backend.
Requirements¶
- Hitachi Hyper Scale-Out Platform (HSP) version 1.1.
- HSP user with
file-system-full-accessrole. - Established network connection between the HSP interface and OpenStack nodes.
Known restrictions¶
The Hitachi HSP allows only 1024 virtual file systems per cluster. This determines the limit of shares the driver can provide.
The Hitachi HSP file systems must have at least 128 GB. This means that all shares created by Shared File Systems service should have 128 GB or more.
Note
The driver has an internal filter function that accepts only requests for shares size greater than or equal to 128 GB, otherwise the request will fail or be redirected to another available storage backend.
Driver options¶
The following table contains the configuration options specific to the share driver.
| Configuration option = Default value | Description |
|---|---|
| [hsp1] | |
share_backend_name = None |
(String) The backend name for a given driver implementation. |
share_driver = manila.share.drivers.generic.GenericShareDriver |
(String) Driver to use for share creation. |
Network approach¶
Note
In the driver mode used by HSP Driver (DHSS = False), the driver does
not handle network configuration, it is up to the administrator to
configure it.
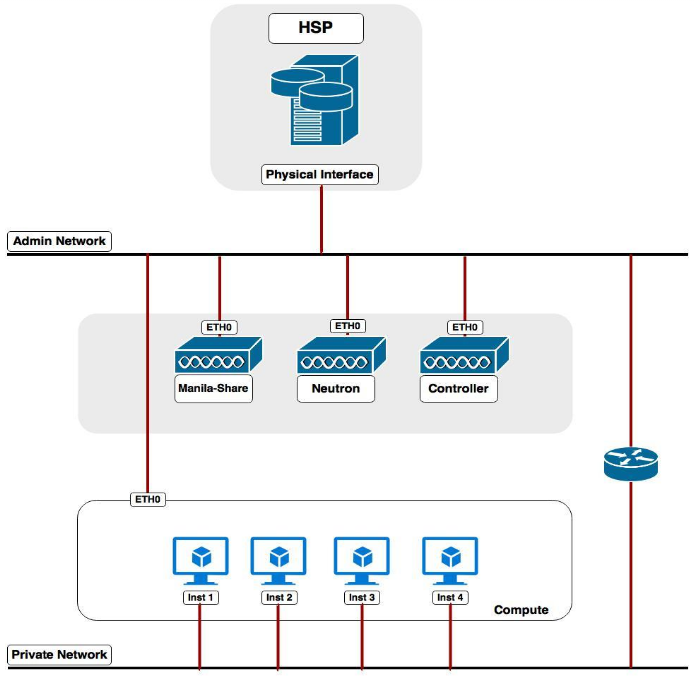
- Configure the network of the manila-share, Compute and Networking nodes to reach HSP interface. For this, your provider network should be capable of reaching HSP Cluster-Virtual-IP. These connections are mandatory so nova instances are capable of accessing shares provided by the backend.
- The following image represents a valid scenario:
Note
To HSP, the Virtual IP is the address through which clients access shares and the Shared File Systems service sends commands to the management interface. This IP can be checked in HSP using its CLI:
$ hspadm ip-address list
Back end configuration¶
Configure HSP driver according to your environment. This example shows a valid HSP driver configuration:
[DEFAULT] # ... enabled_share_backends = hsp1 enabled_share_protocols = NFS # ... [hsp1] share_backend_name = HITACHI1 share_driver = manila.share.drivers.hitachi.hsp.driver.HitachiHSPDriver driver_handles_share_servers = False hitachi_hsp_host = 172.24.47.190 hitachi_hsp_username = admin hitachi_hsp_password = admin_password
Configure HSP share type.
Note
Shared File Systems service requires that the share type includes the
driver_handles_share_serversextra-spec. This ensures that the share will be created on a backend that supports the requesteddriver_handles_share_serverscapability. Also,snapshot_supportextra-spec should be provided if its value differs from the default value (True), as this driver version that currently does not support snapshot operations. For this driver both extra-specs must be set toFalse.$ manila type-create --snapshot_support False hsp FalseRestart all Shared File Systems services (
manila-share,manila-schedulerandmanila-api).
Additional notes¶
- Shares are thin provisioned. It is reported to manila only the real used space in HSP.
- Administrators should manage the tenant’s quota (
manila quota-update) to control the backend usage.

Except where otherwise noted, this document is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. See all OpenStack Legal Documents.