Install and configure a share node running openSUSE and SUSE Linux Enterprise¶
This section describes how to install and configure a share node for the Shared File Systems service.
Note that installation and configuration vary by distribution. This section describes the instructions for a share node running openSUSE and SUSE Linux Enterprise.
Install and configure components¶
Install the packages:
# zypper install openstack-manila-share python-PyMySQLEdit the
/etc/manila/manila.conffile and complete the following actions:In the
[database]section, configure database access:[database] ... connection = mysql+pymysql://manila:MANILA_DBPASS@controller/manila
Replace
MANILA_DBPASSwith the password you chose for the Shared File Systems database.
Complete the rest of the configuration in
manila.conf.In the
[DEFAULT]section, configureRabbitMQmessage queue access:[DEFAULT] ... transport_url = rabbit://openstack:RABBIT_PASS@controller
Replace
RABBIT_PASSwith the password you chose for theopenstackaccount inRabbitMQ.In the
[DEFAULT]section, set the following config values:[DEFAULT] ... default_share_type = default_share_type rootwrap_config = /etc/manila/rootwrap.conf
Important
The
default_share_typeoption specifies the default share type to be used when shares are created without specifying the share type in the request. The default share type that is specified in the configuration file has to be created with the necessary required extra-specs (such asdriver_handles_share_servers) set appropriately with reference to the driver mode used. This is explained in further steps.In the
[DEFAULT]and[keystone_authtoken]sections, configure Identity service access:[DEFAULT] ... auth_strategy = keystone [keystone_authtoken] ... memcached_servers = controller:11211 www_authenticate_uri = http://controller:5000 auth_url = http://controller:5000 auth_type = password project_domain_name = Default user_domain_name = Default project_name = service username = manila password = MANILA_PASS
Replace
MANILA_PASSwith the password you chose for themanilauser in the Identity service.In the
[DEFAULT]section, configure themy_ipoption:[DEFAULT] ... my_ip = MANAGEMENT_INTERFACE_IP_ADDRESS
Replace
MANAGEMENT_INTERFACE_IP_ADDRESSwith the IP address of the management network interface on your share node, typically 10.0.0.41 for the first node in the example architecture shown below: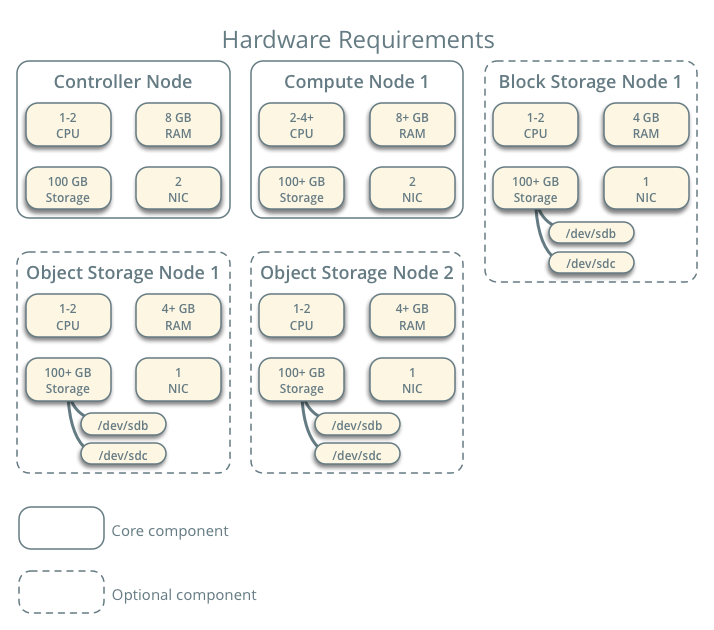
Hardware requirements¶
In the
[oslo_concurrency]section, configure the lock path:[oslo_concurrency] ... lock_path = /var/lib/manila/tmp
Two driver modes¶
The share node can support two modes, with and without the handling of share servers. The mode depends on driver support.
Option 1¶
Deploying the service without driver support for share server management. In this mode, the service does not do anything related to networking. The operator must ensure network connectivity between instances and the NAS protocol based server.
This tutorial demonstrates setting up the LVM driver which creates LVM volumes
on the share node and exports them with the help of an NFS server that is
installed locally on the share node. It therefore requires LVM and NFS packages
as well as an additional disk for the manila-share LVM volume group.
This driver mode may be referred to as driver_handles_share_servers = False
mode, or simply DHSS=False mode.
Option 2¶
Deploying the service with driver support for share server management. In
this mode, the service runs with a back end driver that creates and manages
share servers. This tutorial demonstrates setting up the Generic driver.
This driver requires Compute service (nova), Image service (glance) and
Networking service (neutron) for creating and managing share servers; and
Block storage service (cinder) for creating shares.
The information used for creating share servers is configured with the help of share networks.
This driver mode may be referred to as driver_handles_share_servers = True
mode, or simply DHSS=True mode.
Warning
When running the generic driver in DHSS=True driver mode, the share
service should be run on the same node as the networking service.
However, such a service may not be able to run the LVM driver that runs
in DHSS=False driver mode effectively, due to a bug in some
distributions of Linux. For more information, see LVM Driver section in the
Configuration Reference Guide.
Choose one of the following options to configure the share driver:
Shared File Systems Option 1: No driver support for share servers management¶
For simplicity, this configuration references the same storage node
configuration for the Block Storage service. However, the LVM driver
requires a separate empty local block storage device to avoid conflict
with the Block Storage service. The instructions use /dev/sdc, but
you can substitute a different value for your particular node.
Prerequisites¶
Note
Perform these steps on the storage node.
Install the supporting utility packages:
Install LVM and NFS server packages:
# zypper install lvm2 nfs-kernel-server
Create the LVM physical volume
/dev/sdc:# pvcreate /dev/sdc Physical volume "/dev/sdc" successfully created
Create the LVM volume group
manila-volumes:# vgcreate manila-volumes /dev/sdc Volume group "manila-volumes" successfully created
The Shared File Systems service creates logical volumes in this volume group.
Only instances can access Shared File Systems service volumes. However, the underlying operating system manages the devices associated with the volumes. By default, the LVM volume scanning tool scans the
/devdirectory for block storage devices that contain volumes. If projects use LVM on their volumes, the scanning tool detects these volumes and attempts to cache them which can cause a variety of problems with both the underlying operating system and project volumes. You must reconfigure LVM to scan only the devices that contain thecinder-volumeandmanila-volumesvolume groups. Edit the/etc/lvm/lvm.conffile and complete the following actions:In the
devicessection, add a filter that accepts the/dev/sdband/dev/sdcdevices and rejects all other devices:devices { ... filter = [ "a/sdb/", "a/sdc", "r/.*/"]
Warning
If your storage nodes use LVM on the operating system disk, you must also add the associated device to the filter. For example, if the
/dev/sdadevice contains the operating system:filter = [ "a/sda/", "a/sdb/", "a/sdc", "r/.*/"]
Similarly, if your compute nodes use LVM on the operating system disk, you must also modify the filter in the
/etc/lvm/lvm.conffile on those nodes to include only the operating system disk. For example, if the/dev/sdadevice contains the operating system:filter = [ "a/sda/", "r/.*/"]
Configure components¶
Edit the
/etc/manila/manila.conffile and complete the following actions:In the
[DEFAULT]section, enable the LVM driver and the NFS protocol:[DEFAULT] ... enabled_share_backends = lvm enabled_share_protocols = NFS
Note
Back end names are arbitrary. As an example, this guide uses the name of the driver.
In the
[lvm]section, configure the LVM driver:[lvm] share_backend_name = LVM share_driver = manila.share.drivers.lvm.LVMShareDriver driver_handles_share_servers = False lvm_share_volume_group = manila-volumes lvm_share_export_ips = MANAGEMENT_INTERFACE_IP_ADDRESS
Replace
MANAGEMENT_INTERFACE_IP_ADDRESSwith the IP address of the management network interface on your storage node. The value of this option can be a comma separated string of one or more IP addresses. In the example architecture shown below, the address would be 10.0.0.41:
Hardware requirements.¶
Shared File Systems Option 2: Driver support for share servers management¶
For simplicity, this configuration references the same storage node as the one used for the Block Storage service.
Note
This guide describes how to configure the Shared File Systems service to
use the generic driver with the driver handles share server mode
(DHSS) enabled. This driver requires Compute service (nova), Image service
(glance) and Networking service (neutron) for creating and managing share
servers; and Block storage service (cinder) for creating shares. The
information used for creating share servers is configured as share
networks. Generic driver with DHSS enabled also requires the tenant’s
private network (where the compute instances are running) to be attached
to a public router.
Prerequisites¶
Before you proceed, verify operation of the Compute, Networking, and Block Storage services. This options requires implementation of Networking option 2 and requires installation of some Networking service components on the storage node.
Install the Networking service components:
# zypper install --no-recommends openstack-neutron-linuxbridge-agent
Configure components¶
Edit the
/etc/manila/manila.conffile and complete the following actions:In the
[DEFAULT]section, enable the generic driver and the NFS protocol:[DEFAULT] ... enabled_share_backends = generic enabled_share_protocols = NFS
Note
Back end names are arbitrary. As an example, this guide uses the name of the driver.
In the
[neutron],[nova],[cinder]and[glance]sections, enable authentication for those services:[neutron] ... url = http://controller:9696 www_authenticate_uri = http://controller:5000 auth_url = http://controller:5000 memcached_servers = controller:11211 auth_type = password project_domain_name = Default user_domain_name = Default region_name = RegionOne project_name = service username = neutron password = NEUTRON_PASS [nova] ... www_authenticate_uri = http://controller:5000 auth_url = http://controller:5000 memcached_servers = controller:11211 auth_type = password project_domain_name = Default user_domain_name = Default region_name = RegionOne project_name = service username = nova password = NOVA_PASS [cinder] ... www_authenticate_uri = http://controller:5000 auth_url = http://controller:5000 memcached_servers = controller:11211 auth_type = password project_domain_name = Default user_domain_name = Default region_name = RegionOne project_name = service username = cinder password = CINDER_PASS [glance] ... www_authenticate_uri = http://controller:5000 auth_url = http://controller:5000 memcached_servers = controller:11211 auth_type = password project_domain_name = Default user_domain_name = Default region_name = RegionOne project_name = service username = glance password = GLANCE_PASS
In the
[generic]section, configure the generic driver:[generic] share_backend_name = GENERIC share_driver = manila.share.drivers.generic.GenericShareDriver driver_handles_share_servers = True service_instance_flavor_id = 100 service_image_name = manila-service-image service_instance_user = manila service_instance_password = manila interface_driver = manila.network.linux.interface.BridgeInterfaceDriver
Note
You can also use SSH keys instead of password authentication for service instance credentials.
Important
The
service_image_name,service_instance_flavor_id,service_instance_userandservice_instance_passwordare with reference to the service image that is used by the driver to create share servers. A sample service image for use with thegenericdriver is available in themanila-image-elementsproject. Its creation is explained in the post installation steps (See: Creating and using shared file systems).
Finalize installation¶
Prepare manila-share as start/stop service. Start the Shared File Systems service including its dependencies and configure them to start when the system boots:
# systemctl enable openstack-manila-share.service tgtd.service # systemctl start openstack-manila-share.service tgtd.service
