Policy enforcement¶
Policies are defined and evaluated in the Congress project. The policy language for Congress is Datalog. The congress policy consists of the Datalog rules and facts.
Examples of policies are as follows:
- Minimum 2 GB of RAM for all VM instances.
- A certified version for all Apache server instances.
- Data placement policy: all database instances must be deployed at a given geographic location enforcing some law restriction on data placement.
These policies are evaluated over data in the form of tables (Congress data structures). A deployed Murano environment must be decomposed to the Congress data structures. The decomposed environment is sent to Congress for simulation. Congress simulates whether the resulting state violates any defined policy: deployment is aborted in case of policy violation.
Murano uses two predefined policies in Congress:
- murano_system contains rules and facts of policies defined by the cloud administrator.
- murano contains only facts/records reflecting the resulting state after the deployment of an environment.
Records in the murano policy are queried by rules from the murano_system policy. The Congress simulation does not create any records in the murano policy, and only provides the feedback on whether the resulting state violates the policy or not.
As a part of the policy guided fulfillment, you need to enforce policies on a murano environment deployment. If the policy enforcement fails, the deployment fails as well.
Setting up policy enforcement¶
Before you use the policy enforcement feature, configure Murano and Congress properly.
Note
This article does not cover Murano and Congress configuration options useful for Murano application deployment, for example, DNS setup, floating IPs, and so on.
To enable policy enforcement, complete the following tasks:
In Murano:
- Enable the enable_model_policy_enforcer option in the murano.conf file:
[engine] # Enable model policy enforcer using Congress (boolean value) enable_model_policy_enforcer = true
- Restart murano-engine.
Verify that Congress is installed and available in your OpenStack environment. See the details in the Congress official documentation.
Install the congress command-line client as any other OpenStack command-line client.
For Congress, configure the following policies that policy enforcement uses during the evaluation:
murano policy
It is created by the Congress` murano datasource driver, which is a part of Congress. Configure it for the OpenStack project (tenant) where you plan to deploy your Murano application. Datasource driver retrieves deployed Murano environments and populates Congress’ murano policy tables. See Murano policy enforcement internals for details.
Remove the existing murano policy and create a new murano policy configured for the demo project, by running:
# remove default murano datasource configuration, because it is using 'admin' project. We need 'demo' project to be used. openstack congress datasource delete murano openstack congress datasource create murano murano --config username="$OS_USERNAME" --config tenant_name="demo" --config password="$OS_PASSWORD" --config auth_url="$OS_AUTH_URL"
murano_system policy
It holds the user-defined rules for policy enforcement. Typically, the rules use tables from other policies, for example, murano, nova, keystone, and others. Policy enforcement expects the predeploy_errors table here that is available on the predeploy_errors rules creation.
Create the murano_system rule, by running:
# create murano_system policy openstack congress policy create murano_system # resolves objects within environment openstack congress policy rule create murano_system 'murano_env_of_object(oid,eid):-murano:connected(eid,oid), murano:objects(eid,tid,"io.murano.Environment")'
murano_action policy with internal management rules.
These rules are used internally in the policy enforcement request and stored in a dedicated murano_action policy that is created here. They are important in case an environment is redeployed.
# create murano_action policy openstack congress policy create murano_action --kind action # register action deleteEnv openstack congress policy rule create murano_action 'action("deleteEnv")' # states openstack congress policy rule create murano_action 'murano:states-(eid, st) :- deleteEnv(eid), murano:states( eid, st)' # parent_types openstack congress policy rule create murano_action 'murano:parent_types-(tid, type) :- deleteEnv(eid), murano:connected(eid, tid),murano:parent_types(tid,type)' openstack congress policy rule create murano_action 'murano:parent_types-(eid, type) :- deleteEnv(eid), murano:parent_types(eid,type)' # properties openstack congress policy rule create murano_action 'murano:properties-(oid, pn, pv) :- deleteEnv(eid), murano:connected(eid, oid), murano:properties(oid, pn, pv)' openstack congress policy rule create murano_action 'murano:properties-(eid, pn, pv) :- deleteEnv(eid), murano:properties(eid, pn, pv)' # objects openstack congress policy rule create murano_action 'murano:objects-(oid, pid, ot) :- deleteEnv(eid), murano:connected(eid, oid), murano:objects(oid, pid, ot)' openstack congress policy rule create murano_action 'murano:objects-(eid, tnid, ot) :- deleteEnv(eid), murano:objects(eid, tnid, ot)' # relationships openstack congress policy rule create murano_action 'murano:relationships-(sid, tid, rt) :- deleteEnv(eid), murano:connected(eid, sid), murano:relationships( sid, tid, rt)' openstack congress policy rule create murano_action 'murano:relationships-(eid, tid, rt) :- deleteEnv(eid), murano:relationships(eid, tid, rt)' # connected openstack congress policy rule create murano_action 'murano:connected-(tid, tid2) :- deleteEnv(eid), murano:connected(eid, tid), murano:connected(tid,tid2)' openstack congress policy rule create murano_action 'murano:connected-(eid, tid) :- deleteEnv(eid), murano:connected(eid,tid)'
Creating policy enforcement rules¶
This article illustrates how you can create policy enforcement rules. For testing purposes, create rules that prohibit the creation of instances with the flavor with over 2048 MB of RAM following the procedure below.
Procedure:
Verify that you have configured your OpenStack environment as described in Setting up policy enforcement.
To create the predeploy_errors rule, run:
congress policy rule create murano_system "predeploy_errors(eid, obj_id, msg) :- murano:objects(obj_id, pid, type), murano:objects(eid, tid, \"io.murano.Environment\"), murano:connected(eid, pid), murano:properties(obj_id, \"flavor\", flavor_name), flavor_ram(flavor_name, ram), gt(ram, 2048), murano:properties(obj_id, \"name\", obj_name), concat(obj_name, \": instance flavor has RAM size over 2048MB\", msg)"The command above contains the following information:
predeploy_errors(eid, obj_id, msg) :- murano:objects(obj_id, pid, type), murano:objects(eid, tid, "io.murano.Environment"), murano:connected(eid, pid), murano:properties(obj_id, "flavor", flavor_name), flavor_ram(flavor_name, ram), gt(ram, 2048), murano:properties(obj_id, "name", obj_name), concat(obj_name, ": instance flavor has RAM size over 2048MB", msg)
Policy validation engine checks the predeploy_errors rule, and rules referenced within this rule are evaluated by the Congress engine.
In this example, we create the rule that references the flavor_ram rule we create afterwards. It disables flavors with RAM more than 2048 MB and constructs the message returned to the user in the msg variable.
In this example we use data from policy murano which is represented by murano:properties. There are stored rows with decomposition of model representing murano application. We also use built-in functions of Congress:
- gt stands for ‘greater-than’
- concat joins two strings into one variable
To create the flavor_ram rule, run:
congress policy rule create murano_system "flavor_ram(flavor_name, ram) :- nova:flavors(id, flavor_name, cpus, ram)"This rule resolves parameters of flavor by flavor name and returns the ram parameter. It uses the flavors rule from nova policy. Data in this policy is filled by the nova datasource driver.
Check the rule usage.
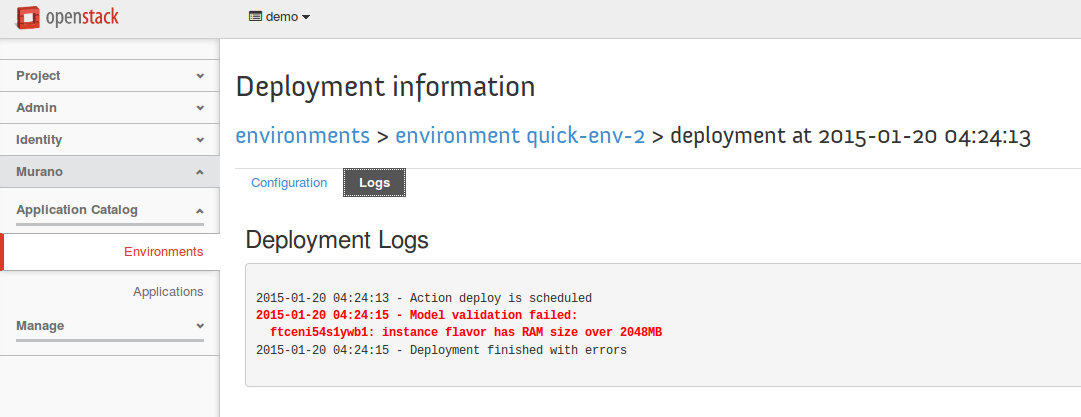
Deployment fails as the rule is violated: environment is in the Deploy FAILURE status. Check the deployment logs for details:
See also
Murano policy enforcement internals¶
This section describes internals of the murano policy enforcement feature.
Model decomposition¶
The data for the policy validation comes from the models of Murano applications. These models are transformed to a set of rules that are processed by Congress.
There are several tables created in murano policy for different kinds of rules that are as follows:
- murano:objects(object_id, parent_id, type_name)
- murano:properties(object_id, property_name, property_value)
- murano:relationships(source, target, name)
- murano:connected(source, target)
- murano:parent_types(object_id, parent_type_name)
- murano:states(environment_id, state)
murano:objects(object_id, parent_id, type_name)
This rule is used for representation of all objects in Murano model, such as environment, application, instance, and other.
Value of the type property is used as the type_name parameter:
name: wordpress-env '?': {type: io.murano.Environment, id: 83bff5ac} applications: - '?': {id: e7a13d3c, type: io.murano.databases.MySql}The model above transforms to the following rules:
- murano:objects+("83bff5ac", "tenant_id", "io.murano.Environment")
- murano:objects+("83bff5ac", "e7a13d3c", "io.murano.databases.MySql")
Note
The owner of the environment is a project (tenant).
murano:properties(object_id, property_name, property_value)
Each object may have properties. In this example we have an application with one property:
applications: - '?': {id: e7a13d3c, type: io.murano.databases.MySql} database: wordpressThe model above transforms to the following rule:
- murano:properties+("e7a13d3c", "database", "wordpress")
Inner properties are also supported using dot notation:
instance: '?': {id: 825dc61d, type: io.murano.resources.LinuxMuranoInstance} networks: useFlatNetwork: falseThe model above transforms to the following rule:
- murano:properties+("825dc61d", "networks.useFlatNetwork", "False")
If a model contains list of values, it is represented as a set of multiple rules:
instances: - '?': {id: be3c5155, type: io.murano.resources.LinuxMuranoInstance} networks: customNetworks: [10.0.1.0, 10.0.2.0]The model above transforms to the following rules:
- murano:properties+("be3c5155", "networks.customNetworks", "10.0.1.0")
- murano:properties+("be3c5155", "networks.customNetworks", "10.0.2.0")
murano:relationships(source, target, name)
Murano application models may contain references to other applications. In this example, the WordPress application references MySQL in the database property:
applications: - '?': id: 0aafd67e type: io.murano.databases.MySql - '?': id: 50fa68ff type: io.murano.apps.WordPress database: 0aafd67eThe model above transforms to the following rule:
- murano:relationships+("50fa68ff", "0aafd67e", "database")
Note
For the database property we do not create the murano:properties+ rule.
If we define an object within other object, they will have relationships between them:
applications: - '?': id: 0aafd67e type: io.murano.databases.MySql instance: '?': {id: ed8df2b0, type: io.murano.resources.LinuxMuranoInstance}The model above transforms to the following rule:
- murano:relationships+("0aafd67e", "ed8df2b0", "instance")
There are special relationships of services from the environment to its applications: murano:relationships+("env_id", "app_id", "services")
murano:connected(source, target)
This table stores both direct and indirect connections between instances. It is derived from murano:relationships:
applications: - '?': id: 0aafd67e type: io.murano.databases.MySql instance: '?': {id: ed8df2b0, type: io.murano.resources.LinuxMuranoInstance} - '?': id: 50fa68ff type: io.murano.apps.WordPress database: 0aafd67eThe model above transforms to the following rules:
- murano:connected+("50fa68ff", "0aafd67e") # WordPress to MySql
- murano:connected+("50fa68ff", "ed8df2b0") # WordPress to LinuxMuranoInstance
- murano:connected+("0aafd67e", "ed8df2b0") # MySql to LinuxMuranoInstance
murano:parent_types(object_id, parent_name)
Each object in murano has a class type. These classes may inherit from one or more parents. For example, LinuxMuranoInstance > LinuxInstance > Instance:
instances: - '?': {id: be3c5155, type: LinuxMuranoInstance}The model above transforms to the following rules:
- murano:objects+("...", "be3c5155", "LinuxMuranoInstance")
- murano:parent_types+("be3c5155", "LinuxMuranoInstance")
- murano:parent_types+("be3c5155", "LinuxInstance")
- murano:parent_types+("be3c5155", "Instance")
Note
The type of an object is also repeated in its parent types (LinuxMuranoInstance in the example) for easier handling of user-created rules.
Note
If a type inherits from more than one parent, and these parents inherit from one common type, the parent_type rule is included only once in the common type.
murano:states(environment_id, state)
Currently only one record for environment is created:
- murano:states+("uugi324", "pending")
Using policy for the base modification of an environment¶
Congress policies enables a user to define modification of an environment prior to its deployment. This includes:
- Adding components, for example, monitoring.
- Changing and setting properties, for example enforcing a given zone, flavors, and others.
- Configuring relationships within an environment.
Use cases examples:
- Installation of the monitoring agent on each VM instance by adding a component with the agent and creating relationship between the agent and instance.
- Enabling a certified version to all Apache server instances: setting the version property to all Apache applications within an environment to a particular version.
These policies are evaluated over data in the form of tables that are Congress data structures. A deployed murano environment must be decomposed to Congress data structures. The further workflow is as follows:
The decomposed environment is sent to Congress for simulation.
Congress simulates whether the resulting state requires modification.
In case the modification of a deployed environment is required, Congress returns a list of actions in the YAML format to be performed on the environment prior to the deployment.
For example:
set-property: {object_id: c46770dec1db483ca2322914b842e50f, prop_name: keyname, value: production-key}
The example above sets the keyname property to the production-key value on the instance identified by object_id. An administrator can use it as an output of the Congress rules.
The action specification is parsed in murano. The given action class is loaded, and the action instance is created.
The parsed parameters are supplied to the action __init__ method.
The action is performed on a given environment (the modify method).
Creating base modification rules¶
This example illustrates how to configure the rule enforcing all VM instances to deploy with a secure key pair. This may be required in a production environment.
Warning
Before you create rules, configure your OpenStack environment as described in Setting up policy enforcement.
Procedure:
To create the predeploy_modify rule, run:
congress policy rule create murano_system 'predeploy_modify(eid, obj_id, action):-murano:objects(obj_id, pid, type), murano_env_of_object(obj_id, eid), murano:properties(obj_id, "keyname", kn), concat("set-property: {object_id: ", obj_id, first_part), concat(first_part, ", prop_name: keyname, value: production-key}", action)'The command above contains the following information:
predeploy_modify(eid, obj_id, action) :- murano:objects(obj_id, pid, type), murano:objects(eid, tid, "io.murano.Environment"), murano:connected(eid, pid), murano:properties(obj_id, "keyname", kn), concat("set-property: {object_id: ", obj_id, first_part), concat(first_part, ", prop_name: keyname, value: production-key}", action)
Policy validation engine checks the predeploy_modify rule. And the Congress engine evaluates the rules referenced inside this rule.
Note
The production-key key pair must already exist, though you can use any other existing key pair.
Deploy the environment.
Instances within the environment are deployed with the specified key pair.
See also