Object Storage characteristics¶
The key characteristics of Object Storage are that:
- All objects stored in Object Storage have a URL.
- “Storage Policies” may be used to define different levels of durability for objects stored in the cluster. These policies support not only complete replicas but also erasure-coded fragments.
- All replicas or fragments for an object are stored in as-unique-as-possible zones to increase durability and availability.
- All objects have their own metadata.
- Developers interact with the object storage system through a RESTful HTTP API.
- Object data can be located anywhere in the cluster.
- The cluster scales by adding additional nodes without sacrificing performance, which allows a more cost-effective linear storage expansion than fork-lift upgrades.
- Data does not have to be migrated to an entirely new storage system.
- New nodes can be added to the cluster without downtime.
- Failed nodes and disks can be swapped out without downtime.
- It runs on industry-standard hardware, such as Dell, HP, and Supermicro.
Object Storage (swift)
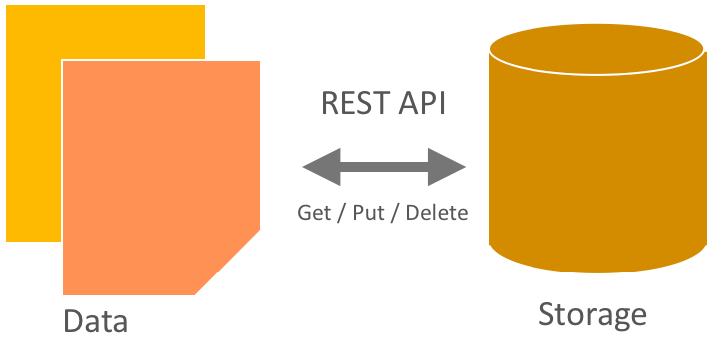
Developers can either write directly to the Swift API or use one of the many client libraries that exist for all of the popular programming languages, such as Java, Python, Ruby, and C#. Amazon S3 and RackSpace Cloud Files users should be very familiar with Object Storage. Users new to object storage systems will have to adjust to a different approach and mindset than those required for a traditional filesystem.

Except where otherwise noted, this document is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. See all OpenStack Legal Documents.