ETSI NFV-SOL VNF Deployment as VM with TOSCA¶
This document describes how to deploy VNF as VM with TOSCA in Tacker using CLI commands.
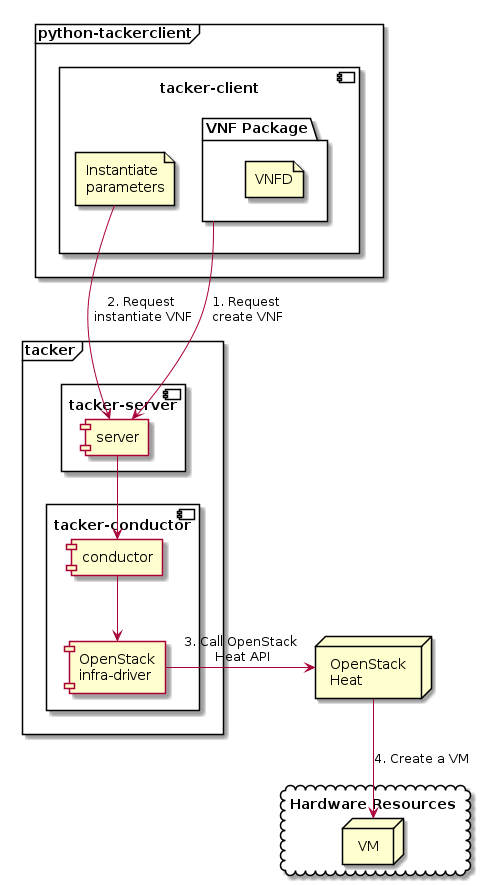
Overview¶
The diagram below shows an overview of the VNF deployment.
Request create VNF
A user requests tacker-server to create a VNF with tacker-client by uploading a VNF Package and requesting
create VNF. The VNF Package should containVNFD. The detailed explanation ofVNFDcan be found in VNF Package.Request instantiate VNF
A user requests tacker-server to instantiate the created VNF by requesting
instantiate VNFwith instantiate parameters.Call OpenStack Heat API
Upon receiving a request from tacker-client, tacker-server redirects it to tacker-conductor. In tacker-conductor, the request is redirected again to an appropriate infra-driver (in this case OpenStack infra-driver) according to the contents of the instantiate parameters. Then, OpenStack infra-driver calls OpenStack Heat APIs to create a VM as a VNF.
Create a VM
OpenStack Heat creates a VM according to the API calls.
Prerequisites¶
The following packages should be installed:
tacker
python-tackerclient
A default VIM should be registered according to VIM Management.
The VNF Package(sample_vnf_pkg.zip) used below is prepared by referring to VNF Package.
VNF Deployment Procedure as VM¶
In order to deploy VNF as VM, it is necessary to execute the following procedure. Details of CLI commands are described in VNF Package Management and VNF Lifecycle Management.
1. Create VNF Package Info¶
Execute the following CLI command to create VNF Package.
$ openstack vnf package create
Result:
+-------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Field | Value |
+-------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| ID | e712a702-741f-4093-a971-b3ad69411ac1 |
| Links | packageContent=href=/vnfpkgm/v1/vnf_packages/e712a702-741f-4093-a971-b3ad69411ac1/package_content, |
| | self=href=s/vnfpkgm/v1/vnf_packages/e712a702-741f-4093-a971-b3ad69411ac1 |
| Onboarding State | CREATED |
| Operational State | DISABLED |
| Usage State | NOT_IN_USE |
| User Defined Data | |
+-------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
After that, execute the following CLI command and confirm that VNF Package creation was successful.
Confirm that the ‘Onboarding State’ is ‘CREATED’.
Confirm that the ‘Operational State’ is ‘DISABLED’.
Confirm that the ‘Usage State’ is ‘NOT_IN_USE’.
$ openstack vnf package show VNF_PACKAGE_ID \
-c 'Onboarding State' -c 'Operational State' -c 'Usage State'
Result:
+-------------------+------------+
| Field | Value |
+-------------------+------------+
| Onboarding State | CREATED |
| Operational State | DISABLED |
| Usage State | NOT_IN_USE |
+-------------------+------------+
2. Upload VNF Package¶
Execute the following CLI command to upload VNF Package.
$ openstack vnf package upload --path sample_csar.zip VNF_PACKAGE_ID
Result:
Upload request for VNF package e712a702-741f-4093-a971-b3ad69411ac1 has been accepted.
After that, execute the following CLI command and confirm that VNF Package uploading was successful.
Confirm that the ‘Onboarding State’ is ‘ONBOARDED’.
Confirm that the ‘Operational State’ is ‘ENABLED’.
Confirm that the ‘Usage State’ is ‘NOT_IN_USE’.
Take a note of the ‘VNFD ID’ because you will need it in the next ‘Create VNF Identifier’.
Note
The state of ‘Onboarding State’ changes in the order of ‘UPLOADING’, ‘PROCESSING’, ‘ONBOARDED’.
$ openstack vnf package show VNF_PACKAGE_ID \
-c 'Onboarding State' -c 'Operational State' -c 'Usage State' -c 'VNFD ID'
Result:
+-------------------+--------------------------------------+
| Field | Value |
+-------------------+--------------------------------------+
| Onboarding State | ONBOARDED |
| Operational State | ENABLED |
| Usage State | NOT_IN_USE |
| VNFD ID | b1bb0ce7-ebca-4fa7-95ed-4840d70a1177 |
+-------------------+--------------------------------------+
3. Create VNF Identifier¶
Execute the following CLI command to create a VNF instance.
$ openstack vnflcm create VNFD_ID
Result:
+--------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Field | Value |
+--------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| ID | 725f625e-f6b7-4bcd-b1b7-7184039fde45 |
| Instantiation State | NOT_INSTANTIATED |
| Links | instantiate=href=/vnflcm/v1/vnf_instances/725f625e-f6b7-4bcd-b1b7-7184039fde45/instantiate, |
| | self=href=/vnflcm/v1/vnf_instances/725f625e-f6b7-4bcd-b1b7-7184039fde45 |
| VNF Instance Description | None |
| VNF Instance Name | None |
| VNF Product Name | Sample VNF |
| VNF Provider | Company |
| VNF Software Version | 1.0 |
| VNFD ID | b1bb0ce7-ebca-4fa7-95ed-4840d70a1177 |
| VNFD Version | 1.0 |
+--------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
After that, execute the following CLI command and confirm that VNF instance creation was successful.
Confirm that the ‘Usage State’ of the VNF Package is ‘IN_USE’.
Confirm that the ‘Instantiation State’ of the VNF instance is ‘NOT_INSTANTIATED’.
$ openstack vnf package show VNF_PACKAGE_ID \
-c 'Usage State'
Result:
+-------------+--------+
| Field | Value |
+-------------+--------+
| Usage State | IN_USE |
+-------------+--------+
$ openstack vnflcm show VNF_INSTANCE_ID \
-c 'Instantiation State'
Result:
+---------------------+------------------+
| Field | Value |
+---------------------+------------------+
| Instantiation State | NOT_INSTANTIATED |
+---------------------+------------------+
4. Instantiate VNF¶
Create a sample_param_file.json file with the following format. This is the file that defines the parameters for an instantiate request. These parameters will be set in the body of the instantiate request.
Required parameter:
flavourID
Note
Details of flavourID is described in VNF Descriptor (VNFD) based on ETSI NFV-SOL001.
Optional parameters:
instantiationLevelId
extVirtualLinks
extManagedVirtualLinks
vimConnectionInfo
Note
You can skip vimConnectionInfo only when you have
the default VIM described in VIM Management.
Note
This operation can specify the vimConnectionInfo
for the VNF instance.
Even if this operation specify multiple vimConnectionInfo
associated with one VNF instance, only one of them will be used for
life cycle management operations.
Param file with only required parameters:
{
"flavourId":"simple"
}
Param file with optional parameters:
{
"flavourId": "simple",
"instantiationLevelId": "instantiation_level_1",
"extVirtualLinks": [
{
"id": "net0",
"resourceId": "4bf3e646-7a24-4f04-a985-d8f4bb1203de", #Set the uuid of the network to use
"extCps": [
{
"cpdId": "CP1",
"cpConfig": [
{
"cpProtocolData": [
{
"layerProtocol": "IP_OVER_ETHERNET"
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
],
"vimConnectionInfo": [
{
"id": "e24f9796-a8e9-4cb0-85ce-5920dcddafa1", #Set a random uuid.
"vimId": "8a0fd79d-e224-4c27-85f5-ee79c6e0d870", #Set the uuid of the VIM to use
"vimType": "ETSINFV.OPENSTACK_KEYSTONE.v_2"
}
]
}
Execute the following CLI command to instantiate VNF instance.
$ openstack vnflcm instantiate VNF_INSTANCE_ID \
./sample_param_file.json
Result:
Instantiate request for VNF Instance 725f625e-f6b7-4bcd-b1b7-7184039fde45 has been accepted.
After that, execute the following CLI command and confirm that VNF instance instantiation was successful.
Confirm that the ‘Instantiation State’ is ‘INSTANTIATED’.
$ openstack vnflcm show VNF_INSTANCE_ID \
-c 'Instantiation State'
Result:
+---------------------+--------------+
| Field | Value |
+---------------------+--------------+
| Instantiation State | INSTANTIATED |
+---------------------+--------------+
5. Terminate VNF¶
Execute the following CLI command to terminate the VNF instance.
$ openstack vnflcm terminate VNF_INSTANCE_ID
Result:
Terminate request for VNF Instance '725f625e-f6b7-4bcd-b1b7-7184039fde45' has been accepted.
After that, execute the following CLI command and confirm that VNF instance termination was successful.
Confirm that the ‘Instantiation State’ is ‘NOT_INSTANTIATED’.
$ openstack vnflcm show VNF_INSTANCE_ID \
-c 'Instantiation State'
Result:
+---------------------+------------------+
| Field | Value |
+---------------------+------------------+
| Instantiation State | NOT_INSTANTIATED |
+---------------------+------------------+
6. Delete VNF Identifier¶
Execute the following CLI command to delete the VNF instance.
$ openstack vnflcm delete VNF_INSTANCE_ID
Result:
Vnf instance '725f625e-f6b7-4bcd-b1b7-7184039fde45' deleted successfully
After that, execute the following CLI command and confirm that VNF instance deletion was successful.
Confirm that the ‘Usage State’ of VNF Package is ‘NOT_IN_USE’.
Confirm that the VNF instance is not found.
$ openstack vnf package show VNF_PACKAGE_ID \
-c 'Usage State'
Result:
+-------------+------------+
| Field | Value |
+-------------+------------+
| Usage State | NOT_IN_USE |
+-------------+------------+
$ openstack vnflcm show VNF_INSTANCE_ID
Result:
Can not find requested vnf instance: 725f625e-f6b7-4bcd-b1b7-7184039fde45
