ETSI NFV-SOL CNF Update with Mgmt Driver¶
This document describes how to update CNF with Mgmt Driver in Tacker v1 API.
Note
This is a document for Tacker v1 API. See ETSI NFV-SOL CNF Update with Mgmt Driver for Tacker v2 API.
Note
The content of this document has been confirmed to using the following VNF Packages.
Overview¶
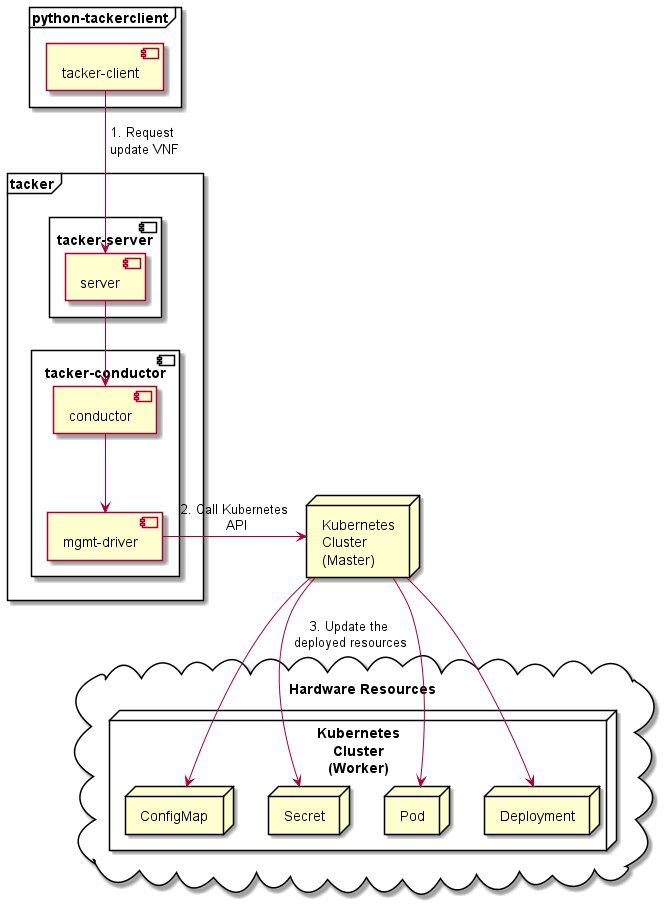
The diagram below shows an overview of the CNF updating.
Request update VNF
A user requests tacker-server to update a CNF with tacker-client by requesting
update VNFas a Modify VNF information operation.Call Kubernetes API
Upon receiving a request from tacker-client, tacker-server redirects it to tacker-conductor. In tacker-conductor, the request is redirected again to the matching Mgmt Driver (in this case the Mgmt Driver of container update) according to the contents of the VNFD in the VNF Package. Then, Mgmt Driver calls Kubernetes APIs.
Update resources
Kubernetes Master update resources according to the API calls.
Mgmt Driver Introduction¶
Mgmt Driver enables Users to configure their VNF before and/or after its VNF Lifecycle Management operation. Users can customize the logic of Mgmt Driver by implementing their own Mgmt Driver and these customizations are specified by “interface” definition in NFV-SOL001 v2.6.1.
The Mgmt Driver in this user guide supports updating CNF with
modify_information_start and modify_information_end operation.
Use Cases¶
In this user guide, the provided sample VNF Packages will be instantiated and then updated. The sample Mgmt Driver will update resources on Kubernetes during update. Update the ConfigMap and Secret, and also update the image in the Pod, Deployment, DaemonSet and ReplicaSet, and other resources will not change.
Prerequisites¶
The following packages should be installed:
tacker
python-tackerclient
After installing the above packages, you also need
to import the sample Mgmt Driver file. You can refer to
Set Tacker Configuration in
ETSI NFV-SOL CNF Update with Mgmt Driver for usage of
Mgmt Driver file.
Note
You can find sample Mgmt Driver file in the following path. samples/mgmt_driver/kubernetes/container_update/container_update_mgmt.py
You can also refer to ETSI NFV-SOL CNF (Containerized VNF) Deployment for the procedure of preparation from “Prepare Kubernetes VIM” to “Instantiate VNF”.
How to Instantiate VNF for Updating¶
You can use the sample VNF package below to instantiate VNF to be updated.
Note
In this document, TACKER_ROOT is the root of tacker’s repository on
the server.
$ cd TACKER_ROOT/samples/tests/etc/samples/etsi/nfv/test_cnf_container_update_before
Copy the official definition files from the sample directory. NFV-SOL001 v2.6.1 specifies the structure and format of the VNFD based on TOSCA specifications.
$ cp TACKER_ROOT/samples/vnf_packages/Definitions/etsi_nfv_sol001_common_types.yaml Definitions/
$ cp TACKER_ROOT/samples/vnf_packages/Definitions/etsi_nfv_sol001_vnfd_types.yaml Definitions/
CSAR Package should be compressed into a ZIP file for uploading. Following commands are an example of compressing a VNF Package:
Note
The sample Mgmt Driver file also needs to be copied into the CSAR Package.
$ mkdir Scripts
$ cp TACKER_ROOT/samples/mgmt_driver/kubernetes/container_update/container_update_mgmt.py Scripts/
$ zip deployment.zip -r Definitions/ Files/ TOSCA-Metadata/ Scripts/
After creating a VNF package with openstack vnf package create, When the Onboarding State is CREATED, the Operational State is DISABLED, and the Usage State is NOT_IN_USE, indicate the creation is successful.
$ openstack vnf package create
+-------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Field | Value |
+-------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| ID | d2e2689f-0850-47b6-bfed-0d8f1612601a |
| Links | { |
| | "self": { |
| | "href": "/vnfpkgm/v1/vnf_packages/d2e2689f-0850-47b6-bfed-0d8f1612601a" |
| | }, |
| | "packageContent": { |
| | "href": "/vnfpkgm/v1/vnf_packages/d2e2689f-0850-47b6-bfed-0d8f1612601a/package_content" |
| | } |
| | } |
| Onboarding State | CREATED |
| Operational State | DISABLED |
| Usage State | NOT_IN_USE |
| User Defined Data | {} |
+-------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Upload the CSAR zip file to the VNF Package by running the following command openstack vnf package upload --path <path of vnf package> <vnf package ID>.
Here is an example of uploading VNF package:
$ openstack vnf package upload --path deployment.zip d2e2689f-0850-47b6-bfed-0d8f1612601a
Upload request for VNF package d2e2689f-0850-47b6-bfed-0d8f1612601a has been accepted.
Create VNF instance by running openstack vnflcm create <VNFD ID>.
Note
The VNFD ID could be found by openstack vnf package show <vnf package ID> command.
Here is an example of creating VNF :
$ openstack vnflcm create b1bb0ce7-ebca-4fa7-95ed-4840d70a7774
+-----------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Field | Value |
+-----------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| ID | beaf9797-ccf5-41f7-a546-0ff675475e5a |
| Instantiation State | NOT_INSTANTIATED |
| Links | { |
| | "self": { |
| | "href": "http://localhost:9890/vnflcm/v1/vnf_instances/beaf9797-ccf5-41f7-a546-0ff675475e5a" |
| | }, |
| | "instantiate": { |
| | "href": "http://localhost:9890/vnflcm/v1/vnf_instances/beaf9797-ccf5-41f7-a546-0ff675475e5a/instantiate" |
| | } |
| | } |
| VNF Configurable Properties | |
| VNF Instance Description | |
| VNF Instance Name | vnf-beaf9797-ccf5-41f7-a546-0ff675475e5a |
| VNF Product Name | Sample VNF |
| VNF Provider | Company |
| VNF Software Version | 1.0 |
| VNFD ID | b1bb0ce7-ebca-4fa7-95ed-4840d70a7774 |
| VNFD Version | 1.0 |
| vnfPkgId | |
+-----------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
The following example shows the yaml files that deploys the Kubernetes
resources.
You can see resource definition files are included as a value of
lcm-kubernetes-def-files in additionalParams here.
$ cat ./instance_kubernetes.json
{
"flavourId": "simple",
"additionalParams": {
"lcm-kubernetes-def-files": [
"Files/kubernetes/configmap_1.yaml",
"Files/kubernetes/deployment.yaml",
"Files/kubernetes/pod_env.yaml",
"Files/kubernetes/pod_volume.yaml",
"Files/kubernetes/replicaset.yaml",
"Files/kubernetes/secret_1.yaml",
"Files/kubernetes/configmap_3.yaml",
"Files/kubernetes/pod_env_2.yaml",
"Files/kubernetes/pod_volume_2.yaml",
"Files/kubernetes/daemonset.yaml",
"Files/kubernetes/deployment_2.yaml",
"Files/kubernetes/secret_3.yaml"
],
"namespace": "default"
},
"vimConnectionInfo": [
{
"id": "8a3adb69-0784-43c7-833e-aab0b6ab4470",
"vimId": "fcb8fc03-5c57-4221-92d5-ebbdf86baf68",
"vimType": "kubernetes"
}
]
}
Instantiate VNF by running the following command openstack vnflcm instantiate <VNF instance ID> <json file>, after the command above is executed.
$ openstack vnflcm instantiate beaf9797-ccf5-41f7-a546-0ff675475e5a instance_kubernetes.json
Instantiate request for VNF Instance beaf9797-ccf5-41f7-a546-0ff675475e5a has been accepted.
CNF Updating Procedure¶
As mentioned in Prerequisites, the VNF must be instantiated before performing updating.
Next, the user can use the original vnf package as a template to make a new vnf package, in which the yaml of ConfigMap, Secret, Pod, Deployment, DaemonSet and ReplicaSet can be changed.
Note
The yaml of ConfigMap and Secret can be changed. The kind, namespace and name cannot be changed, but the file name and file path can be changed.
The yaml of Pod, Deployment, DaemonSet and ReplicaSet can also be changed, but only the image field can be changed, and no other fields can be changed.
No other yaml is allowed to be changed.
If changes other than images are made to the yaml of Pod, Deployment, DaemonSet and ReplicaSet, those will not take effect. However, if heal entire VNF at this time, the resource will be based on the new yaml during the instantiation, and all changes will take effect.
Then after creating and uploading the new vnf package, you can perform the update operation. After the update, the Mgmt Driver will restart the pod to update and recreate the deployment, DaemonSet and ReplicaSet to update.
Note
This document provides the new vnf package, samples/tests/etc/samples/etsi/nfv/test_cnf_container_update_after
Details of CLI commands are described in VNF Lifecycle Management with v1 Tacker.
How to Update CNF¶
Execute Update CLI command and check the status of the resources before and after updating.
This is to confirm that the resources deployed in Kubernetes are updated after update CNF. The following is an example of the entire process. The resources information before update:
ConfigMap
$ kubectl get configmaps NAME DATA AGE cm-data 1 10m cm-data3 1 10m kube-root-ca.crt 1 26d $ $ kubectl describe configmaps cm-data Name: cm-data Namespace: default Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Data ==== cmKey1.txt: ---- configmap data foo bar BinaryData ==== Events: <none> $ $ kubectl describe configmaps cm-data3 Name: cm-data3 Namespace: default Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Data ==== cmKey1.txt: ---- configmap data foo bar BinaryData ==== Events: <none>
Secret
$ kubectl get secrets NAME TYPE DATA AGE default-token-k8svim kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 18h secret-data Opaque 2 12m secret-data3 Opaque 2 12m $ $ kubectl describe secrets secret-data Name: secret-data Namespace: default Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Type: Opaque Data ==== password: 15 bytes secKey1.txt: 15 bytes $ $ kubectl describe secrets secret-data3 Name: secret-data3 Namespace: default Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Type: Opaque Data ==== password: 15 bytes secKey1.txt: 15 bytes
Pod
$ kubectl get pod -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES daemonset-vdu5-r6vvl 1/1 Running 0 13m 10.0.0.89 vagrant <none> <none> deployment2-vdu6-86579d6868-dh57h 1/1 Running 0 13m 10.0.0.112 vagrant <none> <none> env-test 1/1 Running 0 13m 10.0.0.118 vagrant <none> <none> env-test2 1/1 Running 0 13m 10.0.0.104 vagrant <none> <none> vdu1-update-6fcf66b5dd-khdbw 1/1 Running 0 13m 10.0.0.90 vagrant <none> <none> vdu2-update-cqlpw 1/1 Running 0 13m 10.0.0.102 vagrant <none> <none> volume-test 1/1 Running 0 13m 10.0.0.107 vagrant <none> <none> volume-test2 1/1 Running 0 13m 10.0.0.109 vagrant <none> <none> $ $ kubectl describe pod volume-test Name: volume-test Namespace: default ... Containers: nginx: Container ID: cri-o://dd4972166ad302d20ff105df964546603bbba60c21a08ce45a13b4e5e37c8400 Image: nginx Image ID: docker.io/library/nginx@sha256:161ef4b1bf7effb350a2a9625cb2b59f69d54ec6059a8a155a1438d0439c593c ... Volumes: cm-volume: Type: ConfigMap (a volume populated by a ConfigMap) Name: cm-data Optional: false sec-volume: Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret) SecretName: secret-data Optional: false ... $ $ kubectl describe pod volume-test2 Name: volume-test2 Namespace: default ... Containers: nginx: Container ID: cri-o://1227dda5ddca12b95d9c47883eb9eae5f7d0cedfe0db4d5f5247d5002c2c7636 Image: nginx Image ID: docker.io/library/nginx@sha256:161ef4b1bf7effb350a2a9625cb2b59f69d54ec6059a8a155a1438d0439c593c ... Volumes: cm-volume: Type: ConfigMap (a volume populated by a ConfigMap) Name: cm-data3 Optional: false sec-volume: Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret) SecretName: secret-data3 Optional: false ...
Deployment
$ kubectl get deployments.apps -o wide NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR deployment2-vdu6 1/1 1 1 15m nginx nginx app=webserver vdu1-update 1/1 1 1 15m nginx nginx app=webserver $ $ kubectl describe pod vdu1-update-6fcf66b5dd-khdbw Name: vdu1-update-6fcf66b5dd-khdbw Namespace: default ... Containers: nginx: Container ID: cri-o://dbe3738cf68cfd223b484dcca6e9355bed59f4e074366a2fb08da9d41772efa0 Image: nginx Image ID: docker.io/library/nginx@sha256:161ef4b1bf7effb350a2a9625cb2b59f69d54ec6059a8a155a1438d0439c593c ... Environment Variables from: cm-data ConfigMap with prefix 'CM_' Optional: false secret-data Secret with prefix 'SEC_' Optional: false Environment: CMENV: <set to the key 'cmKey1.txt' of config map 'cm-data'> Optional: false SECENV: <set to the key 'password' in secret 'secret-data'> Optional: false ... $ $ kubectl describe pod deployment2-vdu6-86579d6868-dh57h Name: deployment2-vdu6-86579d6868-dh57h Namespace: default ... Containers: nginx: Container ID: cri-o://2a18bd975ba189e93a6dbafd353b1fe5d17612cf685a51dc4669eaa5b104170d Image: nginx Image ID: docker.io/library/nginx@sha256:161ef4b1bf7effb350a2a9625cb2b59f69d54ec6059a8a155a1438d0439c593c ... Environment Variables from: cm-data3 ConfigMap with prefix 'CM_' Optional: false secret-data3 Secret with prefix 'SEC_' Optional: false Environment: CMENV: <set to the key 'cmKey1.txt' of config map 'cm-data3'> Optional: false SECENV: <set to the key 'password' in secret 'secret-data3'> Optional: false ...
DaemonSet
$ kubectl get daemonset.apps -o wide NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR daemonset-vdu5 1 1 1 1 1 <none> 16m nginx nginx app=nginx $ $ kubectl describe pod daemonset-vdu5-r6vvl Name: daemonset-vdu5-r6vvl Namespace: default ... Containers: nginx: Container ID: cri-o://a6f53b97124212db820f951bae869fa38d5ad97f3f02eab2fe196d1e4d8af2e2 Image: nginx Image ID: docker.io/library/nginx@sha256:161ef4b1bf7effb350a2a9625cb2b59f69d54ec6059a8a155a1438d0439c593c ... Environment Variables from: cm-data ConfigMap with prefix 'CM_' Optional: false secret-data Secret with prefix 'SEC_' Optional: false Environment: CMENV: <set to the key 'cmKey1.txt' of config map 'cm-data'> Optional: false SECENV: <set to the key 'password' in secret 'secret-data'> Optional: false ...
ReplicaSet
$ kubectl get replicaset.apps -o wide NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR deployment2-vdu6-86579d6868 1 1 1 17m nginx nginx app=webserver,pod-template-hash=86579d6868 vdu1-update-6fcf66b5dd 1 1 1 17m nginx nginx app=webserver,pod-template-hash=6fcf66b5dd vdu2-update 1 1 1 17m nginx nginx app=webserver $ $ kubectl describe pod vdu2-update-cqlpw Name: vdu2-update-cqlpw Namespace: default ... Containers: nginx: Container ID: cri-o://59a9920844d78f75e5facad7284b95f43684059fe5da3708518be5d75643deef Image: nginx Image ID: docker.io/library/nginx@sha256:161ef4b1bf7effb350a2a9625cb2b59f69d54ec6059a8a155a1438d0439c593c ... Volumes: cm-volume: Type: ConfigMap (a volume populated by a ConfigMap) Name: cm-data Optional: false sec-volume: Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret) SecretName: secret-data Optional: false ...
Update CNF can be executed by the following CLI command.
$ openstack vnflcm update VNF_INSTANCE_ID --I sample_param_file.json
The content of the sample sample_param_file.json in this document is as follows:
{
"vnfdId": "b1bb0ce7-ebca-4fa7-95ed-4840d70a8883",
"vnfInstanceName": "update_vnf_after",
"metadata": {
"configmap_secret_paths": [
"Files/kubernetes/configmap_2.yaml",
"Files/kubernetes/secret_2.yaml"
]
}
}
Note
If you want to update ConfigMap and Secret, not only need to update their yaml, but also need to specify the updated yaml file path in the metadata field of the request input parameter.
The
configmap_secret_pathsspecified in metadata is not stored in the VnfInstance DB.
Here is an example of updating CNF:
$ openstack vnflcm update beaf9797-ccf5-41f7-a546-0ff675475e5a --I sample_param_file.json
Update vnf:beaf9797-ccf5-41f7-a546-0ff675475e5a
The resources information after update:
ConfigMap
$ kubectl describe configmaps cm-data Name: cm-data Namespace: default Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Data ==== cmKey1.txt: ---- configmap2 data2 foo2 bar2 BinaryData ==== Events: <none> $ $ kubectl describe configmaps cm-data3 Name: cm-data3 Namespace: default Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Data ==== cmKey1.txt: ---- configmap data foo bar BinaryData ==== Events: <none>
Secret
$ kubectl describe secrets secret-data Name: secret-data Namespace: default Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Type: Opaque Data ==== password: 16 bytes secKey1.txt: 18 bytes $ $ kubectl describe secrets secret-data3 Name: secret-data3 Namespace: default Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Type: Opaque Data ==== password: 15 bytes secKey1.txt: 15 bytes
Pod
$ kubectl get pod -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES daemonset-vdu5-6nrgg 1/1 Running 0 7m3s 10.0.0.92 vagrant <none> <none> deployment2-vdu6-86579d6868-dh57h 1/1 Running 0 27m 10.0.0.112 vagrant <none> <none> env-test 1/1 Running 1 (7m6s ago) 27m 10.0.0.118 vagrant <none> <none> env-test2 1/1 Running 0 27m 10.0.0.104 vagrant <none> <none> vdu1-update-5d87858fc6-hxqlt 1/1 Running 0 7m6s 10.0.0.103 vagrant <none> <none> vdu2-update-z4t48 1/1 Running 0 7m6s 10.0.0.122 vagrant <none> <none> volume-test 1/1 Running 1 (7m6s ago) 27m 10.0.0.107 vagrant <none> <none> volume-test2 1/1 Running 0 27m 10.0.0.109 vagrant <none> <none> $ $ kubectl describe pod volume-test Name: volume-test Namespace: default ... Containers: nginx: Container ID: cri-o://832b9df0c03b01a16710ea7b19be5dbff5dcf81fbccb080824795e0c3dd4e5ae Image: cirros Image ID: docker.io/library/cirros@sha256:6b2d9f5341bce2b1fb29669ff46744a145079ccc6a674849de3a4946ec3d8ffb ... Volumes: cm-volume: Type: ConfigMap (a volume populated by a ConfigMap) Name: cm-data Optional: false sec-volume: Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret) SecretName: secret-data Optional: false ... $ $ kubectl describe pod volume-test2 Name: volume-test2 Namespace: default ... Containers: nginx: Container ID: cri-o://1227dda5ddca12b95d9c47883eb9eae5f7d0cedfe0db4d5f5247d5002c2c7636 Image: nginx Image ID: docker.io/library/nginx@sha256:161ef4b1bf7effb350a2a9625cb2b59f69d54ec6059a8a155a1438d0439c593c ... Volumes: cm-volume: Type: ConfigMap (a volume populated by a ConfigMap) Name: cm-data3 Optional: false sec-volume: Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret) SecretName: secret-data3 Optional: false ...
Deployment
$ kubectl get deployments.apps -o wide NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR deployment2-vdu6 1/1 1 1 33m nginx nginx app=webserver vdu1-update 1/1 1 1 33m nginx cirros app=webserver $ $ kubectl describe pod vdu1-update-5d87858fc6-hxqlt Name: vdu1-update-5d87858fc6-hxqlt Namespace: default ... Containers: nginx: Container ID: cri-o://4a7b4a264f76b775c2740ed0a6debf77a02c097f15b2ae10fa999718d42afd8d Image: cirros Image ID: docker.io/library/cirros@sha256:6b2d9f5341bce2b1fb29669ff46744a145079ccc6a674849de3a4946ec3d8ffb ... Environment Variables from: cm-data ConfigMap with prefix 'CM_' Optional: false secret-data Secret with prefix 'SEC_' Optional: false Environment: CMENV: <set to the key 'cmKey1.txt' of config map 'cm-data'> Optional: false SECENV: <set to the key 'password' in secret 'secret-data'> Optional: false ... $ $ kubectl describe pod deployment2-vdu6-86579d6868-dh57h Name: deployment2-vdu6-86579d6868-dh57h Namespace: default ... Containers: nginx: Container ID: cri-o://2a18bd975ba189e93a6dbafd353b1fe5d17612cf685a51dc4669eaa5b104170d Image: nginx Image ID: docker.io/library/nginx@sha256:161ef4b1bf7effb350a2a9625cb2b59f69d54ec6059a8a155a1438d0439c593c ... Environment Variables from: cm-data3 ConfigMap with prefix 'CM_' Optional: false secret-data3 Secret with prefix 'SEC_' Optional: false Environment: CMENV: <set to the key 'cmKey1.txt' of config map 'cm-data3'> Optional: false SECENV: <set to the key 'password' in secret 'secret-data3'> Optional: false ...
DaemonSet
$ kubectl get daemonset.apps -o wide NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR daemonset-vdu5 1 1 1 1 1 <none> 35m nginx cirros app=nginx $ $ kubectl describe pod daemonset-vdu5-6nrgg Name: daemonset-vdu5-6nrgg Namespace: default ... Containers: nginx: Container ID: cri-o://7f18db12324ed751f28201bb0957aff513c93ed6b49d80d896dbac919bff5f30 Image: cirros Image ID: docker.io/library/cirros@sha256:6b2d9f5341bce2b1fb29669ff46744a145079ccc6a674849de3a4946ec3d8ffb ... Environment Variables from: cm-data ConfigMap with prefix 'CM_' Optional: false secret-data Secret with prefix 'SEC_' Optional: false Environment: CMENV: <set to the key 'cmKey1.txt' of config map 'cm-data'> Optional: false SECENV: <set to the key 'password' in secret 'secret-data'> Optional: false ...
ReplicaSet
$ kubectl get replicaset.apps -o wide NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR deployment2-vdu6-86579d6868 1 1 1 38m nginx nginx app=webserver,pod-template-hash=86579d6868 vdu1-update-5d87858fc6 1 1 1 18m nginx cirros app=webserver,pod-template-hash=5d87858fc6 vdu1-update-6fcf66b5dd 0 0 0 38m nginx nginx app=webserver,pod-template-hash=6fcf66b5dd vdu2-update 1 1 1 38m nginx celebdor/kuryr-demo app=webserver $ $ kubectl describe pod vdu2-update-z4t48 Name: vdu2-update-z4t48 Namespace: default ... Containers: nginx: Container ID: cri-o://4909dcdf39e101535a603ff5263298f3e52c5993d3822f3a0750860d889f6ebc Image: celebdor/kuryr-demo Image ID: docker.io/celebdor/kuryr-demo@sha256:74102005010b28a4518e08215df992a46b27ffc8b50836f29d8f9c0d7c9d4135 ... Volumes: cm-volume: Type: ConfigMap (a volume populated by a ConfigMap) Name: cm-data Optional: false sec-volume: Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret) SecretName: secret-data Optional: false ...
You can see that only the Pods are restarted whose ConfigMap/Secret or images are updated. When it comes to Deployments, DaemonSets and ReplicaSets whose ConfigMap/Secret or images are updated, their pods will be deleted and recreated.
