ETSI NFV-SOL CNF Scaling¶
This document describes how to scale CNF in Tacker v1 API.
Note
This is a document for Tacker v1 API. See ETSI NFV-SOL CNF Scaling for Tacker v2 API.
Note
The content of this document has been confirmed to work using the following VNF Package.
Overview¶
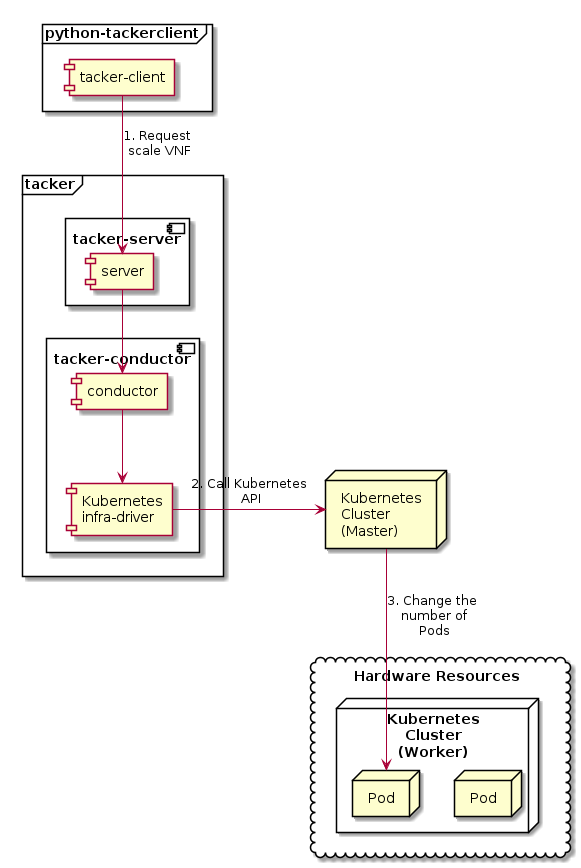
The diagram below shows an overview of the CNF scaling.
Request scale VNF
A user requests tacker-server to scale a VNF or all VNFs with tacker-client by requesting
scale VNF.Call Kubernetes API
Upon receiving a request from tacker-client, tacker-server redirects it to tacker-conductor. In tacker-conductor, the request is redirected again to an appropriate infra-driver (in this case Kubernetes infra-driver) according to the contents of the instantiate parameters. Then, Kubernetes infra-driver calls Kubernetes APIs.
Change the number of Pods
Kubernetes Master change the number of Pods according to the API calls.
Prerequisites¶
The following packages should be installed:
tacker
python-tackerclient
The procedure of prepare for scaling operation that from “register VIM” to “Instantiate VNF”, basically refer to ETSI NFV-SOL CNF (Containerized VNF) Deployment.
This procedure uses an example using the sample VNF package.
How to Create VNF Package for Scaling¶
Using samples/tests/etc/samples/etsi/nfv/test_cnf_scale, describe how to create VNF package for scaling.
$ cd samples/tests/etc/samples/etsi/nfv/test_cnf_scale
Download official definition files from ETSI NFV. ETSI GS NFV-SOL 001 [i.4] specifies the structure and format of the VNFD based on TOSCA specifications.
$ cd Definitions
$ wget https://forge.etsi.org/rep/nfv/SOL001/raw/v2.6.1/etsi_nfv_sol001_common_types.yaml
$ wget https://forge.etsi.org/rep/nfv/SOL001/raw/v2.6.1/etsi_nfv_sol001_vnfd_types.yaml
CSAR Package should be compressed into a ZIP file for uploading. Following commands are an example of compressing a VNF Package:
$ cd -
$ zip deployment.zip -r Definitions/ Files/ TOSCA-Metadata/
$ ls
Definitions deployment.zip Files TOSCA-Metadata
After creating a vnf package with openstack vnf package create, some information including ID, Links, Onboarding State, Operational State, and Usage State will be returned. When the Onboarding State is CREATED, the Operational State is DISABLED, and the Usage State is NOT_IN_USE, indicate the creation is successful.
$ openstack vnf package create
+-------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Field | Value |
+-------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| ID | 094c8abf-b5c8-45a1-9332-3952a710c65c |
| Links | { |
| | "self": { |
| | "href": "/vnfpkgm/v1/vnf_packages/094c8abf-b5c8-45a1-9332-3952a710c65c" |
| | }, |
| | "packageContent": { |
| | "href": "/vnfpkgm/v1/vnf_packages/094c8abf-b5c8-45a1-9332-3952a710c65c/package_content" |
| | } |
| | } |
| Onboarding State | CREATED |
| Operational State | DISABLED |
| Usage State | NOT_IN_USE |
| User Defined Data | {} |
+-------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Upload the CSAR zip file in to the VNF Package by running the following command openstack vnf package upload --path <path of vnf package> <vnf package ID>
Here is an example of uploading VNF package:
$ openstack vnf package upload --path deployment.zip 094c8abf-b5c8-45a1-9332-3952a710c65c
Upload request for VNF package 094c8abf-b5c8-45a1-9332-3952a710c65c has been accepted.
Create VNF instance by running openstack vnflcm create <VNFD ID>.
Here is an example of creating VNF :
$ openstack vnflcm create b1bb0ce7-ebca-4fa7-95ed-4840d70a1177
+-----------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Field | Value |
+-----------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| ID | e9d7c08e-72ed-4c64-bc91-78cd82163969 |
| Instantiation State | NOT_INSTANTIATED |
| Links | { |
| | "self": { |
| | "href": "http://localhost:9890/vnflcm/v1/vnf_instances/e9d7c08e-72ed-4c64-bc91-78cd82163969" |
| | }, |
| | "instantiate": { |
| | "href": "http://localhost:9890/vnflcm/v1/vnf_instances/e9d7c08e-72ed-4c64-bc91-78cd82163969/instantiate" |
| | } |
| | } |
| VNF Configurable Properties | |
| VNF Instance Description | |
| VNF Instance Name | vnf-e9d7c08e-72ed-4c64-bc91-78cd82163969 |
| VNF Package ID | 094c8abf-b5c8-45a1-9332-3952a710c65c |
| VNF Product Name | Sample VNF |
| VNF Provider | Company |
| VNF Software Version | 1.0 |
| VNFD ID | b1bb0ce7-ebca-4fa7-95ed-4840d70a1177 |
| VNFD Version | 1.0 |
+-----------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
After the command is executed, instantiate VNF. Instantiate VNF by running the following command openstack vnflcm instantiate <VNF instance ID> <json file>
The following example shows a json file that deploys the Kubernetes resources
described in deployment_scale.yaml. Please note that additionalParams
includes path of Kubernetes resource definition file and that
lcm-kubernetes-def-files should be a list.
$ cat ./instance_kubernetes.json
{
"flavourId": "simple",
"additionalParams": {
"lcm-kubernetes-def-files": [
"Files/kubernetes/deployment_scale.yaml"
]
},
"vimConnectionInfo": [
{
"id": "8a3adb69-0784-43c7-833e-aab0b6ab4470",
"vimId": "43176042-ca97-4954-9bd5-0a9c054885e1",
"vimType": "kubernetes"
}
]
}
$ openstack vnflcm instantiate e9d7c08e-72ed-4c64-bc91-78cd82163969 instance_kubernetes.json
Instantiate request for VNF Instance e9d7c08e-72ed-4c64-bc91-78cd82163969 has been accepted.
CNF Scaling Procedure¶
As mentioned in Prerequisites, the VNF must be instantiated before performing scaling. Users can scale the number of pod replicas managed by controller resources such as Kubernetes Deployment, StatefulSet, and ReplicaSet.
Note
If kind is Stateful Set and not dynamic provisioning (no-provisioner), user must create the Persistent Volume for the maximum replicas in advance because the increased Persistent Volume is not created during the scale out operation.
Details of CLI commands are described in VNF Lifecycle Management with v1 Tacker.
There are two main methods for CNF scaling.
Scale out CNF
Scale in CNF
How to Identify ASPECT_ID¶
In order to execute scaling, it is necessary to specify ASPECT_ID, which is
the ID for the target scaling group.
First, the method of specifying the ID will be described.
ASPECT_ID is described in VNFD included in the VNF Package.
In the following VNFD excerpt, vdu1_aspect corresponds to ASPECT_ID.
node_templates:
VNF:
type: company.provider.VNF
properties:
flavour_description: A simple flavour
VDU1:
type: tosca.nodes.nfv.Vdu.Compute
properties:
name: vdu1
description: kubernetes controller resource as VDU
vdu_profile:
min_number_of_instances: 1
max_number_of_instances: 3
...snip VNFD...
policies:
- scaling_aspects:
type: tosca.policies.nfv.ScalingAspects
properties:
aspects:
vdu1_aspect:
name: vdu1_aspect
description: vdu1 scaling aspect
max_scale_level: 2
step_deltas:
- delta_1
- vdu1_initial_delta:
type: tosca.policies.nfv.VduInitialDelta
properties:
initial_delta:
number_of_instances: 1
targets: [ VDU1 ]
- vdu1_scaling_aspect_deltas:
type: tosca.policies.nfv.VduScalingAspectDeltas
properties:
aspect: vdu1_aspect
deltas:
delta_1:
number_of_instances: 1
targets: [ VDU1 ]
- instantiation_levels:
type: tosca.policies.nfv.InstantiationLevels
properties:
levels:
instantiation_level_1:
description: Smallest size
scale_info:
vdu1_aspect:
scale_level: 0
instantiation_level_2:
description: Largest size
scale_info:
vdu1_aspect:
scale_level: 2
default_level: instantiation_level_1
- vdu1_instantiation_levels:
type: tosca.policies.nfv.VduInstantiationLevels
properties:
levels:
instantiation_level_1:
number_of_instances: 1
instantiation_level_2:
number_of_instances: 3
targets: [ VDU1 ]
...snip VNFD...
Note
See NFV-SOL001 v2.6.1 annex A.6 for details about ASPECT_ID.
How to Scale Out CNF¶
Execute Scale CLI command and check the number of replicas before and after scaling. This is to confirm that the number of replicas has increased after Scale-out. An example using deployment is described.
Replicas information before scale-out:
$ kubectl get deployment
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
vdu1 1/1 1 1 2d
Scale-out CNF can be executed by the following CLI command.
$ openstack vnflcm scale --type SCALE_OUT --aspect-id vdu1_aspect VNF_INSTANCE_ID
Result:
Scale request for VNF Instance e9d7c08e-72ed-4c64-bc91-78cd82163969 has been accepted.
Replicas information after scale-out:
$ kubectl get deployment
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
vdu1 2/2 2 2 2d
How to Scale in CNF¶
Execute Scale CLI command and check the number of replicas before and after scaling. This is to confirm that the number of replicas has increased after Scale-in. An example using deployment is described.
Replicas information before scale-out:
$ kubectl get deployment
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
vdu1 2/2 2 2 2d
Scale-in VNF can be executed by the following CLI command.
$ openstack vnflcm scale --type SCALE_IN --aspect-id vdu1_aspect VNF_INSTANCE_ID
Result:
Scale request for VNF Instance e9d7c08e-72ed-4c64-bc91-78cd82163969 has been accepted.
Replicas information after scale-in:
$ kubectl get deployment
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
vdu1 1/1 1 1 2d
