Support deploying Kubernetes cluster with MgmtDriver¶
https://blueprints.launchpad.net/tacker/+spec/cnf-support-with-etsi-nfv-specs
This specification describes enhancement of VNF Lifecycle Management for Container Network Function (CNF) in Tacker.
Problem description¶
The Kubernetes Infra Driver in Tacker can deploy CNF on pre-installed Kubernetes cluster [1]. This specification proposes a way to deploy CNF when Kubernetes cluster is not present. The process will consist of VM instantiation, Kubernetes cluster installation on new VMs, and CNF will be deployed on the new Kubernetes cluster.
Proposed Change¶
The following changes are needed:
The CNF instantiation process will be split into two VNF instances. Let’s call the two instances as VNF-A and VNF-B respectively.
VNF-A: Create VMs and set up Kubernetes cluster.
VNF-B: Deploy CNF on the Kubernetes cluster inside VNF-A.
The VIM type and additionalParams parameter provided in the VNF
instantiation request will be important part of this multi-stage deployment
process.
VNF-A: Create VMs and set up Kubernetes cluster¶
As Kubernetes cluster, there are two architectures to be supported.
The Kuryr-Kubernetes.
Additional information required for “Kubernetes with Kube-adm”.
Note
Kubernetes v1.16.0 and Kubernetes python client v11.0 are supported for Kubernetes VIM.
VNF-A: Create VMs and set up Kubernetes cluster (Kuryr-Kubernetes)¶
Kuryr-Kubernetes provides a CNI enabling the Service resource to cooperate with Neutron ports and LBaaS. When users create a Service with their Pods, CNI asks Neutron to create and assign a port on LBaaS. This helps users to expose their applications to the public network.
The diagram below shows Creating VMs and set up Kubernetes cluster:
+---------+ +---------+
| Cluster | | |
| Install | | VNFD |
| Script | | |
+-------+-+ +-+-------+
| |
+--------------+ v v +---------------+
| LCM operation| +----------+ | Instantiation |
| User Data |------>| | | Request with |
+--------------+ | CSAR | | Additional |
+-----------+ +--->| | | Params |
| Heat | | +----+-----+ +-+-------------+
| Template |--+ | |
| (Base HOT)| | |
+-----------+ +-----+----------+--------------+
| v v VNFM |
| +-------------------+ |
| | TackerServer | |
| +-------+-----------+ |
| | |
| v |
2. Kubernetes Cluster | +----------------------+ |
Installation | | +-------------+ | |
+-------------+------------------------+--+----| MgmtDriver | | |
| | | | +-------------+ | |
+-------|-------------|------------+ | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| +----|------+ +---|-------+ | | | | |
| | v | | v | | | | +-------------+ | |
| | +------+ | | +------+ | | 1. Create | | |OpenStack | | |
| | |Worker| | | |Master| |<---------------+--+----|Infra Driver | | |
| | +------+ | | +------+ | | VMs | | +-------------+ | |
| | VM | | VM | | | | | |
| +-----------+ +-----------+ | | | | |
+----------------------------------+ | | Tacker Conductor| |
+----------------------------------+ | +----------------------+ |
| Hardware Resources | | |
+----------------------------------+ +-------------------------------+
The diagram shows related component of this spec proposal and an overview of the following processing:
OpenStackInfraDriver creates new VMs.
MgmtDriver installs the Kubernetes cluster by
instantiate_end.MgmtDriver uses a shell script to install Kubernetes on Master-node and Worker-node.
MgmtDriver registers Kubernetes VIM to tacker.
MgmtDriver appends Kubernetes cluster VIM info to VimConnectionInfo.
Here are the topology of Kuryr-Kubernetes cluster connecting with public network:
+-----------+
| |
| External |
| Network |
| |
+-----------+
|
+-----------+
| |
| LBaaS |
| |
+-----------+
|
+-------------------------------------------------+
|VNF-A | |
|(Kubernetes Cluster)| |
| | Kubernetes Service Network |
| | |
| |Cluster IP |
| +-----*-----+ |
| | | |
| | Service | |
| | | |
| +-----------+ |
| | |
| | Kubernetes Pod Network |
| +-----+-----+ |
| | | |
| +-----------------------------+ |
| | | | | |
| | +---*---+ +---*---+ | |
| | | Pod | | Pod | | |
| | +-------+ +-------+ | |
| | VNF-B (e.g. Deployments) | |
| +-----------------------------+ |
+-------------------------------------------------+
Following sequence diagram describes the components involved and the flow of install Kubernetes cluster with MgmtDriver operation:
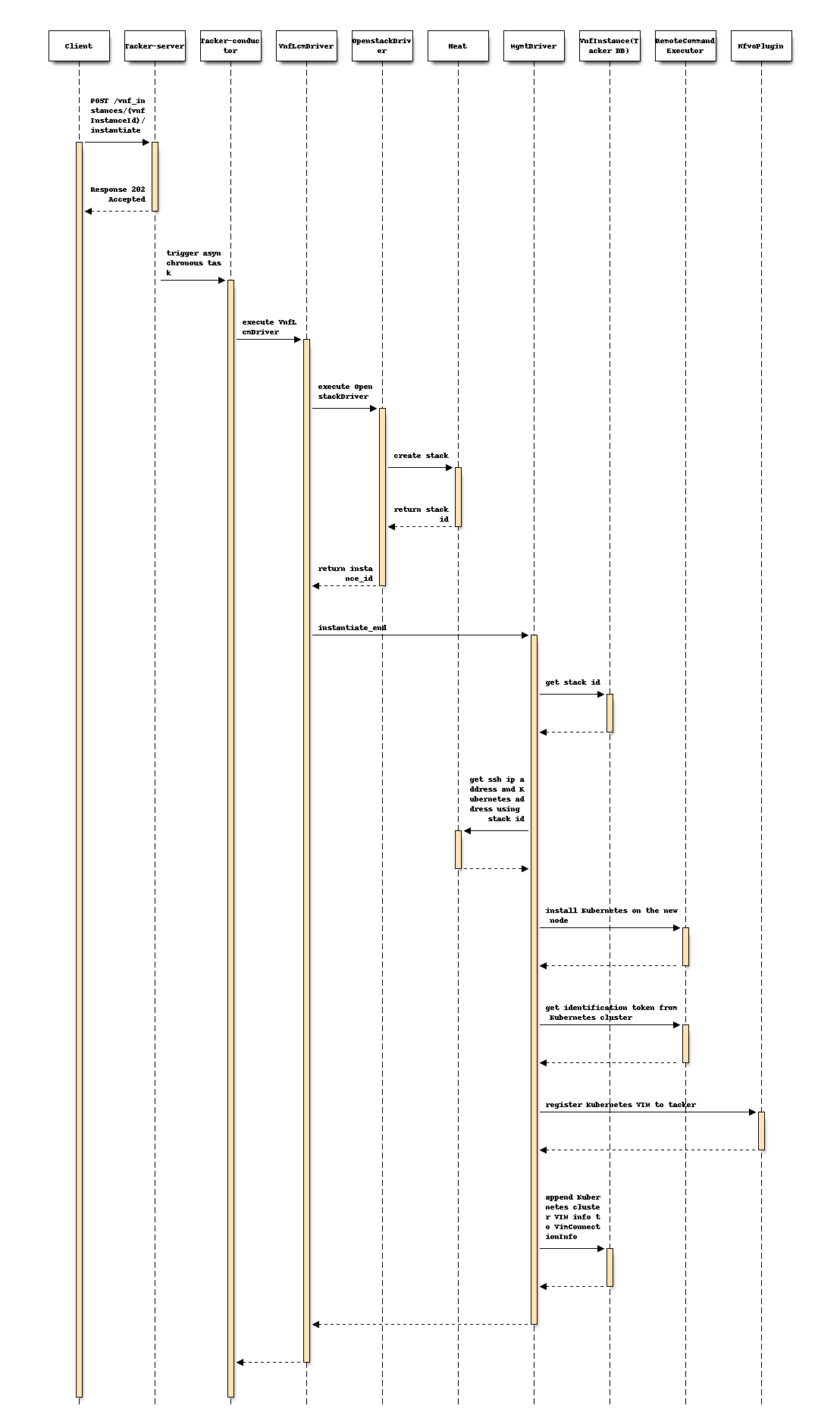
The procedure consists of the following steps as illustrated in above sequence.
Client sends “instantiate” as a POST request.
Basically the same sequence as described in the “2) Flow of Instantiation of a VNF instance” chapter of spec etsi-nfv-sol-rest-api-for-VNF-deployment, except for the MgmtDriver.
The following processes are performed in
instantiate_end.MgmtDriver gets new VM information from Heat.
MgmtDriver installs Kubernetes on the new node by a shell script.
MgmtDriver installs etcd cluster by invoking shell script.
MgmtDriver registers Kubernetes VIM to tacker.
MgmtDriver appends Kubernetes cluster VIM info to VimConnectionInfo.
VNFD for Kuryr-Kubernetes with UserData¶
VMs will be deployed using a Heat template provided in the CSAR as specified in LCM-operation-with-user-data specification. The reason is that the Kubernetes cluster will be set up with Kuryr-Kubernetes. The cluster installation requires some essential network entities such as Router and LoadBalancer.
Note
It is not supported to deploy Kuryr-Kubernetes with TOSCA because LoadBalancer is not supported by heat-translator while TOSCA v1.2 has definition. Router definition is not present in TOSCA v1.2. It is assumed to utilize user-data based instantiation with base HOT.
Note
Although VM resource information can be included in VNFD in future, it is out of scope of this specification.
Following components of CSAR package will be required for VM instantiation:
VNFD
VNFD will not contain any VM resource information such as VDU, Connection points, Virtual links because all required components of VM will be specified in the heat template (Base HOT).
To execute a script to install Kubernetes cluster after instantiation of VM with Base HOT,
Tosca.interfaces.nfv.Vnflcmshould be described in VNFD. According to ETSI SOL001 [2] section 6.7,instantiate_endresource can be defined to enable postamble. The input parameters are provided byadditionalParamsin instantiate parameters.
Note
The logic to enable Tosca.interfaces.nfv.Vnflcm will be
implemented with the MgmtDriver [3]. In this
specification, the scope is to implement the MgmtDriver to
install a Kubernetes cluster.
Heat template (Base HOT)
The heat template will contain resource information for instantiation of VM and network entities such as Router, LoadBalancer. It will be used as mentioned in LCM-operation-with-user-data specification.
LCM operation user data
It will contain a python module for processing parameters required for heat template provided in BaseHOT directory. It will be used as mentioned in LCM-operation-with-user-data specification.
VNFD needs to have instantiate_end definition as the following sample:
node_templates:
VNF:
type: tacker.sample.VNF
properties:
flavour_description: A simple flavour
interfaces:
Vnflcm:
instantiate: []
# inputs:
# key_1: value_1
# additional_parameters:
# type: MyCompany.datatypes.nfv.VnfInstantiateAdditionalParameters
instantiate_start: []
instantiate_end:
implementation: mgmt-drivers-kubernetes
artifacts:
mgmt-drivers-kubernetes:
description: Management driver for Kubernetes cluster
type: tosca.artifacts.Implementation.Python
file: /.../mgmt_drivers/kubernetes_mgmt.py
# data_types:
# MyCompany.datatypes.nfv.VnfInstantiateAdditionalParameters:
# derived_from: tosca.datatypes.nfv.VnfOperationAdditionalParameters
# properties:
# key_1:
# type: string
# required: true
Below is a sample of body provided in the VNF instantiation request POST /vnflcm/v1/vnf_instances/{vnfInstanceId}/instantiate
{
"flavourId": "cluster_install",
"additionalParams": {
"lcm-operation-user-data": "UserData/base_user_data.py",
"lcm-operation-user-data-class": "BaseUserData",
"input_params":""
},
"vimConnectionInfo": [
{
"id": "8a3adb69-0784-43c7-833e-aab0b6ab4470",
"vimId": "7dc3c839-bf15-45ac-8dff-fc5b95c2940e",
"vimType": "openstack"
}
]
}
Note
details of input parameters is written in “Kubernetes cluster installation” section
Kubernetes cluster installation¶
This spec proposes a way to configure a Kubernetes cluster on the VM deployed
in previous step. The cluster will be configured using MgmtDriver to
call mgmt_call() method. The configuration can be implemented as a shell
script or a python script. To call an ansible script deployed as a maintenance
VM in VNF can be an alternative design. The scripts are also responsible for
returning the cluster access information. The cluster access information will
be stored in the database as VIM connection info.
Note
VNFM will access the artifacts directly from the VNF package. APIs specified by Add-artifacts-support-for-VNF-package will be used in future.
Note
Since MgmtDriver is still in development, sequence of MgmtDriver and install script may change in future. Please take them as just a reference.
The needed change in VNF LCM driver will be implemented in the specification of ActionDriver.
The scripts will take script path and parameters required for cluster setup as arguments. The function will return cluster access information in following format.
{
"server" : "https://123.124.64.6:8443",
"username" : "some-username",
"password" : "some-password"
}
The Management driver will map this information to vim_connection_info as
shown below. It will be stored in vim_connection_info column of the
vnf_instances table.
Sample of vim_connection_info record stored in the database:
{
"vim_type": "kubernetes",
"access_info": {
"auth_url":"http://123.124.64.6:8443",
"username": "some-username",
"password": "some-password"
},
"interface_info": {
}
}
The Kubernetes cluster installation requires following parameters:
Kuryr Kubernetes:
ID of Security group for pods
ID of Subnets for Pods
ID of project
ID of Subnet for k8s services
ID of LBaaS
TODO: The list is incomplete. Need to identify all required parameters.
The actual parameters provided in “additionalParams” are like below:
information for each VM:
Cluster role of this VM(Worker/Master)
ssh login information
username
password
k8s cluster information
k8s API cluster subnet
k8s pod subnet
proxy information
http_proxy
https_proxy
no_proxy
name of k8s VIM
These parameters will be parsed from “additionalParams” in request body as described above. And will be parsed to script by script running options.
Note
IP addresses used for ssh access and Kubernetes cluster will be got from heat-client by checking resources of the stack created by instantiate process above. As it is needed to specify master and worker VM in heat client, master/worker’s resource name should follow as masterNode/workerNode.
Note
A sample heat-template will be provided to users.
In instantiate_end phase, MgmtDriver will be called to execute
user’s script on target VM. This function will be included in
mgmt_drivers/kubernetes_mgmt.py:
access target VM through python SSH client
copy user’s script to target VM
execute user’s script and pass the parameters by optional
Note
A Sample Kubernetes Install Script will be provided to users.
VNF-A: Create VMs and set up Kubernetes cluster (Kube-adm)¶
Describes the additional information required for “Kubernetes with Kube-adm”.
The diagram below shows Creating VMs and set up Kubernetes cluster:
+---------+ +---------+
| Cluster | | |
| Install | | VNFD |
| Script | | |
+-------+-+ +-+-------+
| |
v v +---------------+
+----------+ | Instantiation |
| | | Request with |
| CSAR | | Additional |
| | | Params |
+----+-----+ +-+-------------+
| |
| |
+-----+----------+--------------+
| v v VNFM |
| +-------------------+ |
| | TackerServer | |
| +-------+-----------+ |
| | |
| v |
2. Kubernetes Cluster | +----------------------+ |
Installation | | +-------------+ | |
+-------------+------------------------+--+----| MgmtDriver | | |
| | | | +-------------+ | |
+-------|-------------|------------+ | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| +----|------+ +---|-------+ | | | | |
| | v | | v | | | | +-------------+ | |
| | +------+ | | +------+ | | 1. Create | | |OpenStack | | |
| | |Worker| | | |Master| |<---------------+--+----|Infra Driver | | |
| | +------+ | | +------+ | | VMs | | +-------------+ | |
| | VM | | VM | | | | | |
| +-----------+ +-----------+ | | | | |
+----------------------------------+ | | Tacker Conductor| |
+----------------------------------+ | +----------------------+ |
| Hardware Resources | | |
+----------------------------------+ +-------------------------------+
The diagram shows related component of this spec proposal and an overview of the following processing:
OpenStackInfraDriver creates new VMs.
MgmtDriver installs the Kubernetes cluster by
instantiate_end.MgmtDriver uses a shell script to install Kubernetes on Master-node and Worker-node.
MgmtDriver registers Kubernetes VIM to tacker.
MgmtDriver appends Kubernetes cluster VIM info to VimConnectionInfo.
Here are the topology of Kube-adm cluster connecting with public network:
For Kube-adm, user needs to cooperate another SDN-controller to connect public network
+-----------+
| |
| External |
| Network |
| |
+-----------+
|
+------------+
| | +------------+
| External | | SDN |
| Load +-+ Controller |
| Balancer | | |
+------------+ +------------+
|
+-------------------------------------------------+
|VNF-A | |
|(Kubernetes Cluster)| |
| | Kubernetes Service Network |
| | |
| |Cluster IP |
| +-----*-----+ |
| | | |
| | Service | |
| | | |
| +-----------+ |
| | |
| | Kubernetes Pod Network |
| +-----+-----+ |
| | | |
| +-----------------------------+ |
| | | | | |
| | +---*---+ +---*---+ | |
| | | Pod | | Pod | | |
| | +-------+ +-------+ | |
| | VNF-B (e.g. Deployments) | |
| +-----------------------------+ |
+- -----------------------------------------------+
Following sequence diagram describes the components involved and the flow of install Kubernetes cluster with MgmtDriver operation:
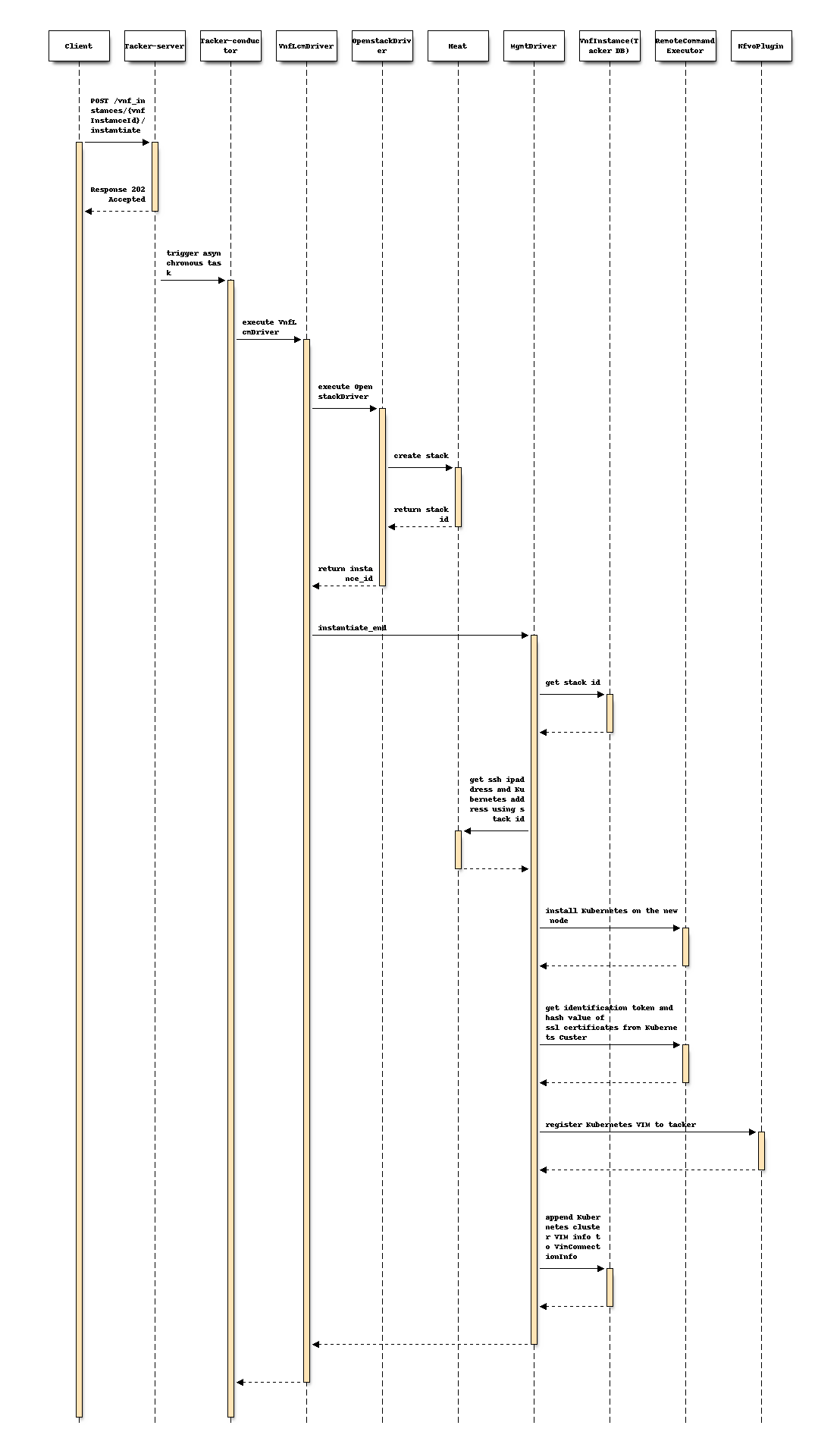
The procedure consists of the following steps as illustrated in above sequence.
Client sends “instantiate” as a POST request.
Basically the same sequence as described in the “2) Flow of Instantiation of a VNF instance” chapter of spec etsi-nfv-sol-rest-api-for-VNF-deployment, except for the MgmtDriver.
The following processes are performed in
instantiate_end.MgmtDriver gets new VM information from Heat.
MgmtDriver installs Kubernetes on the new node by a shell script.
MgmtDriver gets authentication information from Kubernetes cluster.
MgmtDriver registers Kubernetes VIM to tacker.
MgmtDriver appends Kubernetes cluster VIM info to VimConnectionInfo.
VNFD for Kube-adm with TOSCA template¶
In Kube-adm, LCM operation user data will not be used since VM in Kube-adm, Openstack resources is not used. VM information could be included in VNFD file with instantiated_end section in Vnflcm of interface. Here is an example of VNFD file with 1 master node and 1 worker node:
tosca_definitions_version: tosca_simple_yaml_1_2
description: Deployment flavour for MgmtDriver for k8s cluster
imports:
- etsi_nfv_sol001_common_types.yaml
- etsi_nfv_sol001_vnfd_types.yaml
topology_template:
inputs:
id:
type: string
vendor:
type: string
version:
type: version
descriptor_id:
type: string
descriptor_version:
type: string
provider:
type: string
product_name:
type: string
software_version:
type: string
vnfm_info:
type: list
entry_schema:
type: string
flavour_id:
type: string
flavour_description:
type: string
substitution_mappings:
node_type: Company.Tacker.KubernetesCluster
properties:
flavour_id: cluster_install
node_templates:
VNF:
type: company.provider.VNF
properties:
flavour_description: A simple flavour
interfaces:
Vnflcm:
instantiate: []
instantiate_start: []
instantiate_end:
implementation: mgmt-drivers-kubernetes
artifacts:
mgmt-drivers-kubernetes:
description: Management driver for Kubernetes cluster
type: tosca.artifacts.Implementation.Python
file: /.../mgmt_drivers/kubernetes_mgmt.py]
masterNode:
type: tosca.nodes.nfv.Vdu.Compute
properties:
name: masterNode
description: masterNode
vdu_profile:
min_number_of_instances: 1
max_number_of_instances: 1
workerNode:
type: tosca.nodes.nfv.Vdu.Compute
properties:
name: workerNode
description: workerNode
vdu_profile:
min_number_of_instances: 1
max_number_of_instances: 1
masterNodeInternalCP:
type: tosca.nodes.nfv.VduCp
properties:
layer_protocols: [ ipv4 ]
order: 0
requirements:
- virtual_binding: masterNode
- virtual_link: internalVL
masterNodeExternalCP:
type: tosca.nodes.nfv.VduCp
properties:
layer_protocols: [ ipv4 ]
order: 1
requirements:
- virtual_binding: masterNode
# - virtual_link: # the target node is determined in the NSD
workerNodeInternalCP:
type: tosca.nodes.nfv.VduCp
properties:
layer_protocols: [ ipv4 ]
order: 2
requirements:
- virtual_binding: workerNode
- virtual_link: internalVL
workerNodeExternalCP:
type: tosca.nodes.nfv.VduCp
properties:
layer_protocols: [ ipv4 ]
order: 3
requirements:
- virtual_binding: workerNode
# - virtual_link: # the target node is determined in the NSD
internalVL:
type: tosca.nodes.nfv.VnfVirtualLink
properties:
connectivity_type:
layer_protocols: [ ipv4 ]
description: Internal Virtual link in the VNF(for k8s cluster)
vl_profile:
virtual_link_protocol_data:
- associated_layer_protocol: ipv4
l3_protocol_data:
ip_version: ipv4
cidr: 10.10.0.0/24
Note
The name of master/worker node should be started with master/worker to specify ip address from heat client.
Below is a sample of body provided in the VNF instantiation request POST /vnflcm/v1/vnf_instances/{vnfInstanceId}/instantiate
{
"flavourId": "cluster_install",
"additionalParams": {
"input_params":""
},
"vimConnectionInfo": [
{
"id": "8a3adb69-0784-43c7-833e-aab0b6ab4470",
"vimId": "7dc3c839-bf15-45ac-8dff-fc5b95c2940e",
"vimType": "openstack"
}
]
}
Note
details of input_params is discussed in section “Kubernetes cluster installation” below
Kubernetes cluster installation¶
This spec proposes a way to configure a Kubernetes cluster on the VM deployed
in previous step. The cluster will be configured using MgmtDriver to
call mgmt_call() method. The configuration can be implemented as a shell
script or a python script. To call an ansible script deployed as a maintenance
VM in VNF can be an alternative design. The scripts are also responsible for
returning the cluster access information. The cluster access information will
be stored in the database as VIM connection info.
Note
VNFM will access the artifacts directly from the VNF package. APIs specified by Add-artifacts-support-for-VNF-package will be used in future.
Note
Since MgmtDriver is still in development, sequence of MgmtDriver and install script may change in future. Please take them as just a reference.
The needed change in VNF LCM driver will be implemented in the specification of ActionDriver.
The scripts will take script path and parameters required for cluster setup as arguments. The function will return cluster access information in following format.
{
"server" : "https://123.124.64.6:8443",
"username" : "some-username",
"password" : "some-password"
}
The Management driver will map this information to vim_connection_info as
shown below. It will be stored in vim_connection_info column of the
vnf_instances table.
During Kube-adm Kubernetes cluster is deploying, a ca-certificate and a certificate key will be generated by Kube-adm, and will be used in https requests to Kube-adm Kubernetes cluster. The certificate and key will also be stored in vimConnectionInfo in vnf_instance table with identification token during appending Kubernetes cluster VIM info to Tacker DB.
Sample of vim_connection_info record stored in the database:
{
"vim_type": "kubernetes",
"access_info": {
"auth_url":"http://123.124.64.6:8443",
"username": "some-username",
"password": "some-password",
"bearer_token": "value of bearer token",
"ssl_ca_cert_hash": "hash value of ssl ca certification",
"certificate_key": "value of certificate key"
},
"interface_info": {
}
}
Also, Kubernetes VIM information will also be added to Vim table in tackerDB. Comparing to openstack VIM, Kubernetes VIM will have extra attributes in vim_auth table.
Sample of VimAuth record stored in the database:
{
"vim_id": "id of Kubernetes VIM",
"auth_url": "ip address of Kubernetes cluster"
"vim_project": {}
"auth_cred": {
"username": "username",
"password": "password",
"bearer_token": "value of bearer_token",
"ssl_ca_cert_hash": "hash value of ssl ca certification",
"certificate_key": "value of certificate key"
}
}
Note
Username/password and bearer_token is not a required attribute here, but at least one of them should exist. Ssl_ca_cert_hash and certificate_key are required here for https request and joining worker nodes.
Note
In Kube-adm, 3 ways of user authentication are available. Please refer auth-of-kube-adm. In tacker, basic auth/Bearer Token will be supported. For generation of bearer token, service account tokens method will be supported rather than static token file method.
Note
During Kube-adm installation, a service account token will be automatically generated. However this token does not have authority for pods operation. Thus install script will generate a new service account token and store it in tacker DB.
The Kubernetes cluster installation requires following parameters:
Kube-adm:
k8s API cluster IP
k8s API cluster subnet
k8s pod subnet
TODO: The list is incomplete. Need to identify all required parameters.
The actual parameters provided in “additionalParams” are like below:
information for each VM:
Cluster role of this VM(Worker/Master)
ssh login information
username
password
k8s cluster information
k8s API cluster subnet
k8s pod subnet
proxy information
http_proxy
https_proxy
no_proxy
name of k8s VIM
These parameters will be parsed from “additionalParams” in request body as described above. And will be parsed to script by script running options.
Note
IP addresses used for ssh access and Kubernetes cluster will be got from heat-client by checking resources of the stack created by instantiate process above. As it is needed to specify master and worker VM in heat client, master/worker’s resource name should follow as masterNode/workerNode.
Note
A sample heat-template will be provided to users.
In instantiate_end phase, MgmtDriver will be called to execute
user’s script on target VM. This function will be included in
mgmt_drivers/kubernetes_mgmt.py:
access target VM through python ssh client
copy user’s script to target VM
execute user’s script and pass the parameters by optional
Note
A Sample Kubernetes Install Script will be provided to users.
VNF-A: Termination of VNF-A¶
VNF-B needs to be terminated before VNF-A, see termination of VNF-B for detail.
Also, vim connection information needs to be deleted during VNF-A termination.
Same to instantiation, this logic will be executed through MgmtDriver in
terminate_end phase of vnflcm.
Following sequence diagram describes the components involved and the flow of terminate Kubernetes cluster with MgmtDriver operation:
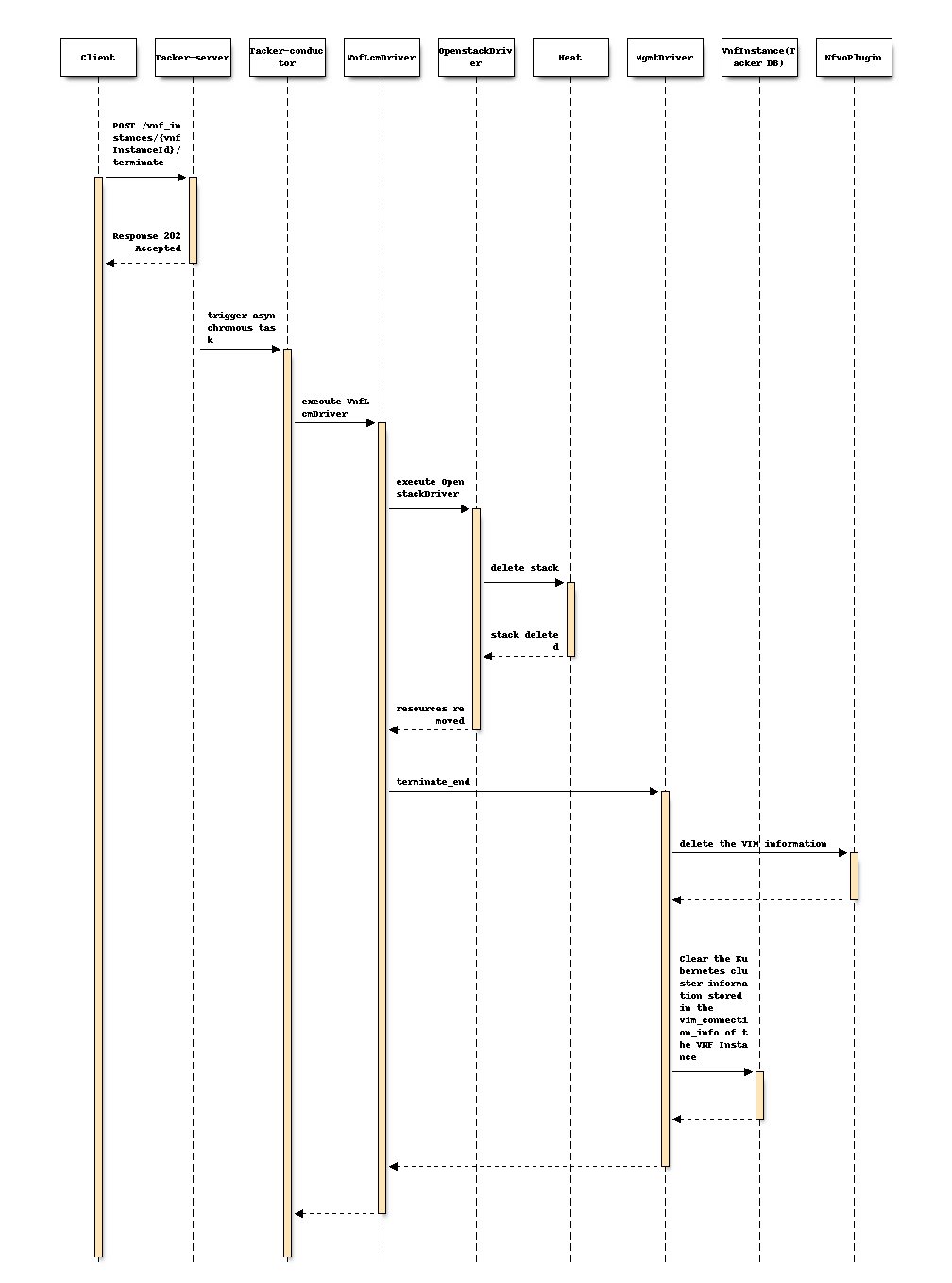
The procedure consists of the following steps as illustrated in above sequence:
Client sends “terminate” as a POST request.
Basically the same sequence as described in the “4) Flow of Termination of a VNF instance” chapter of spec etsi-nfv-sol-rest-api-for-VNF-deployment, except for the MgmtDriver.
The following processes are performed in
terminate_end.Delete VIM information of Kubernetes cluster in Tacker DB.
Clear the old Kubernetes cluster information stored in the vim_connection_info of the VNF Instance.
VNFD needs to have terminate_end definition as the following sample:
node_templates:
VNF:
type: tacker.sample.VNF
properties:
flavour_description: A simple flavour
interfaces:
Vnflcm:
instantiate_start: []
instantiate_end:
implementation: mgmt-drivers-kubernetes
terminate_start: []
terminate_end:
implementation: mgmt-drivers-kubernetes
artifacts:
mgmt-drivers-kubernetes:
description: Management driver for Kubernetes cluster
type: tosca.artifacts.Implementation.Python
file: /.../mgmt_drivers/kubernetes_mgmt.py
VNF-B: Deploy CNF on the Kubernetes cluster inside VNF-A¶
The following shows how to deploy CNF to a Kubernetes cluster in VNF-A.
VNF-B: CNF instantiation¶
CNF instantiation requires a VIM of type kubernetes.
As mentioned in above sections, the access information for the Kubernetes
cluster created in VNF-A will be present in vim_connection_info column of
vnf_instances table.
User will call GET /vnflcm/v1/vnf_instances/{vnfInstanceId} API and manually
register a VIM of type kubernetes using vimConnectionInfo from the
response. CNF instantiation will be done as specified in
Container-Network-Function specification. Hence no design changes will be
required for this step.
The diagram below shows how CNF (VNF-B) will be deployed on Kubernetes cluster created in VNF-A:
+----------+
| |
| VNFD |
| |
+-+--------+
|
v
+----------+ +-------------------+
+---------------+ | | | Instantiation |
| CNF Definition| | CSAR | | Request with |
| File +-----------> | | | Additional Params |
+---------------+ +------+---+ +---+---------------+
| |
+---------------------------------+
| v v VNFM |
+ - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -+ | +----------------+ |
: VNF-B : | | TackerServer | |
: +------------------------------+ : | +----------------+ |
: | +----------+ +----------+ | : | | |
: | | App | | App | | : | +------------------------+ |
: | +----------+ +----------+ | : | | v | |
: | +----------+ +----------+ | : | | +---------------+ | |
: | |Container | |Container | | <-------------+ Kubernetes | | |
: | +----------+ +----------+ | : | | | Infra Driver | | |
: +------------------------------+ : | | +---------------+ | |
+ - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -+ | | ^ | |
| | | | |
+ - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -+ | | +-------+-------+ | |
: VNF-A : | | | VNF LCM | | |
: +------------------------------+ : | | | Driver | | |
: | Kubernetes cluster | : | | +---------------+ | |
: | +----------+ +----------+ | : | | | |
: | | +------+ | | +------+ | | : | | | |
: | | |Worker| | | |Master| | | : | | +---------------+ | |
: | | +------+ | | +------+ | | : | | | OpenStack | | |
: | | VM | | VM | | : | | | Infra Driver | | |
: | +----------+ +----------+ | : | | +---------------+ | |
: +------------------------------+ : | | | |
+ - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -+ | | Tacker Conductor | |
| | | |
+------------------------------+ | +------------------------+ |
| Hardware Resources | | |
+------------------------------+ +---------------------------------+
Implications of dependency of VNF-B on VNF-A¶
Since CNF-B will be deployed on the Kubernetes cluster created inside VNF-A, the operations performed on VNF-A will affect VNF-B.
Termination of VNF-A¶
This will destroy VNF-B and data being processed by VNF-B will become inconsistent. For this reason, VNF-B must be terminated gracefully before VNF-A. Performing such termination sequence automatically is out of scope of this spec, hence the required sequence will be described in the user guide.
Healing of VNF-A¶
The heal use case of VNF LCM sequence terminates existing VM and spawns a new replacement VM. The termination of VM running Kubernetes cluster’s Master or Worker node may break VNF-B. Hence it may be necessary to terminate VNF-B gracefully or to evacuate Pods before performing heal operation on VNF-A. The required sequence will be described in the user guide.
Data model impact¶
None
REST API impact¶
None
Security impact¶
None
Notifications impact¶
None
Other end user impact¶
None
Performance impact¶
None
Other deployer impact¶
None
Developer impact¶
None
Implementation¶
Assignee(s)¶
- Primary assignee:
Yoshito Ito <yoshito.itou.dr@hco.ntt.co.jp>
- Other contributors:
Nitin Uikey <nitin.uikey@nttdata.com>
Tushar Patil <tushar.vitthal.patil@gmail.com>
Prashant Bhole <prashant.bhole@nttdata.com>
Ayumu Ueha <ueha.ayumu@fujitsu.com>
Liang Lu <lu.liang@jp.fujitsu.com>
Work Items¶
Implement Management driver to support:
Kubernetes cluster configuration
Storing and deleting Kubernetes VIM connection info
Provide a sample script to be executed by MgmtDriver to install and/or configure Kubernetes cluster
Add new unit and functional tests.
Dependencies¶
None
Testing¶
Unit and functional tests will be added to cover cases required in the spec.
Documentation Impact¶
Complete user guide will be added to explain CNF instantiation on Kubernetes cluster inside VM.
The procedure for terminating the VNFs will be described in the user guide.
