Cluster Model Objects Wrapper¶
https://blueprints.launchpad.net/watcher/+spec/cluster-model-objects-wrapper
Currently a model of the cluster is constructed every time a strategy is executed, which will not scale in production or in larger environments. If Watcher intends to be used by larger environments it needs a more robust way to construct and maintain a model of the cluster. An in-memory cache of this model can be built up and kept fresh via notifications from services of interest in addition to periodic syncing logic.
Problem description¶
As discussed above, Watcher currently constructs a model of the cluster every
time a strategy is executed via the get_latest_cluster_data_model()
method. As it stands today Watcher only has one model collector defined
(NovaClusterModelCollector). This method then fetches all hypervisors from
Nova using the nova API and then for each hypervisor fetches all servers on
that hypervisor. For each of these hypervisors and servers, a Watcher model
object is created to represent the entity from the JSON response of the API.
These objects are placed into a collection (the cluster data model) which is
then passed to the strategy’s execute() method. The strategy then uses
this model to make certain decisions.
Unfortunately, in a production environment of a decent size, constructing the cluster model like this will not scale. Consider an environment with hundreds of compute nodes and tens of thousands of servers. If Watcher needs to construct the representation of this every time a user wants to run an audit, running an audit will potentially be very slow. Also consider a busy environment where a lot of audits are being requested in short succession - Watcher will need to construct this most recent cluster model via API requests to each service of interest, which is a lot of strain on the overall system for almost no gain, assuming the environment has hardly changed between each audit request.
It would be ideal that a strategy can use an in-memory cache of the cluster model in order to make informed decisions immediately without the need for Watcher to query every service for its most recent representation. This will be especially important when continuous audits are implemented, which will require decisions will be made periodically and often.
Use Cases¶
The primary use case of this is addressing problems of scale. Strategies can be executed much quicker due to minimal delay in constructing the cluster model, which will result in faster audits delivered to the end users of Watcher. It will also reduce load on the overall OpenStack deployment due to the elimination of redundant API requests.
For the developers of Watcher, this will create an easy way to fetch and consume the current cluster model.
Project Priority¶
High
Proposed change¶
Watcher should provide a number of cluster model collectors (reusing the
BaseClusterModelCollector class) that are responsible for maintaining an
in-memory cache of their associated cluster. For example, the
NovaClusterModelCollector class would maintain a cache of all hypervisors
and servers on each hypervisor. In the future this may expand to say a
CinderClusterModelCollector class which would maintain a cache of all
storage providers and block devices (e.g., volumes).
These cluster model collectors would be managed by the existing
CollectorManager class today, which will need to be updated to maintain
references to instantiations of each collector class instead of instantiating
a new one on every call to get_cluster_model_collector(). Methods should
also be added to allow fetching the list of available collectors and fetching
specific collectors.
Each implementation of the BaseClusterModelCollector would continue to
provide a method analogous to the current get_latest_cluster_data_model,
but instead of fetching the model from the service itself it would fetch it
from its internal cache.
Here below is a sequence diagram depicting the workflow to be used in order to retrieve all the cluster data model:
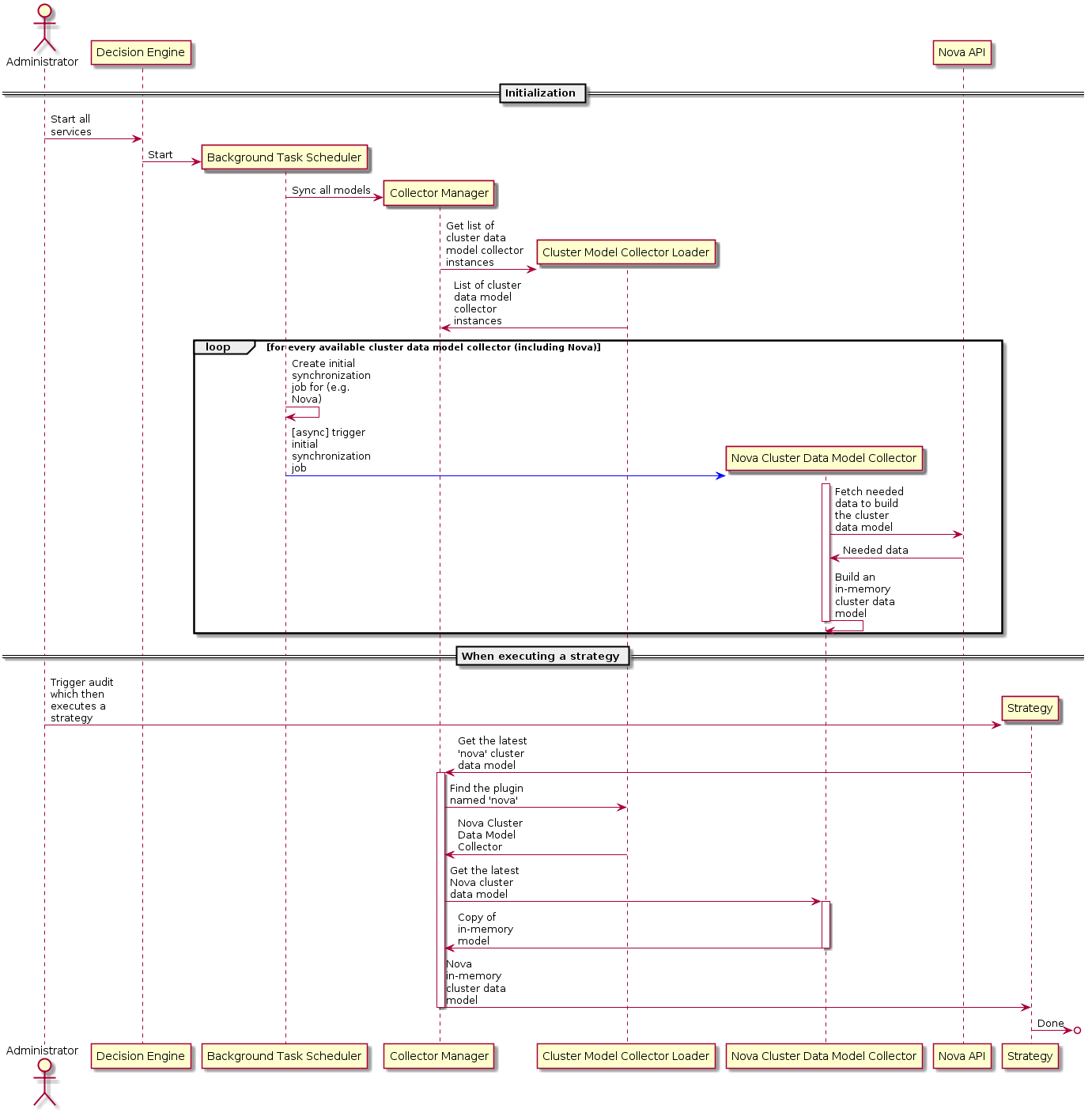
Each implementation of the BaseClusterModelCollector should begin
populating its in-memory cache on instantiation, preferably without blocking
other code execution for quick service stand-up. The implementations should
also define periodic tasks that are responsible for (preferably asynchronously
through the use of threads) syncing the cache with the service. For example,
for NovaClusterModelCollector, this periodic task would be responsible
for making an API request to Nova to fetch all hypervisors and servers. From
the response of that API request, the cache would be updated as appropriate.
The rate at which these sync up tasks are ran should be configurable, but a
sensible default is likely in the every 60 minute range.
Here below is a sequence diagram depicting the workflow to periodically synchronize all the cluster data models:
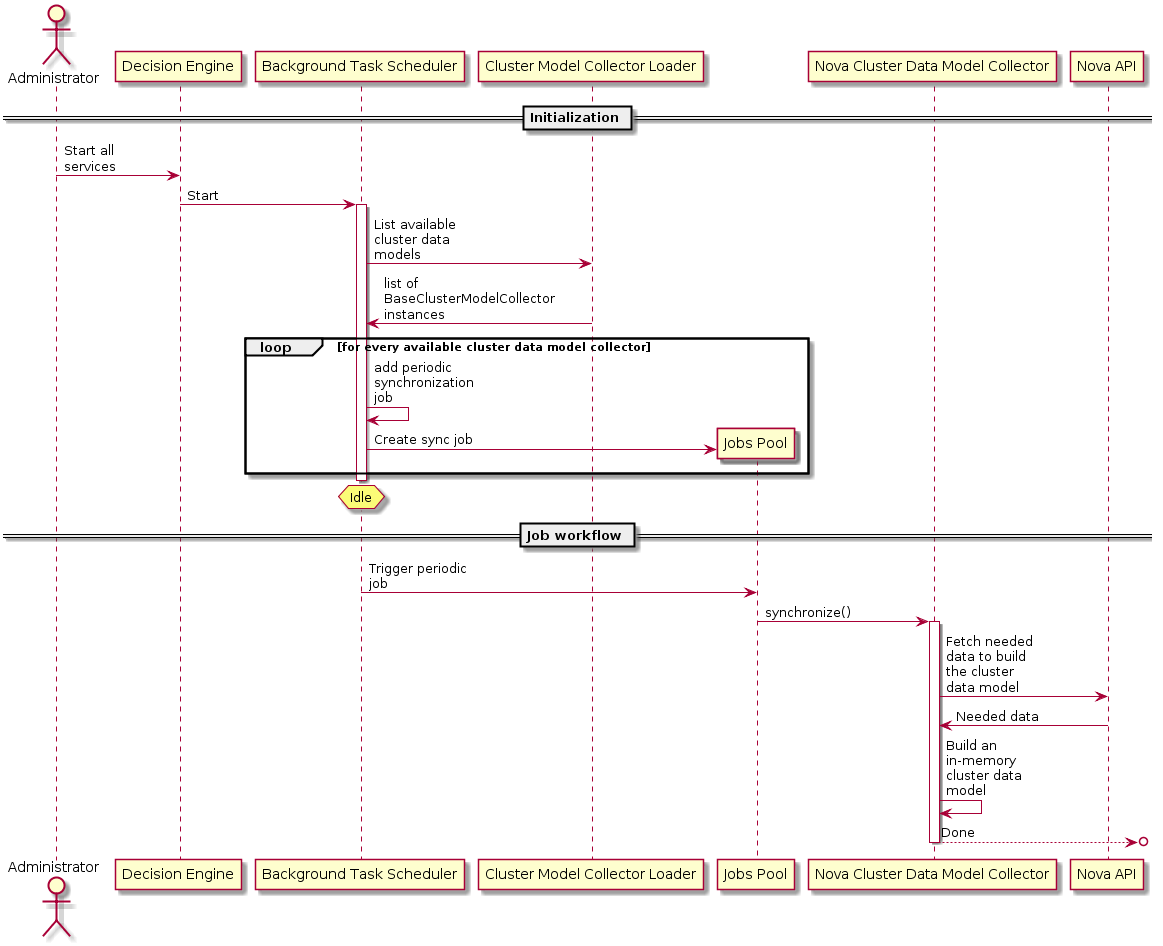
If the periodic sync up tasks are the only method of updating the cache, clearly the cache would quickly become stale. In order to combat this, a notification handler will need to be put in place that asynchronously handles notifications from different services that come in over the AMQP message bus. The notification handler should be able to configure what notifications it is interested in so that it can ignore any other notifications on the bus. The notification handler would determine what type of notification it is handling, then based on that it will spawn a thread that calls a method within specific model collectors that are configured to be interested in notifications of said type. The notification (including the payload) would be passed to the method, which would be responsible for updating its collector’s cache appropriately. It is important the notification handler can deal with notifications asynchronously via threads so that it does not get bogged down when the rate of notifications is high. For example, in the case of Nova, the notification handler would be able to receive notifications such as:
‘compute.instance.create.end’ for instances being created
‘compute.instance.delete.end’ for instances being deleted
‘compute.instance.live_migration._post.end’ for instances being migrated
… and dozens more
Here below is a sequence diagram depicting the workflow to update cluster data models after receiving a notification:
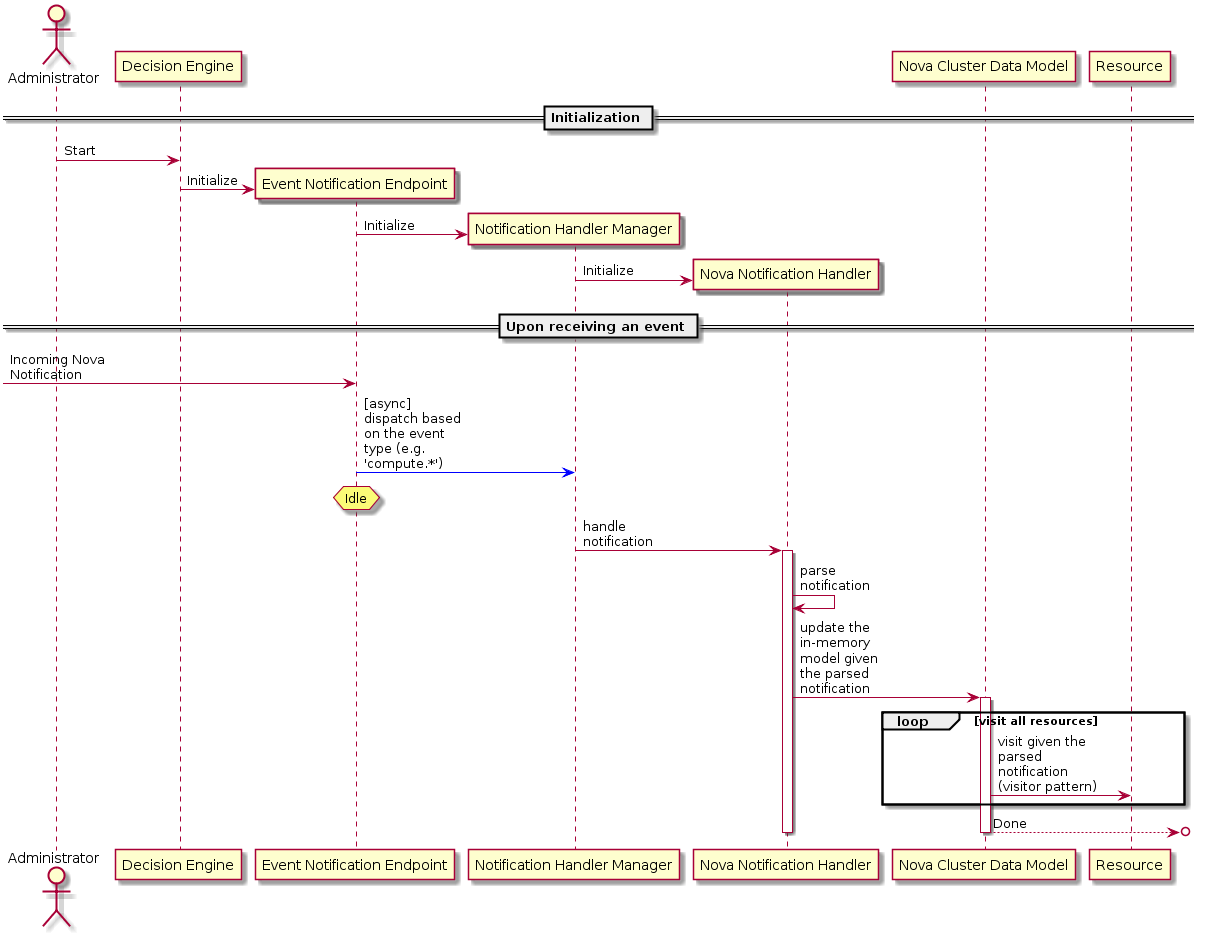
Note that a single notification will not prompt the entire cluster model to be refreshed - only the relevant items in the cache will be refreshed.
The notification handler should preferably have a way for exploiters of Watcher to somehow be able to handle other notifications via some sort of plugin mechanism.
The idea is that the notification handler will allow the collectors to keep their cache predominantly up to date. If the notification handler fails to receive any notifications sent by the services over the AMQP message bus for whatever reason, then the periodic sync up task will serve to correct any staleness of the cache. This boils down to the following idea: Watcher can live with eventual consistency.
Alternatives¶
No caching at all could be done in the collectors, as is today. As discussed at length above, this would only be acceptable for the smallest of cloud environments.
Instead of an in-memory cache, the cached data could be stored in Watcher database tables. This would ultimately mean duplication of potentially a lot of data which is a very big negative.
Data model impact¶
This should not affect the database as the data is being kept within in-memory caches.
REST API impact¶
None, unless we intend on surfacing Watcher’s current representation of the cluster, but that is likely outside the scope of this.
Security impact¶
None
Notifications impact¶
Watcher will not be generating any new notifications, but it will be consuming many more.
Other end user impact¶
None besides better performance and the understanding of what eventual consistency means.
Performance Impact¶
This is described in the “Proposed change” section, but as an overview:
Improved performance for environments of scale since the cluster model does not need to be reconstructed as part of every audit request.
Periodic tasks to sync up cluster model data can potentially be very slow. Therefore they should be done asynchronously preferably.
Notification handler will need to handle a significant number of notifications coming from the AMQP message bus. Spawning threads to the cluster model collectors to do the actual cache updates should allow control to quickly return to the handler to handle the next notification.
Other deployer impact¶
Several config options for the rate at which the periodic sync up tasks will need to be added. The intention is that the default values should work well in real deployments.
This change will take immediate effect after it is merged - it will be part of Watcher’s core architecture.
Developer impact¶
Strategies may need to have some refactoring done to handle the new cluster data models.
Implementation¶
Assignee(s)¶
- Primary assignee:
Vincent Françoise <Vincent.FRANCOISE@b-com.com>
- Other contributors:
Taylor Peoples <tpeoples@us.ibm.com>
Work Items¶
Part 1¶
Enhance the
BaseClusterModelCollectorto allow the creation of plugins:Make
BaseClusterModelCollectorinherit from theLoadableabstract class.
Implement a
ClusterModelCollectorLoaderwhich extends theDefaultLoaderclass so we can dynamically load user-defined cluster data model collectors.Make
CollectorManagercapable of loading entry points/plugins that will be the various cluster model collectors (i.e.NovaClusterModelCollectoronly for now but alsoCinderClusterModelCollectorlater on).Add a
loaderattribute that will be aClusterModelCollectorLoaderinstance.Adapt all existing strategies to now explicit the fact that we use the Nova cluster model collector.
Add a
get_collectors()method that returns a mapping of all the entry point names with their associatedBaseClusterModelCollectorinstances .
Part 2¶
Enhance the
BaseClusterModelCollectorto allow an in-memory model synchronization:Make it inherit from
oslo_service.service.Singletonso we only maintain a single model per type.Add a
cluster_data_modelabstract property which shall have to return aModelRootinstance which will have to be thread-safe.Modify the
get_latest_cluster_data_model()abstract method to now be a plain method that will have to return a deep copy of its in-memorycluster_data_model.Add a
synchronize()abstract method that will be responsible for fetching the full representation of the given cluster data model. This new cluster data model should be a drop-in replacement. Note: thissynchronize()method should be executed asynchronously.Implement the
cluster_data_modelproperty forNovaClusterModelCollector.Implement the
synchronize()method forNovaClusterModelCollector.
Implement a
BackgroundTaskSchedulerbackground scheduling service using apscheduler that will be responsible for periodically triggering a job per cluster data model in order to synchronize them. This scheduling service should be launched as part of theWatcher Decision Enginedaemon.It should inherit from both
oslo_service.service.ServiceBaseandapscheduler.schedulers.background.BackgroundScheduler.Make use of
oslo_service.service.Servicesin order to run bothBackgroundTaskSchedulerand the main decision engine service within the same process.The period will have to be configurable via the configuration file.
A set of basic configuration options about this scheduling service should also be exposed.
Update the
Watcher Decision Enginecommand to now launch the
Part 3¶
Create a
NotificationHandlerManagerclass that will be responsible for dispatching any incoming notification to update the model using the observer pattern.Define a
register()method that will be used to register all the notification handlers.Implement a
dispatch()method that will be responsible to call the right notification handler using an internal registry based on their associated publisher ID. This method should execute notification handlers asynchronously.
Create a
NotificationHandlerabstract class that will be responsible for processing any given notification to update the model.Implement a
handle()method that will be responsible to call the right registered handler method based on the content of the notificationDefine a
get_publisher_id()class method that will be used to associate theNotificationHandlerto a given publisher ( e.g. ‘^compute.*’).Implement an
NotificationParserabstract class that will be responsible for parsing incoming raw notifications.Create a
parse()abstract method that will be responsible for converting the incoming raw notification into some Watcher notification objects which shall be different for all event type.
Using the visitor pattern, explore the in-memory model and apply the associated change wherever needed:
Implement a
NovaNotificationHandlerclass extending theNotificationHandlerbase class:Define handler methods for all the notifications defined by Nova (see this list of notifications).
Use the
event_typeattribute of the Nova notifications as the main dispatching criterion.Register it against the
NotificationHandlerManager.Add a
model_collectorproperty that will be return the rightBaseClusterModelCollectorsingleton.
Enhance the
BaseClusterModelCollectorto allow the collection and processing of notifications in order to maintain the consistency of the in-memory model over time:Add a
notification_handlerabstract property toBaseClusterModelCollectorwhich shall have to be overridden to return aNotificationHandlerinstance.Make the
notification_handlerproperty ofNovaClusterModelCollectorreturn aNovaNotificationHandlerinstance.
Make
CollectorManagerable to find all the notification handlers:Add a
get_notification_handlers()class method toCollectorManagerso that it returns a list of all theNotificationHandlerinstances via
Implement an
EventsNotificationEndpointclass that will be responsible for subscribing to a given notification topic in order to collect and format them:Make
CollectorManagerable to find all the notification handlers viaget_collectors()and their associatednotification_handler.
Dependencies¶
None
Testing¶
Existing tempest tests should provide basic coverage. The bulk of the changes will affect larger environments. If those cannot be obtained for testing, some sort of simulation and analysis of the performance needs to be done.
Documentation Impact¶
Documentation for the new configuration options will be needed. The notion of all of this data being cached by Watcher in memory will also need to be documented.
References¶
None
History¶
None
