[ English | Deutsch | 한국어 (대한민국) | English (United Kingdom) | Indonesia ]
Provider network groups¶
Many network configuration examples assume a homogenous environment, where each server is configured identically and consistent network interfaces and interface names can be assumed across all hosts.
Recent changes to OSA enables deployers to define provider networks
that apply to particular inventory groups and allows for a heterogeneous
network configuration within a cloud environment. New groups can be created
or existing inventory groups, such as network_hosts or
compute_hosts, can be used to ensure certain configurations are applied
only to hosts that meet the given parameters.
Before reading this document, please review the following scenario:
This example environment has the following characteristics:
- A
network_hostsgroup consisting of three collapsed infrastructure/network (control plane) hosts - A
compute_hostsgroup consisting of two compute hosts - Multiple Network Interface Cards (NIC) used as provider network interfaces that vary between hosts
Note
The groups network_hosts and compute_hosts are pre-defined groups
in an OpenStack-Ansible deployment.
The following diagram demonstates servers with different network interface names:
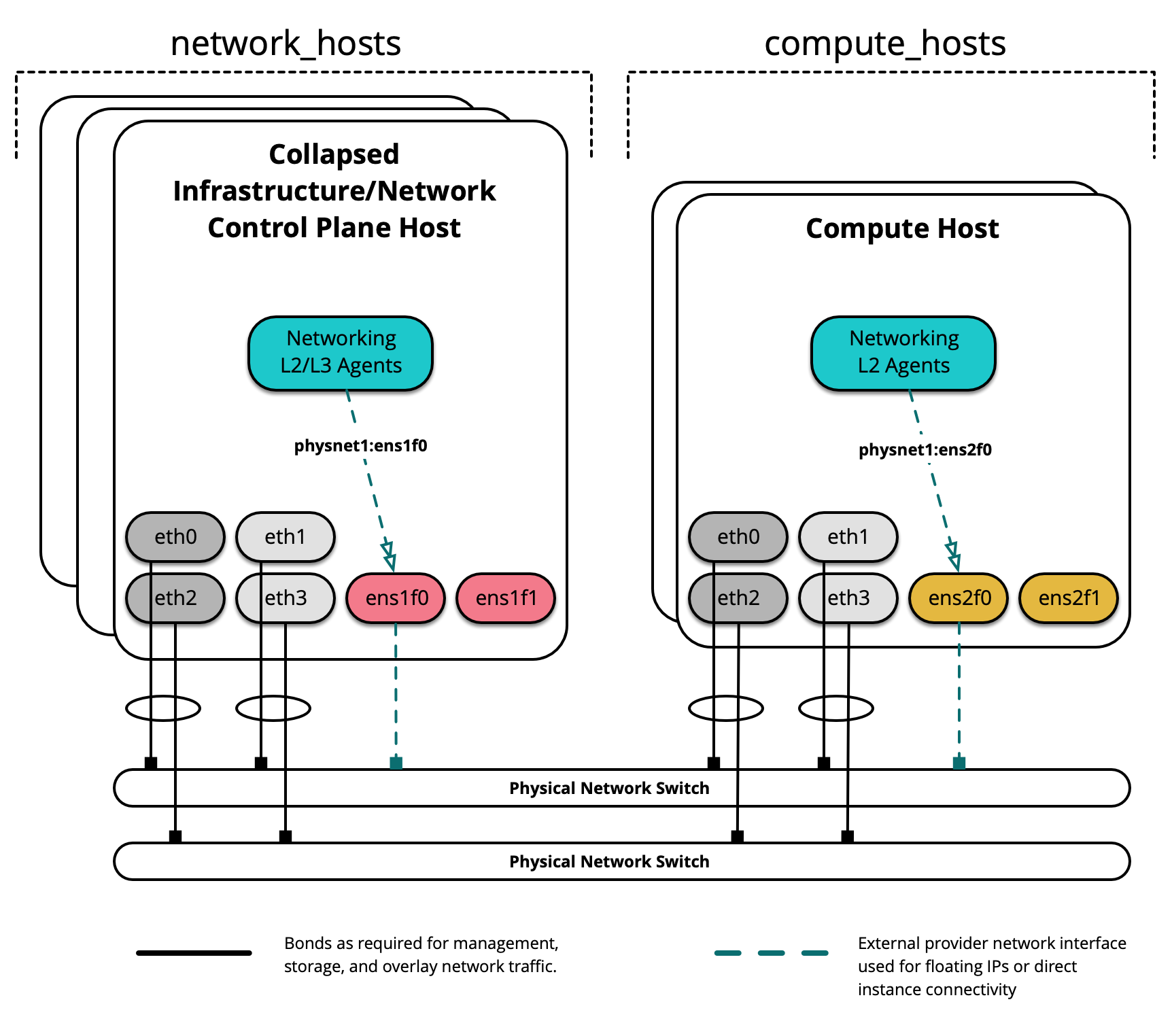
In this example environment, infrastructure/network nodes hosting L2/L3/DHCP
agents will utilize an interface named ens1f0 for the provider network
physnet1. Compute nodes, on the other hand, will utilize an interface
named ens2f0 for the same physnet1 provider network.
Note
Differences in network interface names may be the result of a difference in drivers and/or PCI slot locations.
Deployment configuration¶
Environment layout¶
The /etc/openstack_deploy/openstack_user_config.yml file defines the
environment layout.
The following configuration describes the layout for this environment.
---
cidr_networks:
container: 172.29.236.0/22
tunnel: 172.29.240.0/22
storage: 172.29.244.0/22
used_ips:
- "172.29.236.1,172.29.236.50"
- "172.29.240.1,172.29.240.50"
- "172.29.244.1,172.29.244.50"
- "172.29.248.1,172.29.248.50"
global_overrides:
internal_lb_vip_address: 172.29.236.9
#
# The below domain name must resolve to an IP address
# in the CIDR specified in haproxy_keepalived_external_vip_cidr.
# If using different protocols (https/http) for the public/internal
# endpoints the two addresses must be different.
#
external_lb_vip_address: openstack.example.com
management_bridge: "br-mgmt"
provider_networks:
- network:
container_bridge: "br-mgmt"
container_type: "veth"
container_interface: "eth1"
ip_from_q: "container"
type: "raw"
group_binds:
- all_containers
- hosts
is_container_address: true
#
# The below provider network defines details related to vxlan traffic,
# including the range of VNIs to assign to project/tenant networks and
# other attributes.
#
# The network details will be used to populate the respective network
# configuration file(s) on the members of the listed groups.
#
- network:
container_bridge: "br-vxlan"
container_type: "veth"
container_interface: "eth10"
ip_from_q: "tunnel"
type: "vxlan"
range: "1:1000"
net_name: "vxlan"
group_binds:
- network_hosts
- compute_hosts
#
# The below provider network(s) define details related to a given provider
# network: physnet1. Details include the name of the veth interface to
# connect to the bridge when agent on_metal is False (container_interface)
# or the physical interface to connect to the bridge when agent on_metal
# is True (host_bind_override), as well as the network type. The provider
# network name (net_name) will be used to build a physical network mapping
# to a network interface; either container_interface or host_bind_override
# (when defined).
#
# The network details will be used to populate the respective network
# configuration file(s) on the members of the listed groups. In this
# example, host_bind_override specifies the ens1f0 interface and applies
# only to the members of network_hosts:
#
- network:
container_bridge: "br-vlan"
container_type: "veth"
container_interface: "eth12"
host_bind_override: "ens1f0"
type: "flat"
net_name: "physnet1"
group_binds:
- network_hosts
- network:
container_bridge: "br-vlan"
container_type: "veth"
container_interface: "eth11"
host_bind_override: "ens1f0"
type: "vlan"
range: "101:200,301:400"
net_name: "physnet1"
group_binds:
- network_hosts
#
# The below provider network(s) also define details related to the
# physnet1 provider network. In this example, however, host_bind_override
# specifies the ens2f0 interface and applies only to the members of
# compute_hosts:
#
- network:
container_bridge: "br-vlan"
container_type: "veth"
container_interface: "eth12"
host_bind_override: "ens2f0"
type: "flat"
net_name: "physnet1"
group_binds:
- compute_hosts
- network:
container_bridge: "br-vlan"
container_type: "veth"
container_interface: "eth11"
host_bind_override: "ens2f0"
type: "vlan"
range: "101:200,301:400"
net_name: "physnet1"
group_binds:
- compute_hosts
#
# The below provider network defines details related to storage traffic.
#
- network:
container_bridge: "br-storage"
container_type: "veth"
container_interface: "eth2"
ip_from_q: "storage"
type: "raw"
group_binds:
- glance_api
- cinder_api
- cinder_volume
- nova_compute
###
### Infrastructure
###
# galera, memcache, rabbitmq, utility
shared-infra_hosts:
infra1:
ip: 172.29.236.11
container_vars:
# Optional | Example setting the container_tech for a target host.
container_tech: lxc
infra2:
ip: 172.29.236.12
container_vars:
# Optional | Example setting the container_tech for a target host.
container_tech: nspawn
infra3:
ip: 172.29.236.13
# repository (apt cache, python packages, etc)
repo-infra_hosts:
infra1:
ip: 172.29.236.11
infra2:
ip: 172.29.236.12
infra3:
ip: 172.29.236.13
# load balancer
# Ideally the load balancer should not use the Infrastructure hosts.
# Dedicated hardware is best for improved performance and security.
haproxy_hosts:
infra1:
ip: 172.29.236.11
infra2:
ip: 172.29.236.12
infra3:
ip: 172.29.236.13
# rsyslog server
log_hosts:
log1:
ip: 172.29.236.14
###
### OpenStack
###
# keystone
identity_hosts:
infra1:
ip: 172.29.236.11
infra2:
ip: 172.29.236.12
infra3:
ip: 172.29.236.13
# cinder api services
storage-infra_hosts:
infra1:
ip: 172.29.236.11
infra2:
ip: 172.29.236.12
infra3:
ip: 172.29.236.13
# glance
# The settings here are repeated for each infra host.
# They could instead be applied as global settings in
# user_variables, but are left here to illustrate that
# each container could have different storage targets.
image_hosts:
infra1:
ip: 172.29.236.11
container_vars:
limit_container_types: glance
glance_nfs_client:
- server: "172.29.244.15"
remote_path: "/images"
local_path: "/var/lib/glance/images"
type: "nfs"
options: "_netdev,auto"
infra2:
ip: 172.29.236.12
container_vars:
limit_container_types: glance
glance_nfs_client:
- server: "172.29.244.15"
remote_path: "/images"
local_path: "/var/lib/glance/images"
type: "nfs"
options: "_netdev,auto"
infra3:
ip: 172.29.236.13
container_vars:
limit_container_types: glance
glance_nfs_client:
- server: "172.29.244.15"
remote_path: "/images"
local_path: "/var/lib/glance/images"
type: "nfs"
options: "_netdev,auto"
# nova api, conductor, etc services
compute-infra_hosts:
infra1:
ip: 172.29.236.11
infra2:
ip: 172.29.236.12
infra3:
ip: 172.29.236.13
# heat
orchestration_hosts:
infra1:
ip: 172.29.236.11
infra2:
ip: 172.29.236.12
infra3:
ip: 172.29.236.13
# horizon
dashboard_hosts:
infra1:
ip: 172.29.236.11
infra2:
ip: 172.29.236.12
infra3:
ip: 172.29.236.13
# neutron server, agents (L3, etc)
network_hosts:
infra1:
ip: 172.29.236.11
infra2:
ip: 172.29.236.12
infra3:
ip: 172.29.236.13
# ceilometer (telemetry data collection)
metering-infra_hosts:
infra1:
ip: 172.29.236.11
infra2:
ip: 172.29.236.12
infra3:
ip: 172.29.236.13
# aodh (telemetry alarm service)
metering-alarm_hosts:
infra1:
ip: 172.29.236.11
infra2:
ip: 172.29.236.12
infra3:
ip: 172.29.236.13
# gnocchi (telemetry metrics storage)
metrics_hosts:
infra1:
ip: 172.29.236.11
infra2:
ip: 172.29.236.12
infra3:
ip: 172.29.236.13
# nova hypervisors
compute_hosts:
compute1:
ip: 172.29.236.16
compute2:
ip: 172.29.236.17
# ceilometer compute agent (telemetry data collection)
metering-compute_hosts:
compute1:
ip: 172.29.236.16
compute2:
ip: 172.29.236.17
# cinder volume hosts (NFS-backed)
# The settings here are repeated for each infra host.
# They could instead be applied as global settings in
# user_variables, but are left here to illustrate that
# each container could have different storage targets.
storage_hosts:
infra1:
ip: 172.29.236.11
container_vars:
cinder_backends:
limit_container_types: cinder_volume
nfs_volume:
volume_backend_name: NFS_VOLUME1
volume_driver: cinder.volume.drivers.nfs.NfsDriver
nfs_mount_options: "rsize=65535,wsize=65535,timeo=1200,actimeo=120"
nfs_shares_config: /etc/cinder/nfs_shares
shares:
- ip: "172.29.244.15"
share: "/vol/cinder"
infra2:
ip: 172.29.236.12
container_vars:
cinder_backends:
limit_container_types: cinder_volume
nfs_volume:
volume_backend_name: NFS_VOLUME1
volume_driver: cinder.volume.drivers.nfs.NfsDriver
nfs_mount_options: "rsize=65535,wsize=65535,timeo=1200,actimeo=120"
nfs_shares_config: /etc/cinder/nfs_shares
shares:
- ip: "172.29.244.15"
share: "/vol/cinder"
infra3:
ip: 172.29.236.13
container_vars:
cinder_backends:
limit_container_types: cinder_volume
nfs_volume:
volume_backend_name: NFS_VOLUME1
volume_driver: cinder.volume.drivers.nfs.NfsDriver
nfs_mount_options: "rsize=65535,wsize=65535,timeo=1200,actimeo=120"
nfs_shares_config: /etc/cinder/nfs_shares
shares:
- ip: "172.29.244.15"
share: "/vol/cinder"
Hosts in the network_hosts group will map physnet1 to the ens1f0
interface, while hosts in the compute_hosts group will map physnet1
to the ens2f0 interface. Additional provider mappings can be established
using the same format in a separate definition.
An additional provider interface definition named physnet2 using different
interfaces between hosts may resemble the following:
- network:
container_bridge: "br-vlan2"
container_type: "veth"
container_interface: "eth13"
host_bind_override: "ens1f1"
type: "vlan"
range: "2000:2999"
net_name: "physnet2"
group_binds:
- network_hosts
- network:
container_bridge: "br-vlan2"
container_type: "veth"
host_bind_override: "ens2f1"
type: "vlan"
range: "2000:2999"
net_name: "physnet2"
group_binds:
- compute_hosts
Note
The container_interface parameter is only necessary when Neutron
agents are run in containers, and can be excluded in many cases. The
container_bridge and container_type parameters also relate to
infrastructure containers, but should remain defined for legacy purposes.
Custom Groups¶
Custom inventory groups can be created to assist in segmenting hosts beyond the built-in groups provided by OpenStack-Ansible.
Before creating custom groups, please review the following:
The following diagram demonstates how a custom group can be used to further segment hosts:
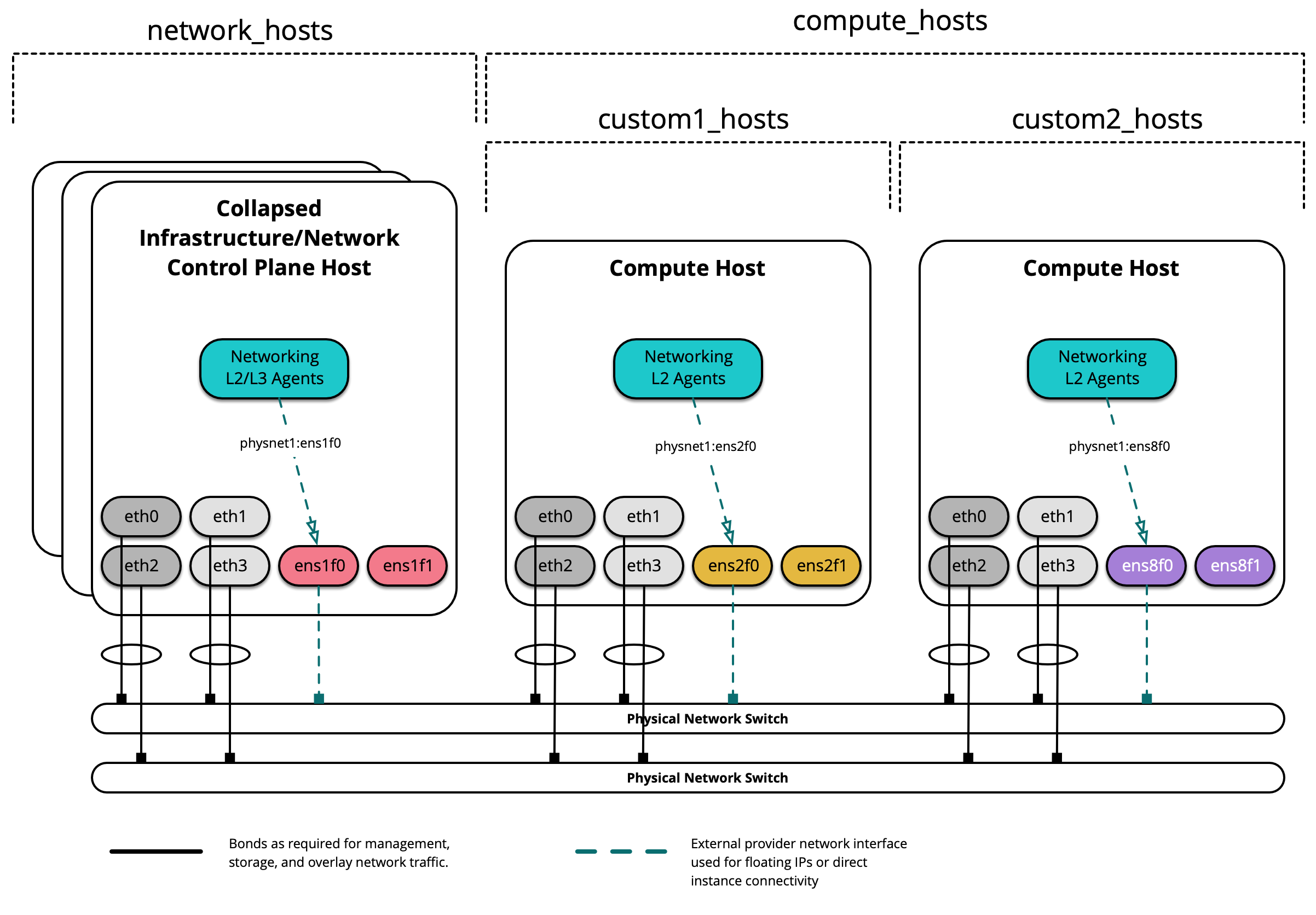
When creating a custom group, first create a skeleton in
/etc/openstack_deploy/env.d/. The following is an example of an inventory
skeleton for a group named custom2_hosts that will consist of bare metal
hosts, and has been created at
/etc/openstack_deploy/env.d/custom2_hosts.yml.
---
physical_skel:
custom2_containers:
belongs_to:
- all_containers
custom2_hosts:
belongs_to:
- hosts
Define the group and its members in a corresponding file in
/etc/openstack_deploy/conf.d/. The following is an example of a group
named custom2_hosts defined in
/etc/openstack_deploy/env.d/custom2_hosts.yml consisting of a single
member, compute2:
---
# custom example
custom2_hosts:
compute2:
ip: 172.29.236.17
The custom group can then be specifed when creating a provider network, as shown here:
- network:
container_bridge: "br-vlan"
container_type: "veth"
host_bind_override: "ens8f1"
type: "vlan"
range: "101:200,301:400"
net_name: "physnet1"
group_binds:
- custom2_hosts

Except where otherwise noted, this document is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. See all OpenStack Legal Documents.