Compute uses the nova-scheduler service to determine how to
dispatch compute and volume requests. For example, the
nova-scheduler
service determines on which host a VM should launch. In the
context of filters, the term host means
a physical node that has a nova-compute service running on it. You can
configure the scheduler through a variety of options.
Compute is configured with the following default scheduler
options in the /etc/nova/nova.conf
file:
scheduler_driver=nova.scheduler.multi.MultiScheduler scheduler_driver_task_period = 60 scheduler_driver = nova.scheduler.filter_scheduler.FilterScheduler scheduler_available_filters = nova.scheduler.filters.all_filters scheduler_default_filters = RetryFilter, AvailabilityZoneFilter, RamFilter, ComputeFilter, ComputeCapabilitiesFilter, ImagePropertiesFilter, ServerGroupAntiAffinityFilter, ServerGroupAffinityFilter
By default, the scheduler_driver is
configured as a filter scheduler, as described in the next
section. In the default configuration, this scheduler
considers hosts that meet all the following criteria:
Have not been attempted for scheduling purposes (
RetryFilter).Are in the requested availability zone (
AvailabilityZoneFilter).Have sufficient RAM available (
RamFilter).Can service the request (
ComputeFilter).Satisfy the extra specs associated with the instance type (
ComputeCapabilitiesFilter).Satisfy any architecture, hypervisor type, or virtual machine mode properties specified on the instance's image properties (
ImagePropertiesFilter).Are on a different host than other instances of a group (if requested) (
ServerGroupAntiAffinityFilter).Are in a set of group hosts (if requested) (
ServerGroupAffinityFilter).
The scheduler caches its list of available hosts; use the
scheduler_driver_task_period option to
specify how often the list is updated.
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
Do not configure |
For information about the volume scheduler, see the Block Storage section of OpenStack Cloud Administrator Guide.
The scheduler chooses a new host when an instance is migrated.
When evacuating instances from a host, the scheduler service does not pick the next host. Instances are evacuated to the host explicitly defined by the administrator. For information about instance evacuation, see Evacuate instances section of the OpenStack Cloud Administrator Guide.
The filter scheduler
(nova.scheduler.filter_scheduler.FilterScheduler)
is the default scheduler for scheduling virtual machine
instances. It supports filtering and weighting to make
informed decisions on where a new instance should be
created.
- AggregateCoreFilter
- AggregateDiskFilter
- AggregateImagePropertiesIsolation
- AggregateInstanceExtraSpecsFilter
- AggregateIoOpsFilter
- AggregateMultiTenancyIsolation
- AggregateNumInstancesFilter
- AggregateRamFilter
- AggregateTypeAffinityFilter
- AllHostsFilter
- AvailabilityZoneFilter
- ComputeCapabilitiesFilter
- ComputeFilter
- CoreFilter
- DifferentHostFilter
- DiskFilter
- GroupAffinityFilter
- GroupAntiAffinityFilter
- ImagePropertiesFilter
- IsolatedHostsFilter
- IoOpsFilter
- JsonFilter
- MetricsFilter
- NumInstancesFilter
- PciPassthroughFilter
- RamFilter
- RetryFilter
- SameHostFilter
- ServerGroupAffinityFilter
- ServerGroupAntiAffinityFilter
- SimpleCIDRAffinityFilter
- TrustedFilter
- TypeAffinityFilter
When the filter scheduler receives a request for a resource, it first applies filters to determine which hosts are eligible for consideration when dispatching a resource. Filters are binary: either a host is accepted by the filter, or it is rejected. Hosts that are accepted by the filter are then processed by a different algorithm to decide which hosts to use for that request, described in the Weights section.
The scheduler_available_filters
configuration option in nova.conf
provides the Compute service with the list of the filters
that are used by the scheduler. The default setting
specifies all of the filter that are included with the
Compute service:
scheduler_available_filters = nova.scheduler.filters.all_filters
This configuration option can be specified multiple
times. For example, if you implemented your own custom
filter in Python called
myfilter.MyFilter and you wanted to
use both the built-in filters and your custom filter, your
nova.conf file would
contain:
scheduler_available_filters = nova.scheduler.filters.all_filters scheduler_available_filters = myfilter.MyFilter
The scheduler_default_filters
configuration option in nova.conf
defines the list of filters that are applied by the
nova-scheduler service. The default
filters are:
scheduler_default_filters = RetryFilter, AvailabilityZoneFilter, RamFilter, ComputeFilter, ComputeCapabilitiesFilter, ImagePropertiesFilter, ServerGroupAntiAffinityFilter, ServerGroupAffinityFilter
The following sections describe the available filters.
Filters host by CPU core numbers with a per-aggregate
cpu_allocation_ratio value. If the
per-aggregate value is not found, the value falls back
to the global setting. If the host is in more than one
aggregate and more than one value is found, the minimum
value will be used. For information about how to use
this filter, see the section called “Host aggregates”. See
also the section called “CoreFilter”.
Filters host by disk allocation with a per-aggregate
disk_allocation_ratio value. If the
per-aggregate value is not found, the value falls back to
the global setting. If the host is in more than one
aggregate and more than one value is found, the minimum
value will be used. For information about how to use this
filter, see the section called “Host aggregates”. See also
the section called “DiskFilter”.
Matches properties defined in an image's metadata against those of aggregates to determine host matches:
If a host belongs to an aggregate and the aggregate defines one or more metadata that matches an image's properties, that host is a candidate to boot the image's instance.
If a host does not belong to any aggregate, it can boot instances from all images.
For example, the following aggregate
myWinAgg has the Windows
operating system as metadata (named 'windows'):
$ nova aggregate-details MyWinAgg +----+----------+-------------------+------------+---------------+ | Id | Name | Availability Zone | Hosts | Metadata | +----+----------+-------------------+------------+---------------+ | 1 | MyWinAgg | None | 'sf-devel' | 'os=windows' | +----+----------+-------------------+------------+---------------+
In this example, because the following Win-2012
image has the windows property,
it boots on the sf-devel host
(all other filters being equal):
$ glance image-show Win-2012 +------------------+--------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +------------------+--------------------------------------+ | Property 'os' | windows | | checksum | f8a2eeee2dc65b3d9b6e63678955bd83 | | container_format | ami | | created_at | 2013-11-14T13:24:25 | | ...
You can configure the
AggregateImagePropertiesIsolation
filter by using the following options in the
nova.conf file:
# Considers only keys matching the given namespace (string). aggregate_image_properties_isolation_namespace = <None> # Separator used between the namespace and keys (string). aggregate_image_properties_isolation_separator = .
Matches properties defined in extra specs for an
instance type against admin-defined properties on a host
aggregate. Works with specifications that are scoped with
aggregate_instance_extra_specs. For
backward compatibility, also works with non-scoped
specifications; this action is highly discouraged because
it conflicts with
ComputeCapabilitiesFilter filter when you enable
both filters. For information about how to use this
filter, see the host
aggregates section.
Filters host by disk allocation with a per-aggregate
max_io_ops_per_host value. If the
per-aggregate value is not found, the value falls back to
the global setting. If the host is in more than one
aggregate and more than one value is found, the minimum
value will be used. For information about how to use this
filter, see the section called “Host aggregates”. See
also the section called “IoOpsFilter”.
Isolates tenants to specific host aggregates.
If a host is in an aggregate that has the
filter_tenant_id metadata key,
the host creates instances from only that tenant or
list of tenants. A host can be in different
aggregates. If a host does not belong to an aggregate
with the metadata key, the host can create instances
from all tenants.
Filters host by number of instances with a per-aggregate
max_instances_per_host value. If the
per-aggregate value is not found, the value falls back to
the global setting. If the host is in more than one
aggregate and thus more than one value is found, the
minimum value will be used. For information about how to
use this filter, see the section called “Host aggregates”. See also the section called “NumInstancesFilter”.
Filters host by RAM allocation of instances with a per-aggregate
ram_allocation_ratio value. If the
per-aggregate value is not found, the value falls back to
the global setting. If the host is in more than one
aggregate and thus more than one value is found, the
minimum value will be used. For information about how to
use this filter, see the section called “Host aggregates”. See also the section called “RamFilter”.
Filters host by per-aggregate
instance_type value. For information
about how to use this filter, see the section called “Host aggregates”. See also the section called “TypeAffinityFilter”.
Filters hosts by availability zone. You must enable this filter for the scheduler to respect availability zones in requests.
Matches properties defined in extra specs for an instance type against compute capabilities.
If an extra specs key contains a colon
(:), anything before the colon
is treated as a namespace and anything after the colon
is treated as the key to be matched. If a namespace is
present and is not capabilities,
the filter ignores the namespace. For backward
compatibility, also treats the extra specs key as the
key to be matched if no namespace is present; this
action is highly discouraged because it conflicts with
AggregateInstanceExtraSpecsFilter filter
when you enable both filters.
Passes all hosts that are operational and enabled.
In general, you should always enable this filter.
Only schedules instances on hosts if sufficient CPU cores are available. If this filter is not set, the scheduler might over-provision a host based on cores. For example, the virtual cores running on an instance may exceed the physical cores.
You can configure this filter to enable a fixed
amount of vCPU overcommitment by using the
cpu_allocation_ratio
configuration option in
nova.conf. The default setting
is:
cpu_allocation_ratio = 16.0
With this setting, if 8 vCPUs are on a node, the scheduler allows instances up to 128 vCPU to be run on that node.
To disallow vCPU overcommitment set:
cpu_allocation_ratio = 1.0
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The Compute API always returns the actual
number of CPU cores available on a compute node
regardless of the value of the
|
Schedules the instance on a different host from a
set of instances. To take advantage of this filter,
the requester must pass a scheduler hint, using
different_host as the key and a
list of instance UUIDs as the value. This filter is
the opposite of the SameHostFilter.
Using the nova command-line tool,
use the --hint flag. For
example:
$ nova boot --image cedef40a-ed67-4d10-800e-17455edce175 --flavor 1 \ --hint different_host=a0cf03a5-d921-4877-bb5c-86d26cf818e1 \ --hint different_host=8c19174f-4220-44f0-824a-cd1eeef10287 server-1
With the API, use the
os:scheduler_hints key. For
example:
{
"server": {
"name": "server-1",
"imageRef": "cedef40a-ed67-4d10-800e-17455edce175",
"flavorRef": "1"
},
"os:scheduler_hints": {
"different_host": [
"a0cf03a5-d921-4877-bb5c-86d26cf818e1",
"8c19174f-4220-44f0-824a-cd1eeef10287"
]
}
}
Only schedules instances on hosts if there is sufficient disk space available for root and ephemeral storage.
You can configure this filter to enable a fixed
amount of disk overcommitment by using the
disk_allocation_ratio
configuration option in
nova.conf. The default setting
is:
disk_allocation_ratio = 1.0
Adjusting this value to greater than 1.0 enables scheduling instances while over committing disk resources on the node. This might be desirable if you use an image format that is sparse or copy on write so that each virtual instance does not require a 1:1 allocation of virtual disk to physical storage.
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
This filter is deprecated in favor of ServerGroupAffinityFilter. |
The GroupAffinityFilter ensures that an instance is
scheduled on to a host from a set of group hosts. To
take advantage of this filter, the requester must pass
a scheduler hint, using group as
the key and an arbitrary name as the value. Using the
nova command-line tool, use the
--hint flag. For
example:
$ nova boot --image IMAGE_ID --flavor 1 --hint group=foo server-1This filter should not be enabled at the same time as GroupAntiAffinityFilter or neither filter will work properly.
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
This filter is deprecated in favor of ServerGroupAntiAffinityFilter. |
The GroupAntiAffinityFilter ensures that each
instance in a group is on a different host. To take
advantage of this filter, the requester must pass a
scheduler hint, using group as the
key and an arbitrary name as the value. Using the
nova command-line tool, use the
--hint flag. For
example:
$ nova boot --image IMAGE_ID --flavor 1 --hint group=foo server-1This filter should not be enabled at the same time as GroupAffinityFilter or neither filter will work properly.
Filters hosts based on properties defined on the instance's image. It passes hosts that can support the specified image properties contained in the instance. Properties include the architecture, hypervisor type, and virtual machine mode. for example, an instance might require a host that runs an ARM-based processor and QEMU as the hypervisor. An image can be decorated with these properties by using:
$ glance image-update img-uuid --property architecture=arm --property hypervisor_type=qemu
The image properties that the filter checks for are:
architecture: Architecture describes the machine architecture required by the image. Examples are i686, x86_64, arm, and ppc64.hypervisor_type: Hypervisor type describes the hypervisor required by the image. Examples are xen, qemu, and xenapi. Note that qemu is used for both QEMU and KVM hypervisor types.vm_mode: Virtual machine mode describes the hypervisor application binary interface (ABI) required by the image. Examples are 'xen' for Xen 3.0 paravirtual ABI, 'hvm' for native ABI, 'uml' for User Mode Linux paravirtual ABI, exe for container virt executable ABI.
Allows the admin to define a special (isolated) set
of images and a special (isolated) set of hosts, such
that the isolated images can only run on the isolated
hosts, and the isolated hosts can only run isolated
images. The flag
restrict_isolated_hosts_to_isolated_images
can be used to force isolated hosts to only run
isolated images.
The admin must specify the isolated set of images
and hosts in the nova.conf file
using the isolated_hosts and
isolated_images configuration
options. For example:
isolated_hosts = server1, server2 isolated_images = 342b492c-128f-4a42-8d3a-c5088cf27d13, ebd267a6-ca86-4d6c-9a0e-bd132d6b7d09
The IoOpsFilter filters hosts by concurrent I/O operations
on it. Hosts with too many concurrent I/O operations will
be filtered out. The max_io_ops_per_host
option specifies the maximum number of I/O intensive
instances allowed to run on a host. A host will be ignored
by the scheduler if more than
max_io_ops_per_host instances in build,
resize, snapshot, migrate, rescue or unshelve task states
are running on it.
The JsonFilter allows a user to construct a custom filter by passing a scheduler hint in JSON format. The following operators are supported:
=
<
>
in
<=
>=
not
or
and
The filter supports the following variables:
$free_ram_mb$free_disk_mb$total_usable_ram_mb$vcpus_total$vcpus_used
Using the nova
command-line tool, use the --hint
flag:
$ nova boot --image 827d564a-e636-4fc4-a376-d36f7ebe1747 \ --flavor 1 --hint query='[">=","$free_ram_mb",1024]' server1
With the API, use the
os:scheduler_hints key:
{
"server": {
"name": "server-1",
"imageRef": "cedef40a-ed67-4d10-800e-17455edce175",
"flavorRef": "1"
},
"os:scheduler_hints": {
"query": "[>=,$free_ram_mb,1024]"
}
}
Filters hosts based on metrics
weight_setting. Only hosts with the
available metrics are passed so that the metrics weigher
will not fail due to these hosts.
Hosts that have more instances running than specified by
the max_instances_per_host option are
filtered out when this filter is in place.
The filter schedules instances on a host if the host has
devices that meet the device requests in the
extra_specs attribute for the flavor.
Only schedules instances on hosts that have sufficient RAM available. If this filter is not set, the scheduler may over provision a host based on RAM (for example, the RAM allocated by virtual machine instances may exceed the physical RAM).
You can configure this filter to enable a fixed
amount of RAM overcommitment by using the
ram_allocation_ratio
configuration option in
nova.conf. The default setting
is:
ram_allocation_ratio = 1.5
This setting enables 1.5 GB instances to run on any compute node with 1 GB of free RAM.
Filters out hosts that have already been attempted for scheduling purposes. If the scheduler selects a host to respond to a service request, and the host fails to respond to the request, this filter prevents the scheduler from retrying that host for the service request.
This filter is only useful if the
scheduler_max_attempts
configuration option is set to a value greater than
zero.
Schedules the instance on the same host as another
instance in a set of instances. To take advantage of
this filter, the requester must pass a scheduler hint,
using same_host as the key and a
list of instance UUIDs as the value. This filter is
the opposite of the
DifferentHostFilter. Using the
nova command-line tool, use the
--hint flag:
$ nova boot --image cedef40a-ed67-4d10-800e-17455edce175 --flavor 1 \ --hint same_host=a0cf03a5-d921-4877-bb5c-86d26cf818e1 \ --hint same_host=8c19174f-4220-44f0-824a-cd1eeef10287 server-1
With the API, use the
os:scheduler_hints key:
{
"server": {
"name": "server-1",
"imageRef": "cedef40a-ed67-4d10-800e-17455edce175",
"flavorRef": "1"
},
"os:scheduler_hints": {
"same_host": [
"a0cf03a5-d921-4877-bb5c-86d26cf818e1",
"8c19174f-4220-44f0-824a-cd1eeef10287"
]
}
}
The ServerGroupAffinityFilter ensures that an
instance is scheduled on to a host from a set of group
hosts. To take advantage of this filter, the requester
must create a server group with an
affinity policy, and pass a
scheduler hint, using group as the
key and the server group UUID as the value. Using the
nova command-line tool, use the
--hint flag. For
example:
$ nova server-group-create --policy affinity group-1 $ nova boot --imageIMAGE_ID--flavor 1 --hint group=SERVER_GROUP_UUIDserver-1
The ServerGroupAntiAffinityFilter ensures that each
instance in a group is on a different host. To take
advantage of this filter, the requester must create a
server group with an anti-affinity
policy, and pass a scheduler hint, using
group as the key and the server
group UUID as the value. Using the
nova command-line tool, use the
--hint flag. For
example:
$ nova server-group-create --policy anti-affinity group-1 $ nova boot --imageIMAGE_ID--flavor 1 --hint group=SERVER_GROUP_UUIDserver-1
Schedules the instance based on host IP subnet range. To take advantage of this filter, the requester must specify a range of valid IP address in CIDR format, by passing two scheduler hints:
build_near_host_ipThe first IP address in the subnet (for example,
192.168.1.1)cidrThe CIDR that corresponds to the subnet (for example,
/24)
Using the nova command-line tool,
use the --hint flag. For example,
to specify the IP subnet
192.168.1.1/24
$ nova boot --image cedef40a-ed67-4d10-800e-17455edce175 --flavor 1 \ --hint build_near_host_ip=192.168.1.1 --hint cidr=/24 server-1
With the API, use the
os:scheduler_hints key:
{
"server": {
"name": "server-1",
"imageRef": "cedef40a-ed67-4d10-800e-17455edce175",
"flavorRef": "1"
},
"os:scheduler_hints": {
"build_near_host_ip": "192.168.1.1",
"cidr": "24"
}
}
Filters hosts based on their trust. Only passes hosts that meet the trust requirements specified in the instance properties.
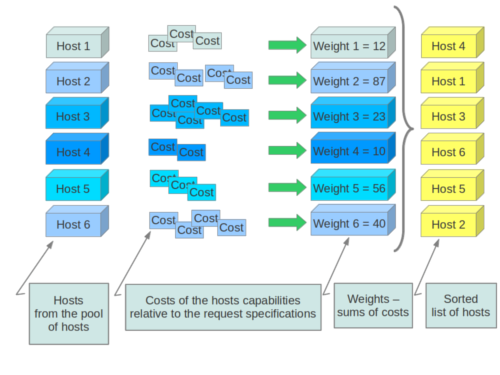
When resourcing instances, the filter scheduler filters and weights each host in the list of acceptable hosts. Each time the scheduler selects a host, it virtually consumes resources on it, and subsequent selections are adjusted accordingly. This process is useful when the customer asks for the same large amount of instances, because weight is computed for each requested instance.
All weights are normalized before being summed up; the host with the largest weight is given the highest priority.
If cells are used, cells are weighted by the scheduler in the same manner as hosts.
Hosts and cells are weighted based on the following
options in the /etc/nova/nova.conf
file:
| Section | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|
| [DEFAULT] | ram_weight_multiplier |
By default, the scheduler spreads instances
across all hosts evenly. Set the
ram_weight_multiplier
option to a negative number if you prefer
stacking instead of spreading. Use a
floating-point value. |
| [DEFAULT] | scheduler_host_subset_size |
New instances are scheduled on a host that is chosen randomly from a subset of the N best hosts. This property defines the subset size from which a host is chosen. A value of 1 chooses the first host returned by the weighting functions. This value must be at least 1. A value less than 1 is ignored, and 1 is used instead. Use an integer value. |
| [DEFAULT] | scheduler_weight_classes |
Defaults to
nova.scheduler.weights.all_weighers,
which selects the
RamWeigher. Hosts are then weighted and sorted
with the largest weight winning. |
| [metrics] | weight_multiplier |
Multiplier for weighting metrics. Use a floating-point value. |
| [metrics] | weight_setting |
Determines how metrics are weighted. Use a
comma-separated list of metricName=ratio. For
example: "name1=1.0, name2=-1.0" results in:
name1.value * 1.0 + name2.value *
-1.0
|
| [metrics] | required |
Specifies how to treat unavailable metrics:
|
| [metrics] | weight_of_unavailable |
If required is set to False,
and any one of the metrics set by
weight_setting is
unavailable, the
weight_of_unavailable
value is returned to the scheduler. |
For example:
[DEFAULT] scheduler_host_subset_size = 1 scheduler_weight_classes = nova.scheduler.weights.all_weighers ram_weight_multiplier = 1.0 [metrics] weight_multiplier = 1.0 weight_setting = name1=1.0, name2=-1.0 required = false weight_of_unavailable = -10000.0
| Section | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|
| [cells] | mute_weight_multiplier |
Multiplier to weight mute children (hosts which have not sent capacity or capacity updates for some time). Use a negative, floating-point value. |
| [cells] | mute_weight_value |
Weight value assigned to mute children. Use a positive, floating-point value with a maximum of '1.0'. |
| [cells] | offset_weight_multiplier |
Multiplier to weight cells, so you can specify a preferred cell. Use a floating point value. |
| [cells] | ram_weight_multiplier |
By default, the scheduler spreads instances
across all cells evenly. Set the
ram_weight_multiplier
option to a negative number if you prefer
stacking instead of spreading. Use a
floating-point value. |
| [cells] | scheduler_weight_classes |
Defaults to
nova.cells.weights.all_weighers,
which maps to all cell weighters included with
Compute. Cells are then weighted and sorted
with the largest weight winning. |
For example:
[cells] scheduler_weight_classes = nova.cells.weights.all_weighers mute_weight_multiplier = -10.0 mute_weight_value = 1000.0 ram_weight_multiplier = 1.0 offset_weight_multiplier = 1.0
As an administrator, you work with the filter scheduler.
However, the Compute service also uses the Chance
Scheduler,
nova.scheduler.chance.ChanceScheduler,
which randomly selects from lists of filtered
hosts.
Host aggregates are a mechanism to further partition an availability zone; while availability zones are visible to users, host aggregates are only visible to administrators. Host Aggregates provide a mechanism to allow administrators to assign key-value pairs to groups of machines. Each node can have multiple aggregates, each aggregate can have multiple key-value pairs, and the same key-value pair can be assigned to multiple aggregates. This information can be used in the scheduler to enable advanced scheduling, to set up hypervisor resource pools or to define logical groups for migration.
The nova command-line tool supports the following aggregate-related commands.
- nova aggregate-list
Print a list of all aggregates.
- nova aggregate-create
<name><availability-zone> Create a new aggregate named
<name>in availability zone<availability-zone>. Returns the ID of the newly created aggregate. Hosts can be made available to multiple availability zones, but administrators should be careful when adding the host to a different host aggregate within the same availability zone and pay attention when using the aggregate-set-metadata and aggregate-update commands to avoid user confusion when they boot instances in different availability zones. An error occurs if you cannot add a particular host to an aggregate zone for which it is not intended.- nova aggregate-delete
<id> Delete an aggregate with id
<id>.- nova aggregate-details
<id> Show details of the aggregate with id
<id>.- nova aggregate-add-host
<id><host> Add host with name
<host>to aggregate with id<id>.- nova aggregate-remove-host
<id><host> Remove the host with name
<host>from the aggregate with id<id>.- nova aggregate-set-metadata
<id><key=value>[<key=value>...] Add or update metadata (key-value pairs) associated with the aggregate with id
<id>.- nova aggregate-update
<id><name>[<availability_zone>] Update the name and availability zone (optional) for the aggregate.
- nova host-list
List all hosts by service.
- nova host-update --maintenance [enable | disable]
Put/resume host into/from maintenance.
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
Only administrators can access these commands. If
you try to use these commands and the user name and
tenant that you use to access the Compute service do
not have the ERROR: Policy doesn't allow compute_extension:aggregates to be performed. (HTTP 403) (Request-ID: req-299fbff6-6729-4cef-93b2-e7e1f96b4864) ERROR: Policy doesn't allow compute_extension:hosts to be performed. (HTTP 403) (Request-ID: req-ef2400f6-6776-4ea3-b6f1-7704085c27d1) |
One common use case for host aggregates is when you want to support scheduling instances to a subset of compute hosts because they have a specific capability. For example, you may want to allow users to request compute hosts that have SSD drives if they need access to faster disk I/O, or access to compute hosts that have GPU cards to take advantage of GPU-accelerated code.
To configure the scheduler to support host aggregates,
the scheduler_default_filters
configuration option must contain the
AggregateInstanceExtraSpecsFilter
in addition to the other filters used by the scheduler.
Add the following line to
/etc/nova/nova.conf on the host
that runs the nova-scheduler service to enable host
aggregates filtering, as well as the other filters that
are typically
enabled:
scheduler_default_filters=AggregateInstanceExtraSpecsFilter,RetryFilter,AvailabilityZoneFilter,RamFilter,ComputeFilter,ComputeCapabilitiesFilter,ImagePropertiesFilter,ServerGroupAntiAffinityFilter,ServerGroupAffinityFilter
This example configures the Compute service to enable
users to request nodes that have solid-state drives
(SSDs). You create a fast-io host
aggregate in the nova availability zone
and you add the ssd=true key-value pair
to the aggregate. Then, you add the
node1, and node2
compute nodes to it.
$ nova aggregate-create fast-io nova
+----+---------+-------------------+-------+----------+
| Id | Name | Availability Zone | Hosts | Metadata |
+----+---------+-------------------+-------+----------+
| 1 | fast-io | nova | | |
+----+---------+-------------------+-------+----------+
$ nova aggregate-set-metadata 1 ssd=true
+----+---------+-------------------+-------+-------------------+
| Id | Name | Availability Zone | Hosts | Metadata |
+----+---------+-------------------+-------+-------------------+
| 1 | fast-io | nova | [] | {u'ssd': u'true'} |
+----+---------+-------------------+-------+-------------------+
$ nova aggregate-add-host 1 node1
+----+---------+-------------------+-----------+-------------------+
| Id | Name | Availability Zone | Hosts | Metadata |
+----+---------+-------------------+------------+-------------------+
| 1 | fast-io | nova | [u'node1'] | {u'ssd': u'true'} |
+----+---------+-------------------+------------+-------------------+
$ nova aggregate-add-host 1 node2
+----+---------+-------------------+---------------------+-------------------+
| Id | Name | Availability Zone | Hosts | Metadata |
+----+---------+-------------------+----------------------+-------------------+
| 1 | fast-io | nova | [u'node1', u'node2'] | {u'ssd': u'true'} |
+----+---------+-------------------+----------------------+-------------------+Use the nova flavor-create command to create
the ssd.large flavor called with an ID of
6, 8 GB of RAM, 80 GB root disk, and four vCPUs.
$ nova flavor-createssd.large68192804+----+-----------+-----------+------+-----------+------+-------+-------------+-----------+-------------+ | ID | Name | Memory_MB | Disk | Ephemeral | Swap | VCPUs | RXTX_Factor | Is_Public | extra_specs | +----+-----------+-----------+------+-----------+------+-------+-------------+-----------+-------------+ | 6 | ssd.large | 8192 | 80 | 0 | | 4 | 1 | True | {} | +----+-----------+-----------+------+-----------+------+-------+-------------+-----------+-------------+
Once the flavor is created, specify one or more
key-value pairs that match the key-value pairs on the host
aggregates. In this case, that is the
ssd=true key-value pair. Setting a
key-value pair on a flavor is done using the nova
flavor-key command.
$ nova flavor-keyssd.largesetssd=true
Once it is set, you should see the
extra_specs property of the
ssd.large flavor populated with a
key of ssd and a corresponding value of
true.
$ nova flavor-show ssd.large
+----------------------------+-------------------+
| Property | Value |
+----------------------------+-------------------+
| OS-FLV-DISABLED:disabled | False |
| OS-FLV-EXT-DATA:ephemeral | 0 |
| disk | 80 |
| extra_specs | {u'ssd': u'true'} |
| id | 6 |
| name | ssd.large |
| os-flavor-access:is_public | True |
| ram | 8192 |
| rxtx_factor | 1.0 |
| swap | |
| vcpus | 4 |
+----------------------------+-------------------+Now, when a user requests an instance with the
ssd.large flavor, the scheduler
only considers hosts with the ssd=true
key-value pair. In this example, these are
node1 and
node2.
To customize the Compute scheduler, use the configuration option settings documented in Table 2.51, “Description of scheduler configuration options”.